How to Perform AI Citation Analysis: Guide, Examples, And Free Template

I’ve been in SEO long enough to remember when keyword stuffing and PageRank sculpting could get you onto page one. Those days are gone. Today’s battleground is generative search.
Today’s SEOs optimize for AI‑powered systems that synthesize information from all over the web and spit out a single, tidy answer.
On the surface, this sounds like magic: ask a question and an omniscient chatbot delivers wisdom on demand. But if you care about sending traffic to your website, it’s a nightmare.
Zero‑click searches now account for nearly 69% of Google queries (July 2025) thanks to AI Overviews.
Generative AI chatbots drive up to 95–96% less referral traffic than traditional search results.
With these new conditions, SEOs’ only hope is to become one of the few links that generative engines cite beneath their answers.
In this article, I’ll show you, step by step, how to perform AI citation analysis using Similarweb’s AI citation analysis tool. Think of it as backlink gap analysis for the AI era, except instead of looking at who links to you, we’re looking at which pages the bots cite when answering queries that matter to your business.
You’ll learn why citations are the new SEO battleground, how to measure your brand’s performance versus competitors, and what optimization strategies (spanning SEO, AEO, and the emerging field of GEO) will help you close the gap. I’ll even share a real example of openai.com to illustrate how the process works in practice, complete with charts and screenshots of the Similarweb platform.
Ready to dive in?
1. New Search Patterns Require New Optimization Tactics
1.1 Generative search vs. traditional search
Let’s start with a clear definition:
- Traditional web search presents a ranked list of links in response to a query. Users then click whichever links look promising, hop back, refine the query, and repeat until satisfied.
- Generative search, on the other hand, employs large language models (LLMs) to retrieve relevant pages and synthesize them into a single, coherent answer. Instead of ten blue links, you get a paragraph or two of AI‑generated prose, often accompanied by a few citations.
This may seem like a simple difference in output format, but it is fundamentally different: generative search covers a wider range of sources than organic SERPs, and it blends external web information with the model’s own internal knowledge. The upshot is that even if your page doesn’t rank on Google, it might still be referenced by ChatGPT or Perplexity.
Because generative engines draw on both internal and external knowledge, they sometimes answer questions without citing any sources. When they do cite sources, the set of links is often wildly different from traditional search results.
An extensive GEO white paper notes that as of August 2025, there is only an 11% citation overlap between ChatGPT and Perplexity, meaning 89% of opportunities are platform‑specific. Even more startling, nearly 50% of cited domains change each month.
If you thought chasing the Google algorithm was exhausting, wait until you try keeping up with generative engines.
1.2 The rise of zero‑click behavior
The dangerous aspect here is that generative search isn’t just a technical shift. Over time, this simple shift is also changing how people behave. As Similarweb reported, the percentage of Google searches that end without any click (the dreaded zero‑click) jumped from 56% to 69% after the launch of AI Overviews.
As AI answer boxes replace organic results, the click‑through rate on traditional links plummets. Some keywords see drops as high as 64%. Meanwhile, AI chatbots handle tens of millions of information‑seeking (or “asking” intent) prompts per day.
A Yext study notes that AI‑driven traffic can be 4.4× more valuable than traditional organic visits, but there’s far less of it. In other words, the handful of citations that appear under an AI answer are now the gatekeepers of your web visibility.
1.3 Sources and biases in AI answers
Where do these citations come from?
A fascinating study by Yext in October 2025 analyzed 6.8 million AI citations across ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. The headline finding: 86% of citations originate from sources that brands already control, such as their own websites, listings, and reviews.
First‑party websites account for 44% of citations and business listings another 42%, while reviews and social content make up only 8%. Forums like Reddit contribute a paltry 2%.
This is great news if you’re proactive: you can influence AI visibility by improving your own content and profiles. It also means that moaning about Reddit’s “unfair advantage” is a cop‑out, and the data simply doesn’t support it.
The same study highlights another twist: generative engines have distinct preferences. Gemini (Google’s model) leans on websites (52.1%), OpenAI’s models favor listings (48.7%), and Perplexity spreads citations across MapQuest and TripAdvisor.
Citation patterns vary by question type, too: unbranded, objective queries favor first‑party websites, while subjective, branded queries lean more on listings and reviews. Understanding these nuances is crucial when planning your AI citation strategy.
2. Why Citations Are the New SEO Battlefield
In the old world of SEO, ranking on page one meant exposure, clicks, and revenue. In generative search, being cited is the new ranking.
Citations are the only links users see alongside an AI answer, and they drive most of the limited referral traffic. iPullRank’s “User Behavior in the Generative Era” report from August 2025 bluntly states that if your brand doesn’t appear in the answer, “you don’t exist in the session.” It’s that simple.
Because generative search uses completely different sources, competition is no longer limited to your SERP neighbors. You might lose a citation to an obscure Wikipedia page, an arXiv paper, or a competitor’s pricing guide. Even worse, AI engines sometimes hallucinate citations or misattribute them.
That means that the landscape is volatile: Citation sets can change by up to 50% each month, and there’s very little overlap between platforms. If you’re not monitoring, you’ll be blindsided.
But citations aren’t just about traffic, they’re about trust and authority.
When an AI chatbot cites your site, it implicitly endorses you as an authoritative source. This can boost brand perception, especially in niches where users are wary of misinformation. Conversely, if competitors monopolize citations, they become the de facto experts in your space.
That’s why citation analysis should be part of every modern SEO/AEO/GEO strategy.
3. How to Perform AI Citation Analysis (Step by Step)
Enough theory, let’s roll up our sleeves. Naturally, Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility is my go-to tool for performing citation analysis. I get comprehensive data from multiple generative engines that I can slice by brand, competitor, source category, topic, and even individual prompts.
Here’s my battle‑tested process:
3.1 Define your objectives and select competitors
Begin by clarifying what you want to achieve: Are you trying to increase overall brand awareness, win high‑intent queries, or outshine a specific competitor?
Set measurable goals: for instance, “increase my AI citation share on [topic] by 5% in the next quarter” or “secure citations on three new high‑authority domains.”
Next, choose one or two competitors whose offerings overlap with yours. Going head‑to‑head with Apple if you’re a niche SaaS company won’t teach you much.
3.2 Collect baseline visibility metrics
Open Similarweb and navigate to Gen AI Intelligence → AI Brand Visibility. In the search bar, enter your domain and the domains of your chosen competitors.
The Overview tab will show:
- Visibility share: % of AI answers that cite your site
- Total citations: count of citations across engines
- Breakdown by engine: ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, etc.
- Topics summary: top topics by share
- Competitor share of voice: your brand vs. peers
For example, when I analyzed openai.com (see full data in the example section), the topics summary revealed that AI Tools was by far the dominant topic, accounting for about 23% of the brand’s AI visibility. Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing each made up roughly 3%, while Digital Transformation barely registered.
These metrics tell us two things:
- Openai.com’s authority is concentrated in a handful of topics.
- Generative engines often mix the brand, its products, and its related services/channels and treat them as the same thing. For example: Saying “OpenAI rolled out a new feature” when it was actually ChatGPT (product) using GPT-4 (model) via the API (platform).
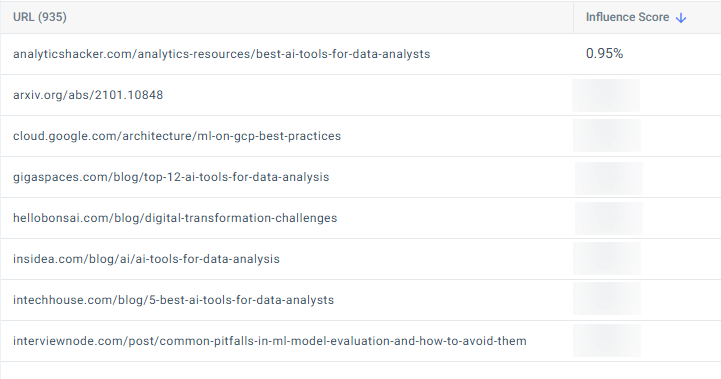
I recommend exporting these baseline GEO metrics or capturing screenshots for reference. They’ll help you measure progress later. In the image below, you’ll see the URLs cited for OpenAI’s topics:
3.3 Analyze citation source websites
What you’ll get: A target list of trusted domains to pitch, partner with, or co-author content.
Next, click the Citation Analysis tab. This report shows which domains and URLs generative engines cite when mentioning your brand.
The report also categorizes sources into news/publishers, reviews/UGC, your own domain, competitor domains, marketplaces, social platforms, and “other”. For each source, you’ll see an influence score, which indicates how much that domain contributes to your citations, and a citation count.
In OpenAI’s case, the top domains included research repositories like arxiv.org, blogs like medium.com, encyclopedic pages like en.wikipedia.org, journals like mdpi.com, programming resources like geeksforgeeks.org, and business consultancies like mckinsey.com.
These sources all have high authority in the AI and technology space, which explains why generative engines trust them. If OpenAI doesn’t appear on these domains within their vertical, they’re invisible.
3.4 Analyze citation source URLs
What you’ll get: A prioritized set of high-influence URLs to update and earn links from.
The Cited URLs table provides even more granular insight. For openai.com, the Word embedding article on Wikipedia carried an influence score of roughly 0.48% and was cited by three prompts. Several arXiv papers and industry reports from EY and McKinsey each contributed around 0.95% influence and two prompts.
This is where you can also identify citation gaps:
- Sort the domains by influence score and compare your list with that of your competitor.
- Highlight any high‑authority domains that cite your competitors but not you.
- Compare website categories for more insights (If reviews/UGC and news sites account for 60% of your competitor citations but only 20% of yours, you’re overly reliant on your own blog and need to diversify.)
For example, if techradar.com lists “Best AI tools” and cites grok.com but not OpenAI, that’s a gap.
3.5 Analyze citation-source prompts and topical gaps
What you’ll get: A prompt/intent gap map that guides the next pages to publish.
It’s time to dig into actual prompts and topics you want to improve your visibility on. From the URL chart, choose one of your tracked topics and see the cited URLs that are relevant only for that topic.
From here, you can analyze your visibility gaps and opportunities by topic and uncover question or answer patterns that are relevant for each topic. You can start with the topic that has the most citation sources, or the one that’s the most relevant for your business. You can also filter further by domain and pick only citation sources that are relevant to your topic.
For openai.com, questions like “Which industries benefit most from machine learning?” and “Which industries are leading in AI adoption?” generated many citations but did not mention the brand at all. Conversely, “What are the top AI tools for data analysis?” produced a positive mention with multiple citations.
These gaps tell us exactly what content to create: comprehensive sector‑focused AI adoption guides, industrial impact analyses, and developer tool round‑ups.
Next, analyze the prompts by intent stage (informational, consideration, transactional) and by topic to prioritize where to invest your resources.
3.6 Prioritize and plan
Not all gaps are created equal. Focus on high‑influence domains and high‑intent prompts first. Build a spreadsheet with columns like Domain/URL, Category, Competitor cited?, Influence score, Associated prompts, and Recommended action. Use your own judgment and domain knowledge to triage.
You can download this template: Citations Tracker Template by Similarweb
For example, an industry blog with moderate influence but a highly relevant audience might be more valuable than a high‑influence general news site. In my experience, targeting 5–10 high‑impact sources can get better results than chasing every site that ever mentioned a competitor.
3.7 Monitor changes and iterate
Citation sets are volatile: 50% of cited domains change every month, and our own experience confirms it. If that’s true, how can you properly monitor your citations?
- Set a recurring schedule (weekly/monthly or quarterly) to rerun your analysis.
- Track improvements in your citation count, declines in competitor citations, and new sources that emerge.
- Repeat the content creation and outreach cycle based on the latest data.
To avoid drowning in numbers, focus on a few key metrics:
- Share of voice
- Number of citations
- Top categories
- Influence scores
Similarweb’s dashboard makes it easy to track my visibility metrics over time for any topic that matters to my business, compare them to my competitors, and view them across different time ranges.
3.8 Complete your view with AI traffic data
One final step: combine citation analysis with AI referral traffic data.
Similarweb’s AI Traffic Analytics (also under Gen AI Intelligence) shows how many visits you actually receive from AI engines. Sometimes, a domain might contribute many citations but little traffic, but even a low‑citation domain might send high‑value visitors.
Use traffic data to calibrate your efforts. Without traffic context, you risk optimizing for vanity metrics.
Now let’s see how this plays out in real life with an example from OpenAI.
4. Citation analysis example: openai.com
To make this process less abstract, I’ll pretend that I’m OpenAI’s new SEO and walk you through a citation analysis process for openai.com, using Similarweb’s platform.
The goal was to understand how OpenAI’s own site fares against competitors in AI‑powered search and where it could improve. (I chose OpenAI, testing the king with its own crown.)
Measurement context:
Country: United States (US)
Period: Last 7 days (rolling)
Engines: ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity
Metrics: Visibility share, total citations, influence score, topic share, prompts/mentions
Source: Similarweb → Gen AI Intelligence → AI Brand Visibility
4.1 Inspecting overall visibility metrics
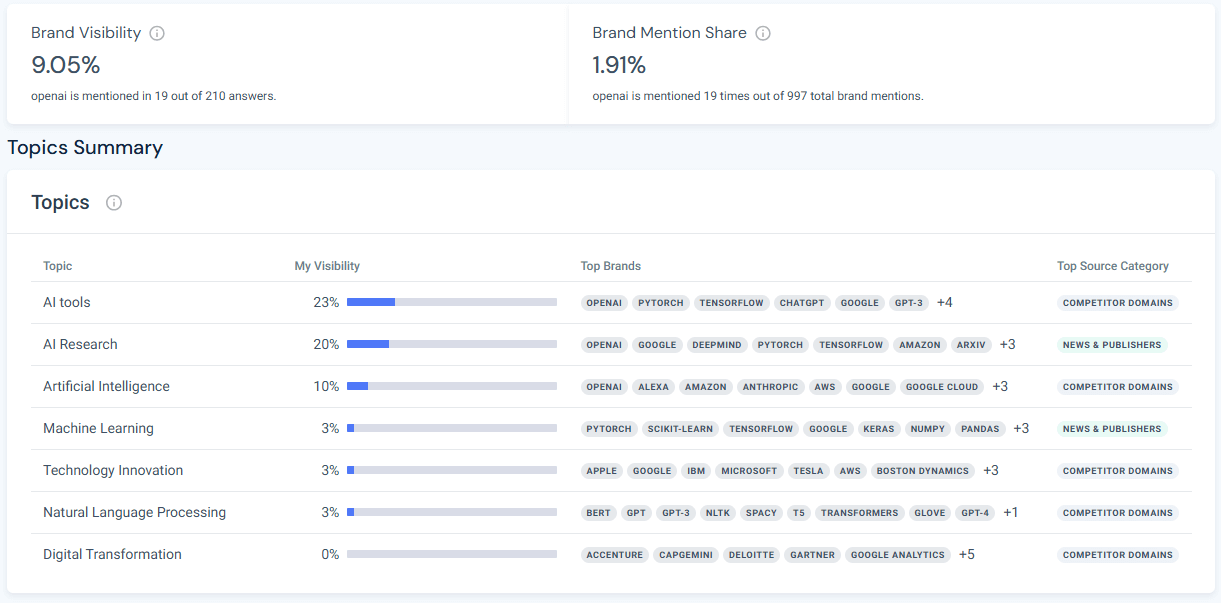
In the Overview tab, I can see that over the last 7 days, openai.com has a visibility share of around 9% in the US within AI answers, and an almost 2% brand mentions share within the AI ecosystem.
The topics summary above shows me I am dominant in AI tools (~23%) and AI Research (~20%) topics, with secondary topics such as Artificial Intelligence (~10%) and Natural Language Processing (~3%) that I might be able to improve on.
The competitor share‑of‑voice chart showed that generic product terms (GPT, Alexa, AWS) commanded about 3% each, showing that large tech brands and product names are competing for mindshare even when the search is about OpenAI.
4.2 Analyzing Top Citation Website Sources
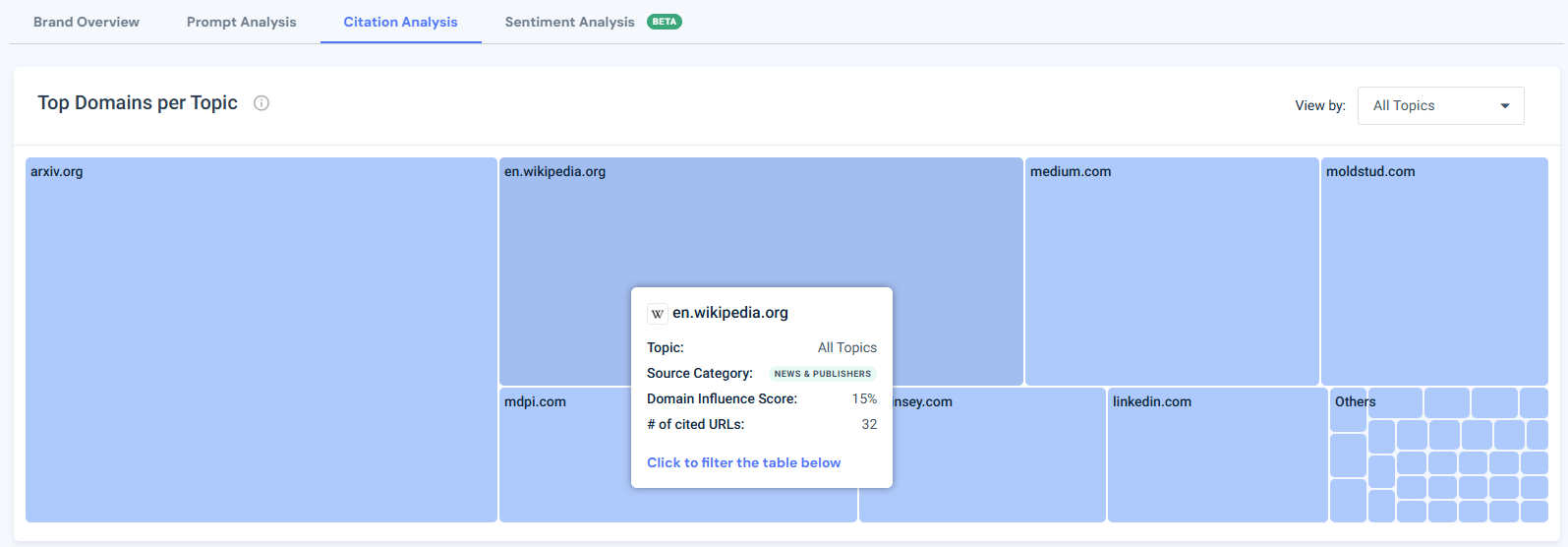
In the Citation Analysis tab, the top domains citing openai.com were arxiv.org, medium.com, en.wikipedia.org, mdpi.com, and mckinsey.com. The sources are sorted by their “Influence Score”, showing their weight across Gen AI answers.
I can prioritize these sources by influence score and type, and dig into each of them to understand where and how my visibility can be improved. I like to do this analysis by topic, meaning to first filter the topic I’d like to analyze, and then into each citation source.
For example, the source distribution of the chart above looks a bit different when I filter only to “AI Research”. See how MIT and Stanford are popping out.
These sources also reflect OpenAI’s relevance to its main topics of AI research and AI tools, supported by both academic and technical institutions.
Now that I understand OpenAI’s stronger topics, I’ll continue to analyze the data to understand how I can get more citations and influence my overall visibility per topic.
4.3 Analyzing Top Citation URLs
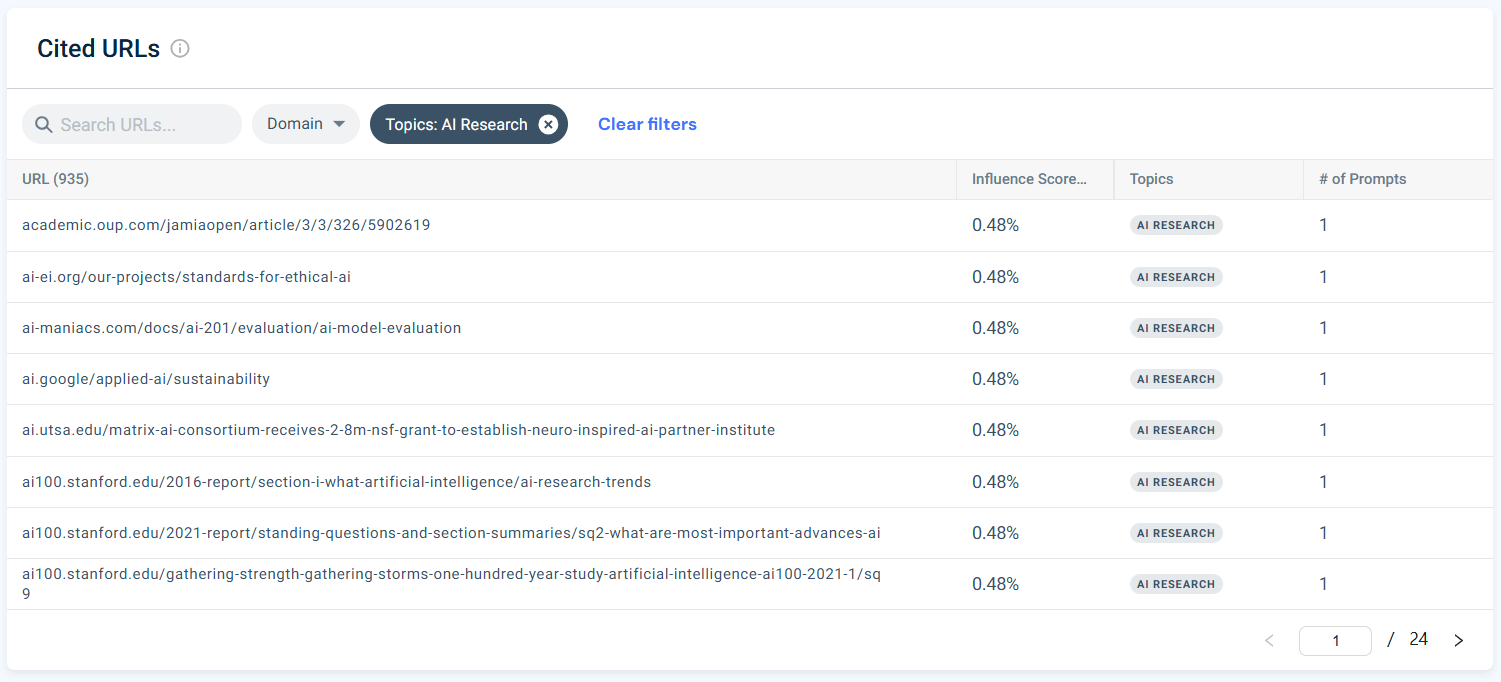
Now it’s time to check the individual URLs of my citations. I can analyze all URLs for all topics, or filter by topic and source, just like in the chart above. I’ll continue looking into the “AI research” topic.
Here are the top cited URLs:
The table is sorted by influence scores for individual URLs. It allows me to see which URLs and websites carry the most weight for my target topic in AI. I can’t say I’m surprised to see ai.google up there.
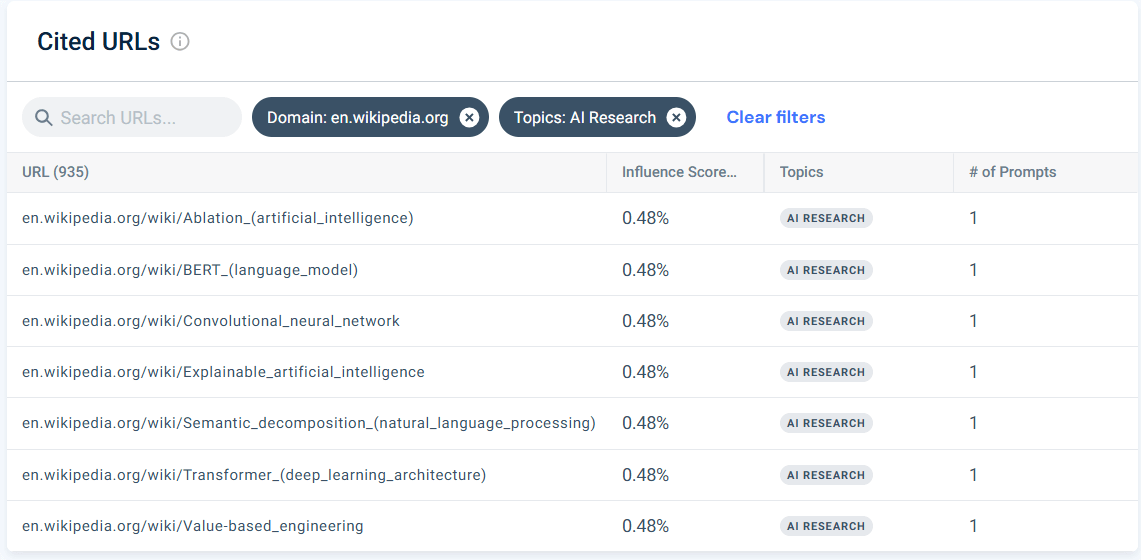
Now I’ll filter by domain. This way, I can see which pages are relevant for me in each domain, and work in a more organized way.
I chose en.wikipedia.org and got a nice list of URLs with good influence scores within Wikipedia:
Wikipedia URLs’ influence scores are among the highest, meaning Generative AI engines value the information there when it comes to the AI research topic. They also have friendly, easy-to-read URLs that help me understand upfront any page’s topic and its real relevance to me, as OpenAI’s SEO.
As OpenAI’s SEO, ideally, I want to be mentioned in all of the above URLs, preferably in a positive or helpful context. However, I understand my relevance for each topic is not the same, and that I’ll have to prioritize the pages with the highest relevance to me, leaving the others as nice-to-haves or second-tier.
Let’s examine an interesting URL: Explainable Artificial Intelligence.
4.4 Analyzing Top Citation Prompts and Topics
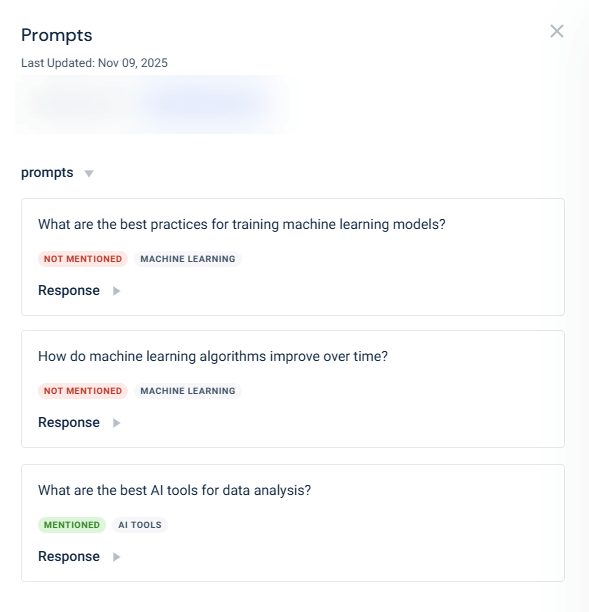
For its 2nd-strongest topic of AI research, OpenAI isn’t mentioned that much. I click on my target URL and see the prompts that get my targeted Wikipedia page cited, so let’s see what I have:
You might ask, “How does this relate to OpenAI?” Well, that gap is the opportunity: The goal of citation analysis is to discover new opportunities to increase visibility in areas where it’s weaker, as well as uncover citation gaps with competitors around core topics.
4.4.1. What can I do to increase OpenAI’s chances of being mentioned when this URL is cited?
- I can add an OpenAI example of LLM-assisted interpretability that might be pulled into an overview answer in the “Transparency & Documentation” and “Providing explanations of AI decisions.”
- I can add a paragraph about accountability and transparency under the “Regulation” section, providing specific, verifiable facts that turn a vague “ethics + transparency” claim into something concrete and policy-relevant.
Once I know where AI engines point to when discussing my topics, I can try to expand my share and increase my visibility.
The lesson: even AI darlings have work to do to broaden their citation footprint.
4.5 What should OpenAI do next to increase AI citations?
If I were the SEO at OpenAI, I’d recommend these three main things:
- Build authority: Publish vertical industry guides.
Create in‑depth resources on AI adoption in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and education. Link them to case studies and research. Not only will these pages earn citations for prompts like “Which industries benefit most from machine learning?”, but they’ll also build trust.- Expected impact: More citations for sector prompts and broader topic coverage
- How to measure:
- Topic-level visibility share before/after (US, rolling 30 days).
- Citation count and influence score for consultancy/news domains
- Prompts & mentions numbers for your top target topics
- Expand citation sources: Partner with high‑influence publications.
Contribute articles to business outlets (e.g., McKinsey, Harvard Business Review) and developer platforms (e.g., GitHub blogs). Include structured data (FAQPage, Article schema) to help AI models parse the content. This will diversify citation sources beyond arXiv and Wikipedia.- Expected impact: Diversify citation sources and reduce dependency on single sources
- How to measure:
- New citing domains & their influence score (goal: +X high-influence domains/quarter).
- The top-10 domains influence scores.
- Website category distribution moving toward third-party publishers/UGC where relevant
- Enable the user: Curate product comparison and pricing pages.
Developers searching for “best AI tools” will appreciate side‑by‑side comparisons of ChatGPT versus other platforms. Use a neutral tone and disclose limitations. AI engines often cite comparison articles, and they’re a natural fit for OpenAI’s brand.- Expected impact: Win consideration/transactional prompts and earns AI citations that convert
- How to measure:
- Citations & prompts tied to comparison/pricing URLs (by engine & prompt intent).
- AI referral visits to those URLs (and assisted conversions if you track them).
- Topic/keyword visibility share lift around “best tools” and “pricing” queries.
5. Citation Optimization Strategies for SEO, AEO, and GEO
Once I’ve analyzed my entire citation profile, it’s time to optimize it.
The strategies below blend traditional SEO best practices with new tactics for Answer Engine optimization (AEO) and Generative Engine optimization (GEO). I’ve ordered them roughly by impact (from my own experience, different experiences may vary).
5.1 Create high‑quality, human‑first content
Generative engines are trained to favor content that reads well and answers questions comprehensively.
- Use clear structure and authentic storytelling to help AI models parse and cite your content.
- Use descriptive headings (H1‑H4), bullet points, tables, and diagrams to break up information.
- Use real data, add original research, and unique perspectives (AI models often cite pages with facts and numbers).
Above all, write for humans first. Nothing triggers an “AI penalty” faster than keyword‑stuffed gibberish. In other words, if your blog reads like it was generated by ChatGPT, don’t expect ChatGPT to cite it.
5.2 Implement structured data and technical standards
Structured data helps AI understand your pages. Use Schema.org markup such as FAQPage, Product, HowTo, and Article. This makes your content machine‑readable and increases the chance of being cited for Q&A, product, and how‑to prompts.
Implement llms.txt (the new wannabe equivalent of robots.txt for LLMs) and check how it helps your visibility and citability.
Don’t overlook SEO basics: Make your site fast, mobile‑friendly, and crawlable. Optimize your internal linking distribution, and make sure your canonical tags are set correctly to prevent content duplication issues.
5.3 Target high‑influence domains and directories
Because 86% of citations come from brand‑controlled sources, your own content and profiles are your best friends:
- Create or claim profiles on business directories like G2, Capterra, Trustpilot, and industry‑specific marketplaces. Encourage reviews and keep information up‑to‑date.
- Pitch guest posts or thought‑leadership pieces to high‑authority publications identified in your citation analysis.
- If you’re in a technical field, publish research on arXiv, collaborate with universities, and contribute to Wikipedia (ethically and transparently). Even smaller blogs can be valuable if they carry an influence score.
5.4 Create comparison and review pages
Generative engines love unbiased comparisons and product reviews. They answer queries like “best project management software” by citing lists and head‑to‑head analyses.
Write thorough comparison pages that include objective criteria, pros and cons, and when to use each product. Use neutral language, and don’t trash your competitors. Your main goal is to make the readers feel that you provide a balanced perspective.
If you’re a SaaS provider, create a pricing guide with detailed feature breakdowns and annotate with schema markup. For physical products, include specs, user reviews, and third‑party ratings.
5.5 Engage in communities and social platforms
While forums account for only 2% of citations overall, they can be influential in certain niches. Participate in subreddits, Slack groups, Discord servers, and industry forums. Provide helpful answers, link back to authoritative content, and encourage satisfied customers to share their experiences.
Authentic engagement builds authority and may yield citations from community‑driven platforms like Reddit or Stack Overflow.
5.6 Maintain diversification across AI platforms and languages
Since AI engines’ citations overlap by only 11% between major AI engines, it’s critical to closely monitor ChatGPT, Gemini (Google), Perplexity, and others separately.
Tailor content to each platform’s preferences: fact‑heavy and balanced for Gemini, community‑driven for Perplexity, research‑oriented for OpenAI. If you operate globally, publish content in multiple languages, and use translation and localization services, but ensure nuance isn’t lost.
5.7 Ensure freshness and recency
Citations shift monthly, and AI models tend to prioritize recent sources. Establish a content refresh schedule (quarterly at minimum) to update your articles with new data, examples, and references. Simply changing a publication date won’t fool the bots. You need real updates.
This is where the AI Brand Visibility dashboard comes in extra handy, in my opinion. I use it to spot declines in my citation share and respond with fresh content.
5.8 Build trust through accuracy and transparency
Surveys show that while 70% of users somewhat trust AI answers, 75% worry about misinformation. To position your brand as a trustworthy source, cite authoritative research (like the studies referenced in this article), include author credentials and bios, disclose conflicts of interest, and correct errors quickly.
You can also publish “AI answer corrections” pages to address hallucinations and misattributions, and report inaccurate citations via the feedback mechanisms in each AI platform. That will provide you with another way to manage (and optimize) your brand trust in AI.
5.9 Measure and iterate
Citation analysis isn’t a one‑off. Track your metrics over time: citation counts, share of voice versus competitors, sentiment and accuracy of mentions, referral traffic from AI platforms, and conversion rates.
Use dashboards to connect citation metrics with business KPIs. Experiment, measure, adjust, repeat.
6. Benefits and ROI of Citation Analysis
If you’re still not convinced this is worth your time, let me summarize the pay‑offs:
- Enhanced visibility in AI search: Securing citations puts you in front of users when they ask questions. In a zero‑click world, that’s priceless.
- Better quality traffic: AI visitors stay longer, view more pages, and bounce less than average. High‑intent queries often originate from AI chats.
- Competitive intelligence: Comparing your citation profile against competitors reveals their content, link-building, and GEO strategies.
- Data‑driven content planning: Citation analysis highlights which topics and queries drive AI citations. You can allocate resources to match demand trends.
- Outreach prioritization: Influence scores and category breakdowns show which domains matter most, so you don’t waste time on low‑impact sites.
- Risk mitigation: Monitoring citations helps you spot misinformation or hallucinations early. You can correct them before they damage your brand.
- Future proofing: AI search usage is surging. Brands that invest early will control more of the narrative in the years to come.
7. Limitations and Caveats
No tool is perfect. Similarweb’s AI visibility platform provides excellent breadth but may not capture every AI engine, especially emerging or niche models. Influence scores are relative measures, not absolute, meaning that a domain with a 1% score may still be critical if it’s tied to a high‑value query.
Data can lag, especially for rapidly evolving topics. Furthermore, some AI answers rely purely on internal knowledge, leaving no trail to analyze. Treat citation analysis as one input among many, not a crystal ball.
Also, AI platforms themselves are evolving. Google’s AI Overviews still heavily favor Google‑owned properties, and nearly half of their citations link back to Google. ChatGPT may soon integrate real‑time search more deeply. Regulatory changes (think copyright law) could require different citation behaviors. In short, stay nimble.
8. Conclusion
AI search is rewriting the rules of discovery. Where SEOs once obsessed over ranking signals and backlink profiles, we now need to think like librarians: which books (i.e., pages) will the AI recommend?
Citation analysis is the compass that guides you through this uncharted territory. With Similarweb’s GEO tools, starting with AI Brand Visibility, you can see where you stand, where your competitors excel, and where there are opportunities to insert your expertise.
By producing high‑quality content, structuring it for machines, targeting influential domains, and continually measuring and iterating, you’ll not only survive but thrive in the age of generative search. True, this is not so different from SEO as you know it, but if you choose to completely ignore these changes, you’ll be stuck optimizing title tags while your competitors write the future.
FAQ
How does the Similarweb AI Brand Visibility Tracker work?
This feature reveals how visible your brand is in AI-generated answers for the topics you care about most. It enables you to: Track your brand’s mentions across Gen AI answers. Benchmark your visibility against competitors. Analyze the specific prompts that trigger AI-generated content where your brand is, or isn’t, mentioned or sourced
What is generative search, and how is it different from traditional search?
Generative search retrieves relevant pages and synthesizes them into a single answer, whereas traditional search returns a ranked list of independent pages. Generative engines may incorporate internal knowledge as well as external sources, resulting in answers that draw from a wider range of sources than typical SERPs.
How do I perform citation analysis?
Use Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool to measure your visibility share, examine topics and competitor share‑of‑voice, dive into the Citation Analysis report to see which domains and URLs are cited, and analyze the Prompt Analysis report to identify topical and prompt gaps. Prioritize high‑influence sources and high‑intent prompts, then monitor and iterate monthly.
Do citations really matter if there’s little traffic?
Yes. Although AI referrals are fewer than traditional clicks, they’re more engaged and more likely to convert. Moreover, citations confer trust and authority. If you’re absent, your competitors get the halo effect.
Do citations vary across platforms?
Dramatically. Only about 11% of citations overlap between ChatGPT and Perplexity, and sets change monthly. Monitor each engine separately and tailor your strategy to its quirks.
How do I handle incorrect or hallucinated citations?
Publish a corrections page on your site, and optimize it for relevant queries. Use platform feedback tools to report errors. Engage in communities to correct misinformation. Maintain transparency and factual accuracy to build trust.
What is a citation gap?
A citation gap arises when AI engines cite your competitors’ pages but not yours for relevant queries. This leaves your brand invisible in generative answers, even if your SEO is strong. Closing citation gaps ensures your brand is recommended alongside (or instead of) competitors.
Can I compare my performance to competitors in Gen AI?
Yes. The Similarweb AI Brand Visibility tool shows the top 30 brands for every topic you track, and you can see how you perform against them over time.
How often should I update my content to stay relevant to AI engines?
Refresh key pages at least quarterly. Substantive updates matter more than superficial date changes. Use AI visibility tools to spot drops in citation share and respond accordingly.
What kind of content works best?
Long‑form research, data‑driven articles, detailed how‑to guides, comparison pages, and structured FAQs perform well. Generative engines favor comprehensive, well‑structured sources. Use schema markup to make them machine‑readable.
How can I ensure my claims are verifiable to AI engines?
Link your statements to authoritative sources and embed structured citations. Avoid unfounded marketing fluff. The Yext study shows that 44% of citations come from first‑party websites and 42% from listings, so make sure your site contains verifiable facts.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!











![GEO Framework For Growth Leaders [+Free Template]](https://www.similarweb.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/attachment-growth-leader-geo-decision-framework-768x429.png)