Negative GEO: How Competitors Can Harm Your Reputation on AI

Think about the last time you asked ChatGPT, Claude, or Perplexity a question. You probably trusted the answer, right? Most people do. That’s exactly why AI-powered search is changing the game for online reputation management.
As more people are turning to AI for answers instead of Google, AI responses are increasingly influencing what people think about your brand. And just like the early days of SEO, competitors are already exploring ways to influence these systems.
If you’ve heard of negative SEO, where competitors try to tank your search rankings, then you need to know about its newer, potentially more dangerous cousin: negative GEO (Generative Engine Optimization).
Let’s talk about what it is, how it works, and most importantly, how to protect yourself.
What is negative GEO?
Negative GEO is when a competitor deliberately manipulates AI language models to make them say negative things about you or your brand.
Here’s the thing: AI doesn’t think. It synthesizes information from sources it’s been trained on or can access. If someone floods those sources with negative content about you, the AI may gradually start repeating those narratives as if they’re facts.
How is this different from negative SEO?
Negative SEO is about hurting your rankings and organic traffic:
- Pushing your site down in search results causes a loss of traffic
- Malicious link building to undermine your authority signals
Negative GEO is about controlling the narrative:
- AI gives one synthesized answer, not ten blue links
- Users trust it because it sounds authoritative and usually affirms a user prompt, telling them what they want to hear
- Much harder to detect and fix
- The damage is in perception, not just visibility
Why does this matter so much?
When someone Googles your company, they see multiple perspectives. When they ask an AI, they get one answer that sounds definitive. That answer becomes their truth.
Reboot’s experiment: Early evidence of negative GEO risk
I first came across this experiment in a Reddit thread in r/SEO_for_AI, where the Reboot team shared their findings and methodology. This is one of the first structured attempts to explore this question. They designed a controlled experiment to directly test whether AI models could be influenced by strategically placed negative content about a fictional persona.
In their study, they published negative claims across selected third-party websites and then monitored how different AI systems responded over time. In some cases, certain models began surfacing or referencing the test content, while others applied stronger scepticism and either contextualised or dismissed it.

Source: Reboot
Importantly, the results were mixed. Not all models were influenced, and those that did reference the content handled it differently. This suggests that while influencing AI responses may be possible under specific conditions, model behaviour varies significantly and is still evolving.
The experiment doesn’t prove that negative GEO is universally effective, but it does show that AI systems can, in some cases, surface strategically placed content. That alone is enough to take AI reputation management seriously.
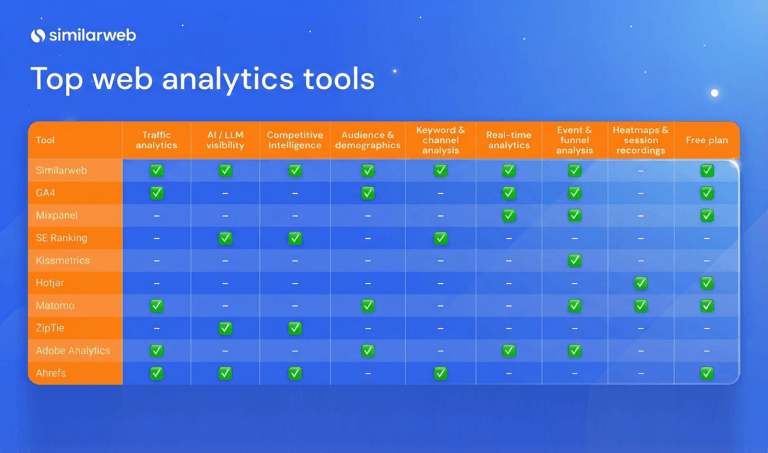
How to measure negative GEO with Similarweb
So how do you know if someone’s running a negative GEO campaign against you? This is where Similarweb’s AI brand visibility tool comes in.
You need structured ways to track brand mentions in AI, monitor, and understand how your brand is being positioned inside LLM-generated responses.
Let’s walk through what you should be tracking using a hypothetical example.
Imagine you run a company called “TechFlow Solutions“, a project management software company. For fun, I asked Gemini to create an image of the employees of this company, with their logo, relatable, right?
OK, let’s get busy. Here’s what you’d want to monitor:
Prompt Analysis: What questions trigger your brand?
What you’re measuring:
Simply put – when do AI models mention your brand, and in what context?
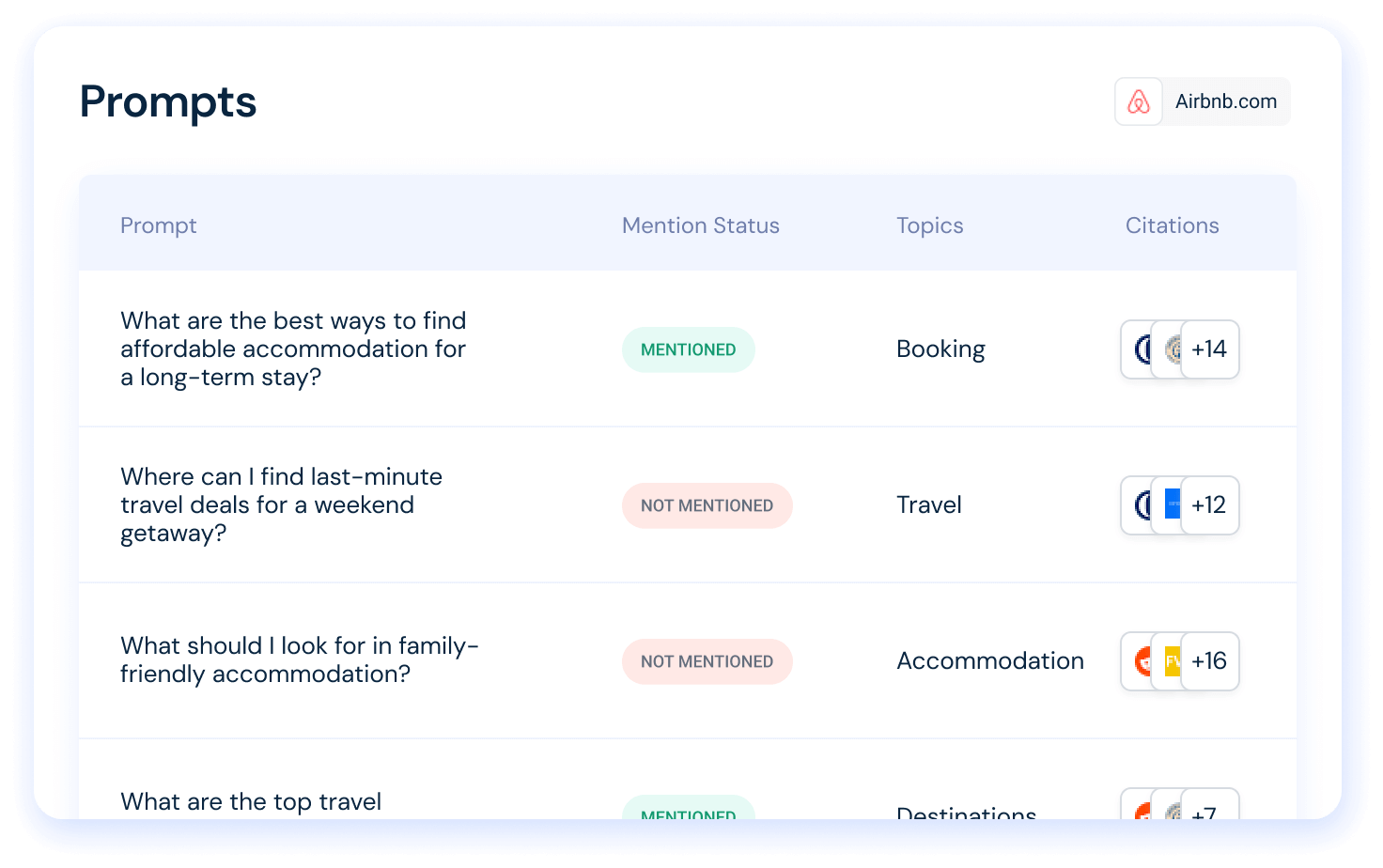
Similarweb’s Prompt Analysis tool shows the prompts users are asking ChatGPT and other chatbots for the topics you are tracking.
You can see whether your brand appears in each answer, which competitors are mentioned (in order of appearance), and the precise citations used. You can also edit and refine the prompts you’re tracking, allowing you to adapt your monitoring strategy as new themes, risks, or opportunities emerge.
Example for TechFlow:
Good prompts (what you want):
- “What are the best project management tools?”
- “Tell me about TechFlow Solutions”
- “Project management software for remote teams”
Bad prompts (red flags):
- “What are the problems with TechFlow?”
- “TechFlow Solutions complaints”
- “Why did people stop using TechFlow?”
How competitors may attempt to influence this:
Tactic #1: Prompt Poisoning – Competitors can create content specifically designed to answer negative questions:
- Articles titled “5 Reasons We Left TechFlow Solutions”
- Blog posts like “TechFlow Problems: A Cautionary Tale”
- These become AI’s go-to sources for negative prompts
Tactic #2: Comparison Hijacking – Injecting your brand into comparison content negatively:
- “Why We Switched from TechFlow to [Competitor]”
- “TechFlow vs. Better Tools: Here’s Why We Made the Switch”
Tactic #3: Forum and Q&A Manipulation – Planting negative answers on Reddit, Quora, and other sites AI loves to cite:
- “Has anyone used TechFlow? Would NOT recommend…”
- Detailed “horror stories” that sound authentic
What to watch for:
- Your brand suddenly starts to appear in negative question contexts
- Increase in “problems”, “complaints”, or “alternatives” mentions
- Prompts that didn’t trigger your brand before suddenly do
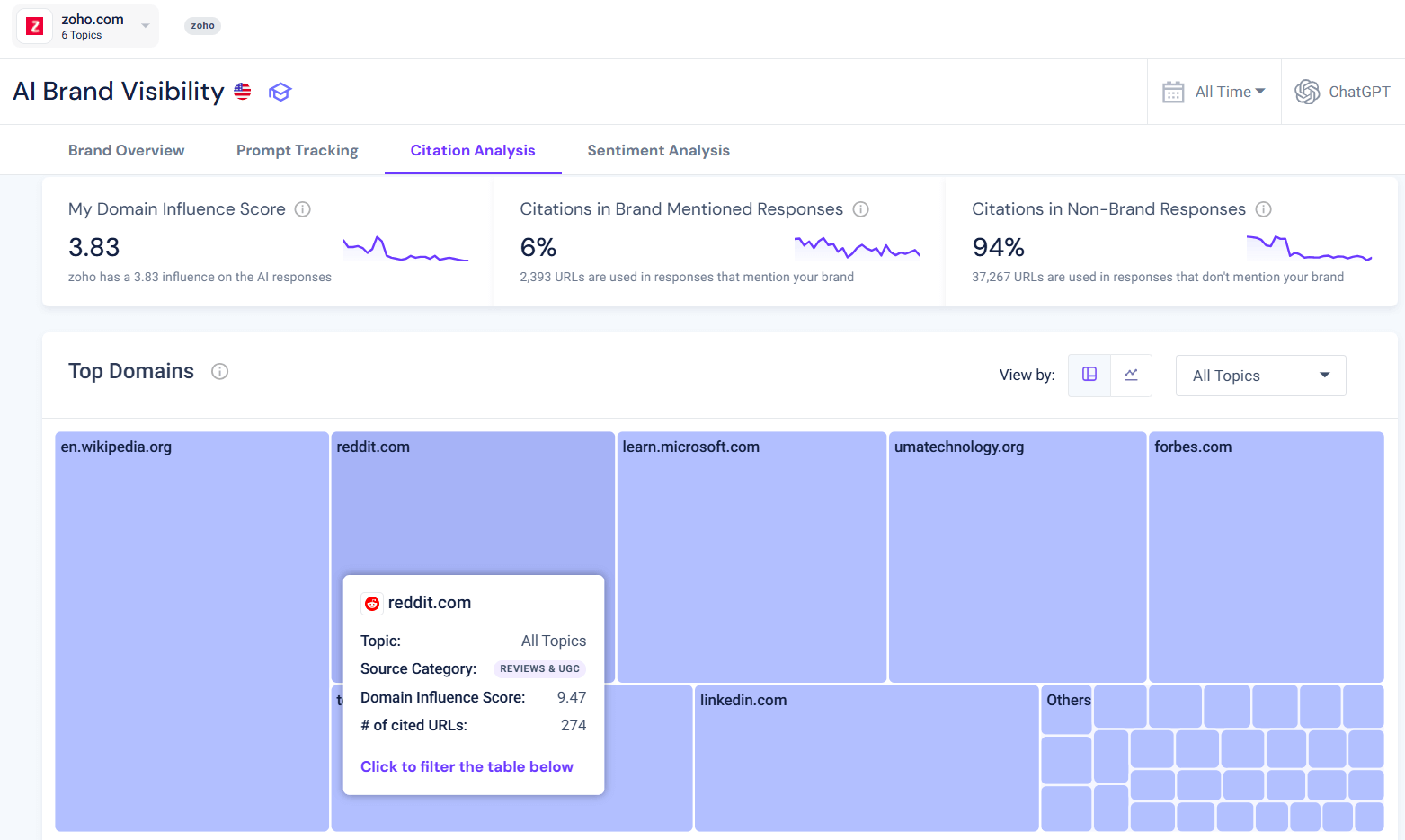
Citation analysis: Where is AI getting its information?
What you’re measuring:
Which websites and sources do AI models reference when they talk about you?
Similarweb’s Citation Analysis tool answers this by showing the domains shaping AI answers and allowing you to drill down to the individual source URLs influencing specific topics and prompts.
You can see which domains Gen AI trusts most, their Influence Score (how frequently they are cited), the category they fall into (news, reviews & UGC, competitor domains, social media, marketplaces, your own site, etc.), and exactly which prompts each URL impacted.
Example for TechFlow:
Healthy sources:
- Your own website
- Reputable review sites (G2, Capterra)
- Industry publications (TechCrunch, Forbes, etc.)
- Legitimate customer stories
Suspicious sources:
- Brand-new blogs you’ve never heard of
- Low-quality press release sites
- Random blogs all saying similar negative things
- Review sites with sudden spikes in bad reviews
How competitors may attempt to influence this:
Tactic #1: Content Flooding – Create dozens of low-quality articles across different websites:
- Same negative story, 20 different domains
- AI sees “multiple sources” and gives them more weight
- Hard to tell they’re all from the same bad actor
Tactic #2: Review Bombing – Coordinate negative reviews across platforms:
- Sudden wave of 1-star reviews on G2 or Trustpilot
- AI cites these platforms as authoritative
- A dozen bad reviews can shift AI’s perception
Tactic #3: Fake News Sites – Publish on sites that look legitimate but aren’t:
- “TechFlow Faces Customer Backlash” on obscure news sites
- Press releases distributed to hundreds of low-quality outlets
- AI can’t always tell real journalism from fake
Tactic #4: Wikipedia Gaming – Try to edit Wikipedia or similar knowledge bases:
- Add negative information to your company’s page
- Create “Criticism” or “Controversies” sections
- AI trusts Wikipedia highly, so this is particularly damaging
What to watch for:
- Lots of new, unfamiliar domains suddenly mention you
- Spikes in citations from review platforms
- More low-quality sources, fewer reputable ones
- Patterns that suggest coordinated publishing (same day, similar language)
Sentiment analysis: What tone is AI using about you?
This is where structured AI sentiment analysis becomes critical, especially if you need to fix negative AI brand sentiment before it spreads across platforms.
What you’re measuring:
Is AI saying positive, neutral, or negative things about your brand? And is that changing over time?
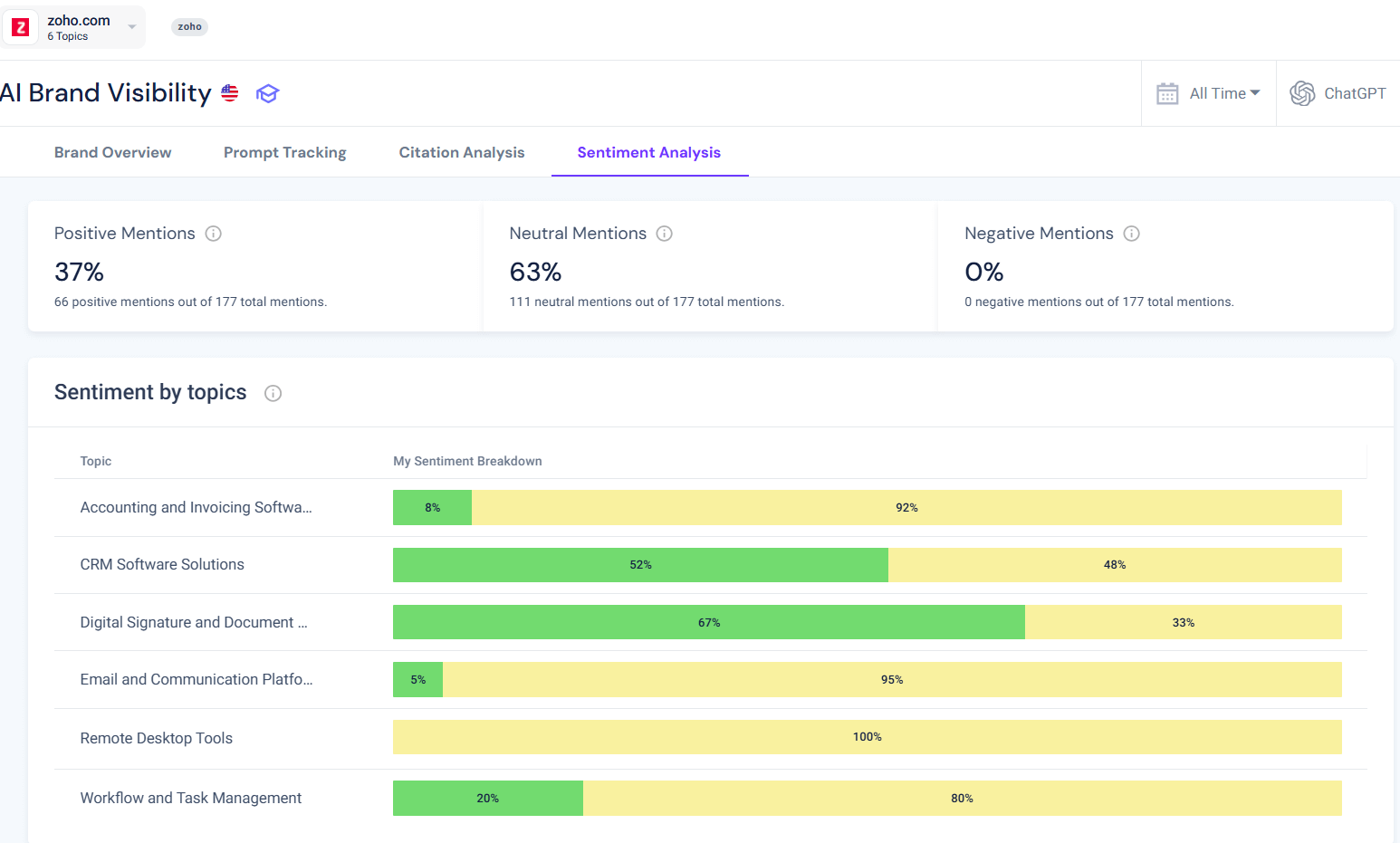
Similarweb’s Sentiment Analysis tool gives you a clear breakdown of positive, negative, and neutral mentions across every topic and prompt you track, along with a comparable score to benchmark perception across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and AI Mode.
Check out this example of Sentiment Analysis for Zoho, on an example campaign I created:
No negative mentions, which is great, but it seems most mentions are neutral, and Zoho can explore how they can make their sentiment more positive.
You can drill down to the exact prompts, AI responses, and source citations driving each mention, compare sentiment side-by-side with competitors, and monitor for updates to spot risks early or identify opportunities to strengthen positive narratives.
Example for TechFlow:
Healthy baseline:
- 35%-55% positive mentions
- 40%-65% neutral mentions
- 10% negative mentions (some criticism is normal!)
- Consistent across ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity
Warning signs:
- Sudden drop to 10% positive in a month
- One AI platform is much more negative than others
- Negative sentiment where there was none before
How competitors may attempt to influence this:
Tactic #1: Emotional Language – Use dramatic, charged language in their content:
- Not “TechFlow has some issues”
- But “TechFlow’s catastrophic failures cost us thousands”
- AI picks up on emotional intensity
Tactic #2: Fake Controversies – Make up scandals and spread them:
- “TechFlow data breach concerns”
- “Questions about TechFlow’s business practices”
- Even if baseless, AI may mention them for “balance”
Tactic #3: Repetition Strategy – Say the same negative thing everywhere:
- “Poor customer service” across 20 websites
- AI sees consistency and may think “there must be something to this”
Tactic #4: Timing Attacks – Flood the brand with negativity all at once:
- 30 negative articles in one month
- AI prioritizes recent information
- Can drastically shift sentiment fast
Tactic #5: Guilt by Association – Link you to negative topics or scandals:
- Mention your brand alongside industry failures
- Associate you with controversial topics
- AI makes connections that affect how it talks about you
Red flags that you’re under attack:
- Sudden drops: Your sentiment falls 20–30% in just a few weeks
- Weird inconsistencies: One AI is super negative while others aren’t (targeted attack)
- New negative topics: Sentiment tanks in areas that were fine before
- Small source, big impact: Just a few articles causing massive sentiment shifts
- No real reason: Your sentiment drops, but nothing actually happened in your business
What to monitor regularly:
- Weekly and monthly sentiment trends
- Compare sentiment across different AI platforms
- Check if sentiment changes match real events (if not, something’s fishy)
- Watch for sentiment drops that seem disproportionate to the number of negative sources
Protecting your brand: Tips on what you can do
Now that you know what to look for, here’s how to fight back:
Monitor constantly
- Use AI brand visibility tools to track your mentions
- Check weekly at minimum, daily if you’re high-profile
- Set up alerts for sudden changes, if possible
Build a positive foundation
Proactive brands are already thinking about defensive and ethical LLM seeding strategies, ensuring accurate, authoritative information about their company exists across trusted, crawlable sources before competitors attempt to shape the narrative.
- Create high-quality, authoritative content about your brand
- Get covered by reputable publications
- Encourage genuine positive reviews
- Make sure your own website is a strong, authoritative source
Diversify your sources
- Don’t put all your eggs in one basket
- Have positive content across many reputable platforms
- The more good sources AI can find, the harder you are to attack
Respond quickly
- If you spot an attack early, you can minimize damage
- Address false information directly
- Reach out to platforms hosting fake content
- Publish response content to set the record straight
Be proactive, not just reactive
- Don’t wait for an attack to start monitoring
- Build your positive AI presence now
- It’s way easier to prevent than to fix
What’s coming next
Negative GEO is still new. Here’s where I believe this field is heading:
It will get more sophisticated
In my view, competitors experimenting with this space are only scratching the surface. As they learn what influences different models, I expect tactics to become more subtle, more strategic, and harder to detect.
AI companies will push back, but it will be iterative
I believe companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google are actively improving safeguards. But this will likely become an ongoing cycle: new manipulation tactics emerge, then new defenses follow.
New monitoring and response tools will mature quickly
From what I’m seeing, the market for AI reputation monitoring is just beginning. I expect much more advanced tools for detection, verification, and response to appear over the next few years.
Regulation is likely, though not immediate
As AI becomes more central to business reputation and consumer trust, I wouldn’t be surprised to see regulatory conversations expand around AI manipulation and accountability.
Early adopters will have a structural advantage
In my opinion, the brands that start taking AI visibility and reputation seriously now will be far better positioned than those who treat this as a future problem.
Bottom line
Here’s the reality: AI is starting to be a big part of how people find information now. And just like SEO before it, bad actors will try to manipulate it.
Negative GEO is real. It works to some degree. And it’s probably easier to execute than you’d hope.
But here’s the good news: if you monitor your AI presence, build strong positive content, and catch attacks early, you can protect yourself.
The brands that will thrive are the ones that understand this isn’t a one-time project, it’s an ongoing part of reputation management. Just like you monitor your SEO, your social media, and your reviews, you need to monitor what AI is saying about you.
Start now. Because your competitors might already be thinking about this.
Try a free trial of Similarweb’s Web Intelligence platform today.
FAQs
Is negative GEO illegal?
It’s complicated. There aren’t specific laws against it yet, but it could fall under existing laws about defamation, fraud, or unfair business practices, depending on the tactics used. The legal landscape is still developing. That said, just because something isn’t clearly illegal doesn’t mean it won’t have consequences, platforms can ban accounts, and civil lawsuits are possible.
How fast can a negative GEO attack hurt my brand?
It varies, but you could see impacts within weeks. AI models that access real-time information can start reflecting new content almost immediately. Models that update their training data periodically might take a few months. The speed also depends on how aggressive and widespread the campaign is.
Can I reverse negative GEO damage?
Yes, but it takes time and effort. You’ll need to:
- Create and promote high-quality positive content
- Get negative false content removed when possible
- Build up authoritative positive sources
- Wait for AI models to re-index or retrain with the new balance
Recovery can take anywhere from a few months to a year, depending on severity.
Which industries should worry most about negative GEO?
High-risk industries:
- Professional services (lawyers, consultants, agencies)
- B2B SaaS and tech companies
- Healthcare and medical practices
- Financial services
- Ecommerce and consumer brands
- Public figures and executives
Basically, if your reputation directly impacts your revenue, you should be paying attention.
Do all AI platforms respond the same way to negative GEO?
Nope. Different AI models have different training data, different update frequencies, and different ways of weighing sources. An attack might be super effective on one platform and barely register on another. That’s why you need to monitor across multiple AI platforms.
What does it cost to monitor for negative GEO attacks?
It depends on your approach:
- Manual monitoring (checking AI responses yourself): Free but time-consuming
- AI brand visibility tools: Varies by provider and scale
- Full reputation monitoring service: More expensive but comprehensive
The real question is: what’s the cost of NOT monitoring? A damaged reputation can cost you customers, talent, and opportunities. For most businesses, the ROI of monitoring is clear.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!








![GEO Framework For Growth Leaders [+Free Template]](https://www.similarweb.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/attachment-growth-leader-geo-decision-framework-768x429.png)