How to Identify and Fix Negative AI Brand Sentiment
Artificial intelligence assistants and modern search engines now shape much of the public’s first impression of a business. When a large language model describes your company, it can either reinforce trust or cast doubt.
In a previous article, our SEO expert, Maayan Zohar, shared methods and best practices on how to analyze AI brand sentiment and understand these signals. However, learning how to analyze sentiment is just the first step.
The real question is how to identify when you have brand perception issues (i.e, negative sentiment) and how to fix them.
This article will teach you how to identify negative brand sentiment and, more importantly, how to fix it. It combines research on AI sentiment analysis with real data from Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool on the Avis brand to give examples of what to look for and where to intervene.
What is AI Brand Sentiment?
AI Brand sentiment refers to how often a brand is described positively, neutrally, or negatively across AI‑generated answers.
Generative engines’ responses are usually classified into three sentiment categories, yielding a “sentiment mix”:
The way that ChatGPT and other chatbots refer to your brand can set a potential customer’s opinion for or against your brand. A positive description of your brand means more sales, while a negative description means losing potential sales.
Understanding what causes your audience to have positive sentiment and trust in your brand, as well as why they have negative sentiment, is the basis of your ability to improve your brand perception in AI engines.
This means that a critical part of your AEO and GEO efforts should also be set for sentiment analysis and management.
Since LLMs rely on their own data, along with external sources, reviews, and other user conversations when synthesizing their responses, those are the sources you’d like to influence to showcase your brand positively.
Let’s start with understanding how LLMs “understand” sentiment. Leveraging this knowledge later on will help you trigger the correct sentimental interpretations from AI engines.
How do LLMs classify negative or positive sentiment?
Large language models (LLMs) determine whether a text expresses positive or negative sentiment through a combination of learned language representations and a classification mechanism. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Encoding the input text: Each sentence is first converted into a numerical representation (a sequence of token embeddings).
- Classification head: A small feed-forward network on top of the language model produces a single score per sentiment class (positive, neutral, or negative). These scores are passed through a function to convert them into probabilities. The class with the highest probability is selected as the sentiment label.
- Attention to context and nuances: Unlike keyword‑based methods, LLMs analyze the entire sentence, capturing tone shifts, sarcasm, and context.
- Tweaking and label output: In a fine‑tuned classifier, the sentiment classes are fixed (e.g., positive = 1, neutral = 0, negative = -1).
- Challenges and biases: LLM‑based sentiment analysis is not flawless: subjectivity, ambiguous context, sarcasm, and idioms still present challenges. Early models sometimes showed a “positive bias,” but newer instruction‑tuned LLMs like GPT‑5 reduce this by calibrating their outputs against more balanced data.
LLMs don’t “feel” or hold opinions. They rely on mathematics to classify sentiment.
Even in zero‑shot settings, where you simply prompt a model to label sentiment, it isn’t choosing based on preference, but predicting what someone might say based on patterns from its own knowledge graphs and training data.
The final choice of “positive,” “neutral,” or “negative” comes down to which option is mathematically most likely given the input and the model’s training, not any subjective feeling detection. This choice, eventually, is how your brand will be presented to the reader of the LLM-generated answer.
How to Tell if Your Brand Has Negative Sentiment Issues
Spotting a sentiment problem requires more than just glancing at an overall score.
Negative feelings can stem from many sources: insufficient information, product flaws, pricing concerns, misinformation, or simply a lack of enthusiasm. To determine which of these issues you face, you need to interpret the data in context.
The framework below explains what each metric tells you, why it matters, and how to reason about the numbers. Each step uses the Avis data to illustrate how an SEO should connect the dots between the raw figures and actionable insights.
1. Examine Your Sentiment Mix
Begin with the ratio of positive, neutral, and negative mentions across all topics and channels. Think of this as a high‑level health check.
A healthy brand usually has a majority of positive mentions, a moderate neutral share (for users who are researching or comparing options), and a minimal negative share.
If negative answers consistently outweigh positive ones, you clearly have an issue. But even a small negative fraction can hurt when neutral sentiment is high because it signals that a large audience is still undecided or confused.
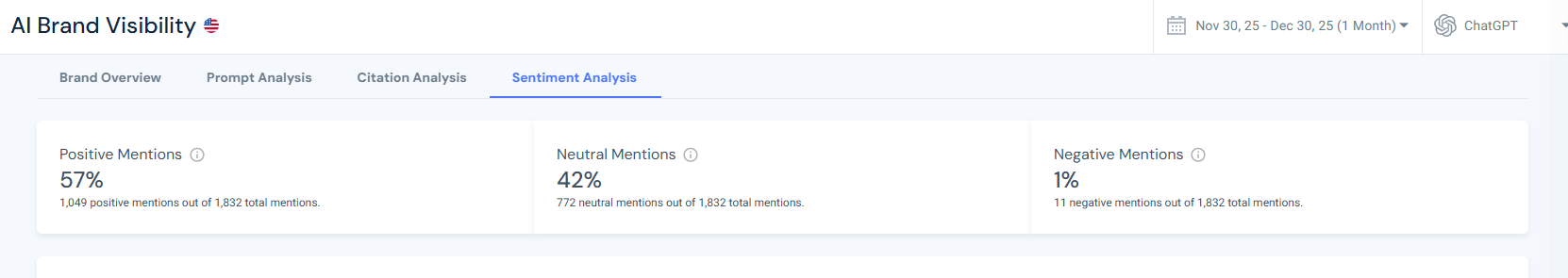
In the Avis campaign, 1,076 mentions across ChatGPT responses were split into 37% positive, 61% neutral, and 2% negative.
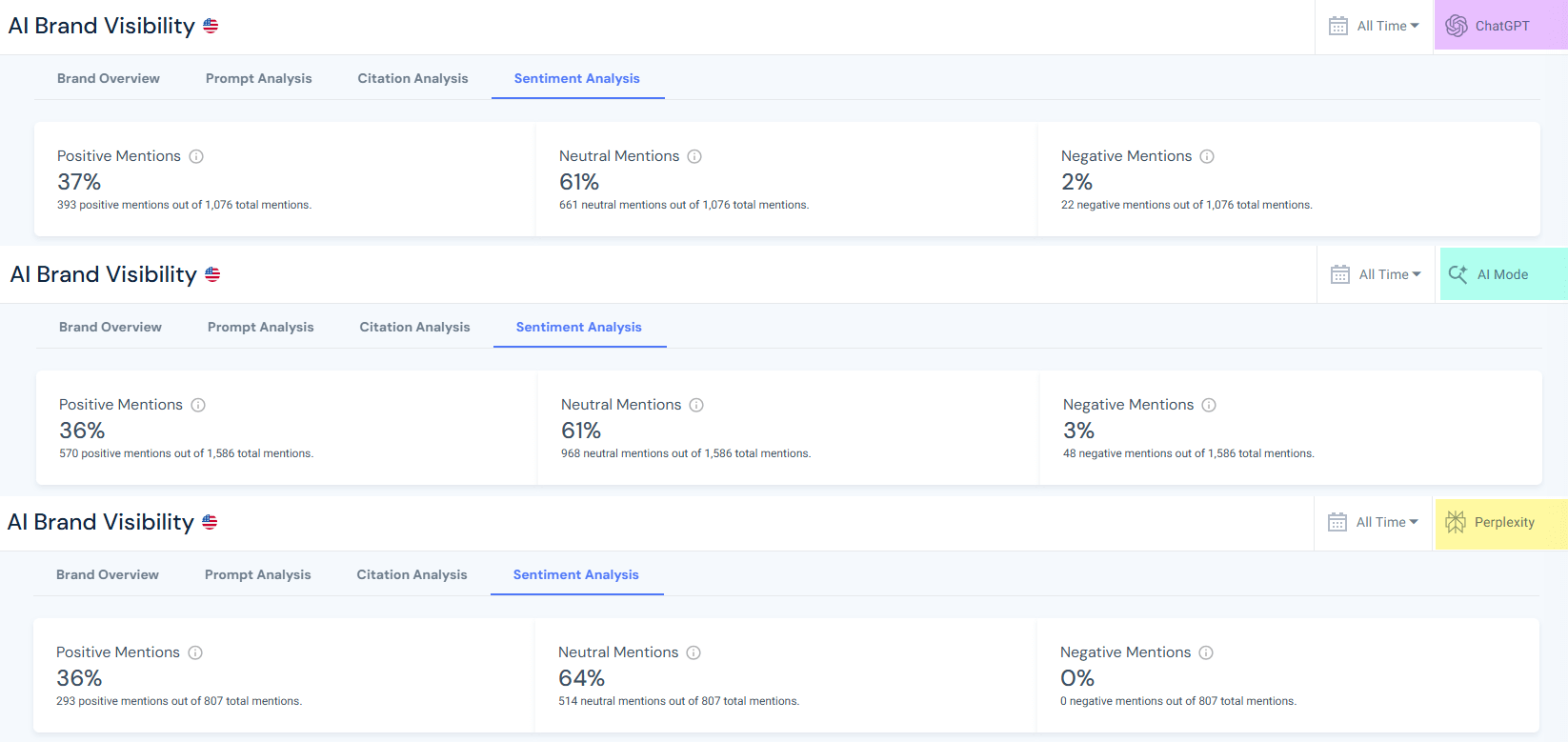
Checking Avis’ AI Mode visibility showed 3% negativity in responses vs 36% positivity (for 1,586 total mentions), and 0% negative sentiment in Perplexity (807 mentions).
This example will zero in on ChatGPT’s negative AI sentiment for Avis, despite AI Mode’s 3%.
At first glance, negativity is very low, but that’s no reason to ignore it.
You practice AEO and GEO to get mentioned in AI answers. Leaving your hard-earned AI mentions unmanaged can hinder your efforts and hurt your performance.
Every mention you earn should be tracked, preferably analyzed periodically, to make sure not only that your brand is mentioned, but that it’s mentioned the way you want it to be.
Now that you know the overall negative score, it’s time to break it down by topics.
2. Break Sentiment Down by Topic
Aggregate statistics mask problem areas. To find the fundamental drivers of neutral or negative sentiment, segment your data by topic, product line, or user intent. This helps you pinpoint which aspects of your offering confuse or disappoint people.
For Avis, the topic Car Rental Companies has the strongest positive sentiment (63%), followed by Luxury and Specialty Car Rentals (38%). However, this analysis focuses on the negative sentiment.
Avis has negative sentiment in the topics Airport Car Rentals (4%), Car Rental Companies (3%, despite the high positivity), and Van & Truck Rentals (5%). Below is the full chart:
What can cause negative AI sentiment toward Avis on airport car rental topics?
This category had the highest absolute number of negative mentions.
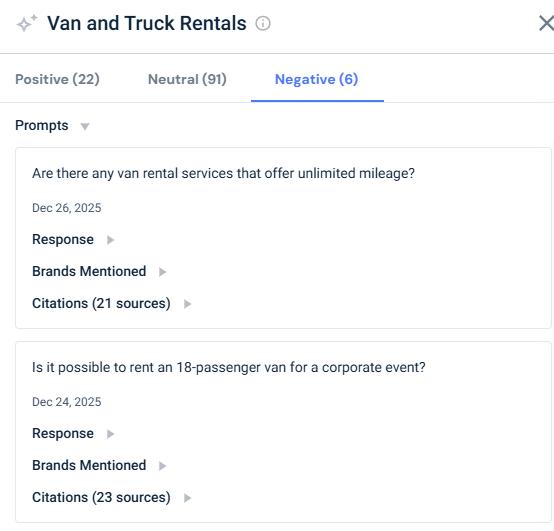
Understanding what causes negativity in this category is easy: click the blue arrow next to the topic’s name, then review the prompts and AI responses for that topic.
In this topic, most complaints centered on high fees, strict mileage policies, and limited vehicle availability.
Addressing these concerns means being transparent about pricing, simplifying fee structures, and ensuring sufficient fleet availability during peak times.
What can cause negative AI sentiment toward Avis on car rental companies topics?
At the brand level, negative sentiment was relatively low (3%) but still notable.
Checking the topic’s prompts showed users were experiencing confusion over which company offered the best value, with occasional mentions of hidden costs or poor customer service.
To reduce the negative sentiment surrounding car rental companies, Avis should clarify what distinguishes it from competitors, publish transparent pricing (including insurance and deposit policies), and highlight service‑quality guarantees.
What can cause negative AI sentiment toward Avis on van & truck rentals topics?
This category had the highest negative share across topics (5%).
Many queries complained about mileage restrictions and questioned whether unlimited‑mileage options existed.
Expanding mileage options, communicating them clearly, and ensuring competitive rates for larger vehicles can help move sentiment from negative to neutral or positive.
3. Read the Prompts Driving Each Sentiment
Numbers alone don’t explain why people feel a certain way.
To understand sentiment, you need to analyze the actual user prompts or queries the model is responding to, as well as the response.
Negative prompts in the Avis data highlight specific pain points:
- “What are the best car rental companies for renting a car in NYC?”
- “Are there any van rental services that offer unlimited mileage?”
Reading these questions tells you that concerns about uptime and service quality are influencing sentiment.
Analyzing the responses hints at how and where you should address these questions:
- Was the response mentioning you taken from a 3rd party review?
- Is it due to a lack of information on your website?
- Can you influence the response to list you as a source, or should you influence the 3rd-party website to change the text they mention you in?
This granular understanding allows you to tailor content and product changes to real user concerns rather than guessing. For example, if many negative prompts mention hidden costs, you may need to publish clearer pricing information.
4. Benchmark sentiment scores against competitors
Your sentiment scores must be understood in context. Even if your overall sentiment looks decent, competitors may still outperform you on key topics, especially those where you face negative sentiment toward your brand.
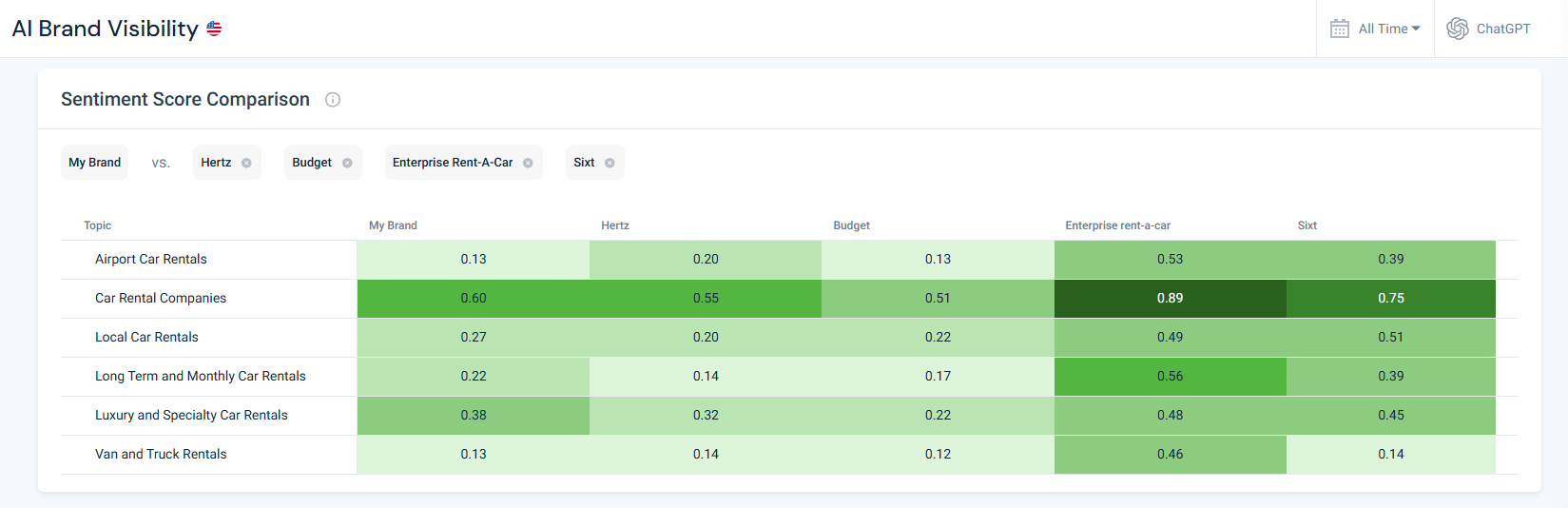
In the Avis heat‑map, the Van and Car Rentals sentiment score was only 0.13, well below Enterprise’s 0.46. However, when looking at the rest of the competitors in this topic, it’s clear that they also have scores similar to Avis’s rather than Enterprise’s (with Budget having even lower scores).
These types of gaps mean users perceive competitor offerings more positively than your brand.
When benchmarking sentiment, don’t just look at differences. To shift your brand sentiment, you also need to think about why they exist.
A higher competitor score could stem from superior features, better marketing, or more authoritative coverage in high‑influence domains.
Understanding the cause helps you decide whether to improve your product, amplify existing strengths, or seed content on authoritative sites. Without competitor comparison, you might underestimate the urgency of a problem or misallocate resources.
5. Monitor regularly and watch for changes over time
Sentiment is fluid. External events (product outages, price changes, news stories, or competitor campaigns) can trigger spikes in negativity. Regular monitoring of your brand’s sentiment mix in AI (weekly or monthly) reveals whether it’s improving or deteriorating.
For instance, if you observe a sudden uptick in negative sentiment around Local Car Rentals, you might investigate whether a service disruption occurred or a competitor released a viral comparison.
To verify the reason, all you need to do is dive into the sentiment analysis tool and analyze the prompts and citations around that topic.
Add metrics like time to detect and time to repair negative citations to your tracking. They will help you measure how quickly you spot changes in negative sentiment and fix misrepresentations. A shorter repair time indicates good operational responsiveness, while slow reaction times may allow misinformation (and negative sentiment) to spread.
Common reasons for negative brand sentiment and how to fix them
Once you identify where sentiment problems occur, you need to address them with targeted actions.
Each issue below includes recommended practices followed by tangible examples drawn from the Avis AI Brand Visibility data.
Note: Many of the listed practices are similar for different types of issues (i.e. update documentation), so when it comes to creating your roadmap, you can decide if you’d like to address them by topic or by fix type.
How to fix confusion or lack of information
Symptoms: Repeated questions about how to use your product for specific purposes, and prompts indicating users complain they don’t understand pricing or features.
Why it happens: Users might not know what’s included in a free versus paid plan, how to implement a feature, or whether your product suits their niche.
Negative sentiment around Airport Car Rentals and Van & Truck Rentals suggests that many renters lacked clarity about pickup policies, mileage allowances, young‑driver fees, and other service specifics.
Best practices:
Create intent‑driven guides and FAQs: Develop pages that answer popular prompts.
For example, several negative queries in the Avis data asked about young-driver requirements, insurance options, hidden fees, and bookings at specific airports. Publishing step‑by‑step guides that answer these questions (complete with pricing explanations, mileage policies, and age restrictions) helps AI tools find and cite your answers.
Clarify plan differences and pricing: Confusion often comes from unclear fee structures.
Provide comparison charts that show what is included in each rental category, highlight insurance coverage, deposit requirements, mileage limits, and add‑on fees.
For Avis, this includes explaining that economy rentals have lower daily rates but stricter mileage caps, whereas premium rentals include unlimited mileage and comprehensive insurance.
Publish canonical explainers with structured data: Use a single, authoritative page for each key topic and embed structured data (FAQ, how‑to, breadcrumb). Models reference structured data more confidently.
Tailor content to niches: Build landing pages or templates for specific audiences.
When users ask “Which car rental companies offer discounts for AAA members?” or “What are the best car rental companies for renting a car in NYC?”, those niche landing pages and FAQs can be cited, shifting neutral sentiment to positive.
Simplify technical explanations: Offer plain‑language summaries, infographics, and videos to demystify complex policies (like insurance coverage or mileage restrictions). Clear, jargon‑free explanations reduce confusion and cut down on negative or neutral questions.
Request updates to high‑influence domains: The most cited websites on each of your core topics have a strong influence on AI engines.
Dig into each of these websites cited URLs to see which of their pages are cited by ChatGPT. If their articles omit your brand or misdescribe your offering, contact their editors with accurate information or collaborate on updated guides.
Securing even a single paragraph mentioning your rental services can improve how generative engines answer questions about airport rentals, mileage policies, or vehicle options.
How to fix product or service problems?
Symptoms:
- Negative prompts complaining about hidden fees, mileage restrictions, or limited vehicle selection.
- Neutral questions hinting at dissatisfaction, such as “Are there any van rental services that offer unlimited mileage?”
Why it happens: Renters encounter unexpected surcharges, unclear mileage policies, poor fleet availability, or unresponsive service. Lack of transparency about fees or terms can magnify frustration.
Best practices:
Triangulate issues using sentiment and prompts: When a topic shows high negative sentiment, cross‑check the actual questions and user feedback.
For example, if several prompts ask about unlimited mileage or unexpected fees in airport rentals, investigate whether your pricing pages, terms, or customer communications create unrealistic expectations.
Improve onboarding and self‑service resources: Offer wizards, booking tools, and interactive tutorials that walk users through selecting vehicles, understanding insurance options, or applying discounts. Transparent pricing calculators and availability dashboards reassure customers and reduce negative surprises.
Enhance customer support: Highlight live chat, community forums, and knowledge bases, and make support responses accessible to AI crawlers. When users ask about roadside assistance or customer service, generative answers should cite your official support resources rather than third‑party complaints.
Communicate updates and improvements: Publish changelogs or announcements when you refresh your fleet, introduce new vehicle categories, reduce fees, or improve policies. Share these updates on high‑authority travel and automotive domains.
Pitching articles about your latest electric‑vehicle offerings or unlimited‑mileage promotions to respected sites can generate authoritative citations that influence generative answers.
Feature positive reviews on weak topics: If your sentiment score in key topics lags competitors, highlight testimonials and case studies on those topics.
Encourage satisfied renters to post on influential travel and automotive comparison sites that appear in the top airport‑rental citations. Include structured data (e.g., a review schema) on your testimonial pages to help AI systems better capture sentiment.
How to correct inaccurate or hallucinated AI outputs?
Symptoms: AI answers omit your brand from relevant queries or invent features you don’t offer. This is not exclusive to negative sentiment. Even if sentiment is neutral or positive, misinformation can mislead users.
Why it happens: Large language models sometimes rely on outdated content or misinterpret information. If reliable sources don’t mention your brand, the model may fill the gap with competitor names.
Best practices:
Maintain a single source of truth: Consolidate specs, pricing, policies, and FAQs into authoritative pages. Keep them up to date and accessible to AI crawlers. For example, ensure your official rental policies and pricing pages are comprehensive and structured so they appear in citations.
Ground generative answers: Use retrieval‑augmented generation in your own chatbots to anchor responses to verified documents. When users ask, “Does Avis offer unlimited mileage options?” the chatbot should reference your official documentation rather than speculate.
Provide corrections via feedback channels: Platforms like ChatGPT allow you to report inaccurate responses. When you find hallucinations, submit corrections with links to your authoritative pages. Maintaining a log of corrections can help you track and measure improvement.
Engage with high‑influence domains: For car‑rental topics, the most cited URLs include blog.getrentacar.com, carandrentals.com, and other high‑authority travel guides. If these articles exclude your brand or present outdated comparisons, reach out to the site owners and ask them to update their content.
Refreshing these pages reduces hallucinations because generative models rely heavily on them.
How to avoid brand safety risks and negative associations?
Symptoms: Your brand appears near inappropriate content, or your marketing team unintentionally engages with risky trends. This may not always appear as sentiment scores, but it can still damage a reputation.
Why it happens: AI models sometimes associate brands with irrelevant or controversial topics due to ambiguous language, and social teams might chase viral trends without vetting them.
Best practices:
Use negative keyword lists and brand safety filters: When publishing ads or content, exclude terms related to controversial topics. Regularly monitor trending queries to ensure your brand doesn’t appear alongside off‑brand topics.
Audit third‑party affiliates and contributors: Many high‑influence domains in the Avis data set are third‑party blogs and comparison sites. Before partnering with or advertising on these sites, review their broader content to avoid unintentional association with problematic material.
Educate social teams and influencers: Provide guidelines on acceptable language and topics. Create a clear escalation path for removing unauthorized or misleading posts.
Prepare a crisis response plan: Should your brand become linked to unsafe content, quickly publish clarifications on your site and contact the sources. Use the AI Visibility dashboard to monitor whether those clarifications propagate into generative answers.
How to fix negative citations and misleading sources?
Symptoms: Generative answers cite biased, outdated, or low‑quality sources that portray your brand negatively.
For Avis, the Airport Car Rentals topic is often dominated by third‑party articles that compare rental companies or list fees and restrictions, many of which emphasize limitations such as mileage caps or hidden surcharges.
Why it happens: AI systems rely on whatever high‑authority sources are available. If the most influential sites do not include your perspective, the model may default to competitor messaging or negative viewpoints.
Best practices:
Monitor citations across topics: Regularly review which domains generative engines cite when answering questions about your brand. Similarweb’s citation analysis tool shows each URL’s influence score. Focus your outreach on sites with the highest influence score because changes there have an outsized impact.
Pitch updated stories to high‑influence publishers: If the most influential websites cited on your topics don’t mention your offering or present outdated comparisons, propose content partnerships or guest posts that fairly compare the options and include your services.
Publish independent proof points: Provide audits, certifications, or performance benchmarks to support claims. When you have objective evidence (e.g., statistics, success stories) and host them on your site, third‑party writers are more likely to reference your data.
Document and share correction logs: Keep a public or internal record of incorrect citations you’ve identified, the actions taken (emails sent, edits made), and the outcomes. This ensures accountability and helps measure improvement over time.
Top methods to turn negative sentiment in AI into positive
Your brand receives a small but noticeable share of negative mentions. Negative sentiment often reflects real pain points or misinformation.
Here’s a recap of the top ways to address and fix negative brand sentiment issues in AI:
Identify and fix root causes.
Dive into negative prompts to understand recurring grievances and address them. For example, simplify pricing structures, expand service availability, and offer more flexible usage options to remove the triggers for complaints.
Close feature gaps.
Identify why competitors receive higher sentiment scores. If analysis shows that users praise your competitors’ loyalty program, seamless service, or wider feature selection, invest in similar capabilities or partnerships to close the gap.
Communicate improvements clearly.
When you solve a problem, publicize it on your website and work with high‑influence sites to update their comparisons. Make sure generative models and users see that the issue has been fixed.
Showcase resolved customer stories.
Encourage customers who had initial issues but were satisfied with resolutions to share their experiences on authoritative blogs and review sites. Positive testimonials about how you handled problems can outweigh prior negative sentiment.
Provide responsive support.
Offer live chat and comprehensive self‑service resources so that frustrated users can quickly find solutions. When customer service turns a negative experience into a positive one, ask for feedback and highlight it in your communications.
Surprise users with unexpected extras.
Offer limited‑edition templates, AI‑powered design suggestions, or seasonal promotions. Delight generates organic buzz and can tip negative and neutral sentiment into positive.
Monitor and iterate.
Track negative sentiment over time to see if corrective actions are working. If specific topics continue to generate complaints, revisit your policies and messaging. Continuous improvement is key to turning negativity into enthusiasm.
Conclusion
Managing brand sentiment in the era of generative AI requires vigilance and targeted action.
Fixing negative sentiment isn’t one‑size‑fits‑all. Each cause of negativity demands a different approach or action to counteract it.
By dissecting sentiment by topic, reading the questions behind the numbers, and comparing your performance to competitors, you can pinpoint exactly where perceptions fall short.
When you combine these actions with sentiment analysis tools and proper monitoring, you can turn negative sentiment into positive advocacy. The result is that your brand not only appears positively in generative answers but also transforms former critics into fans.
FAQs
What is brand sentiment in AI chatbots?
Brand sentiment measures the emotional tone of AI‑generated answers about your brand. Responses are categorized as positive, neutral, or negative. Tracking sentiment helps you understand public perception and prioritize improvements.
How do I detect negative brand sentiment?
Start by examining the mix of positive, neutral, and negative mentions. Break sentiment down by topic to locate weak spots, read user prompts to understand what drives confusion or complaints, benchmark against competitors, and monitor changes over time.
Why is benchmarking against competitors important?
Your sentiment scores only matter relative to the market. If competitor brands earn much higher scores on key topics, it shows customers perceive them as better choices. This comparison informs where to invest resources and how urgent the problem is.
What solutions provide sentiment analysis of brand mentions in AI-driven search results?
Similarweb’s Generative AI Intelligence suite provides all the tools you need to research and track brand visibility in AI chatbots. It allows tracking by topic and provides the most accurate data and insights on AI brand visibility.
What are high‑influence domains, and why should I care?
High‑influence domains are websites that generative models cite most often. Changes to the content on these sites have a greater impact on how AI answers questions. Ensuring these pages accurately represent your brand can shift neutral or negative sentiment toward positive.
How can I fix negative sentiment in AI chatbots?
Address common questions with clear guides, improve onboarding and support, correct AI hallucinations, implement brand safety measures, fix negative citations by engaging high‑influence publishers, and inspire users with compelling stories and new features. Constant monitoring will help you spot issues early and adapt accordingly.
How often should I monitor AI platforms for negative sentiment about my brand?
To catch issues early, review how major AI engines describe your brand at least once a month. Weekly checks are better if your brand is fast‑moving or highly visible. Regular monitoring helps you detect spikes caused by news events, product changes, or competitor campaigns so you can react quickly.
What should I do first when I discover a negative AI mention?
Start by examining the question that triggered the response and the sources the AI cites. Drill into the prompt to understand whether the negativity stems from missing information, an actual service flaw, or a misunderstanding. Then review the cited websites or reviews to see if they misrepresent your brand and decide whether to update your own content, contact external publishers, or fix an underlying product issue.
How do I prioritize which negative sentiments to address first?
Focus on topics where the negative share is highest or where the volume of mentions is large. A 5% negative share on one topic may be less urgent if it represents only a handful of mentions, whereas a 3% negative share on another could reflect hundreds of queries. Also, weigh the severity of the complaint and the business impact. Address the most damaging or widely repeated issues first.
What if negative sentiment is driven by sources I don’t control?
Generative AI engines cite whatever authoritative pages they find. If high‑influence sites omit your brand or portray it negatively, reach out to their editors with updated facts or guest content. If you cannot get a correction, publish clear counter‑content on your own site and other authoritative platforms to give AI models alternative sources.
How can I correct AI misinformation or hallucinations about my brand?
Maintain a single source of truth on your site, like an authoritative page with up‑to‑date details on your products, pricing, policies, and features. Submit feedback through the AI platform’s error‑reporting channels, including a link to your official documentation. Update high‑influence third‑party sites so that AI models have accurate references to learn from.
How do I measure whether my fixes are working?
Track two metrics: time to detect and time to repair negative citations. A shorter detection time indicates strong monitoring, while a shorter repair time shows you’re addressing issues quickly. You should also monitor sentiment scores over time to see whether your actions are affecting the sentiment mix.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!