LLM Seeding is a Data Problem. Here’s How to Solve It.

For the last decade or two, SEO was simple: You fought for the “10 blue links” on Google.
But the behavior has shifted. Today, your customers aren’t just searching; they are conversing. They are asking ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude to recommend software, debug code, and compare pricing.
If you aren’t in that answer, you don’t exist.
This has given rise to a new discipline: LLM Seeding. While competitors suggest vague tactics like “posting on Reddit” or “pitching journalists”(Which I’m also going to mention, haha), I would suggest that the reality is that LLM seeding is a data problem. You cannot solve it with guesswork. You need to map the digital supply chain of information.
Here is my data-backed LLM seeding strategy to move from “hoping for mentions” to engineering them.
What is LLM seeding?
LLM seeding is the strategic practice of placing your brand’s content within the specific datasets and high-authority domains that Large Language Models (LLMs) trust and cite.
While traditional SEO has always leveraged off-site signals, such as backlinks, reviews, brand mentions, and even posting content on platforms like LinkedIn Pulse or Medium, its primary goal was to boost your domain’s authority. LLM Seeding shifts the focus. It optimizes your off-site digital footprint not just to pass link equity, but to serve as a primary source of information for AI models. It is the engine behind GEO (Generative Engine Optimization).
The goal is Brand Memory. You are training the model to associate your brand entity with a specific topic (e.g., “Enterprise CRM”) so that it recommends you even without a direct search.
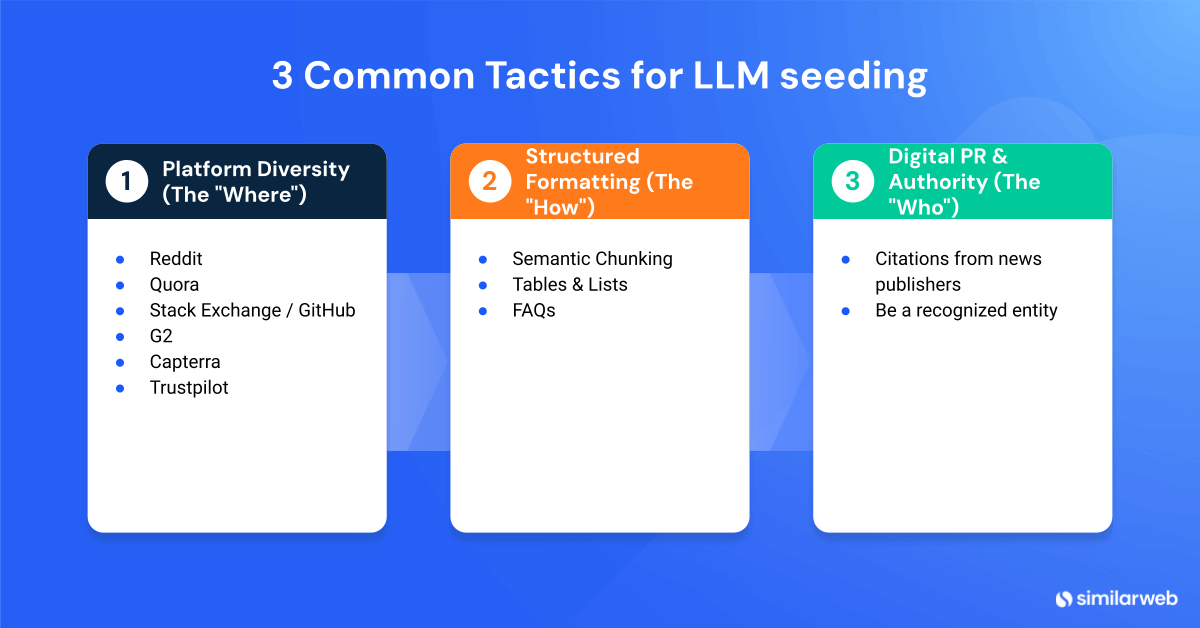
The fundamentals: 3 common tactics for LLM seeding
Before diving into the data, you need to understand the “seeds” themselves. Most successful LLM seeding strategies rely on three core tactical pillars. These are the formats and locations that AI models are naturally inclined to ingest.
1. Platform diversity (The “Where”)
AI models crave human consensus. This is why they heavily weight user-generated content (UGC) and third-party validation.
- Forums: Reddit, Quora, and Stack Exchange are goldmines for training data because they represent real human answers.
- Review Sites: Platforms like G2, Capterra, and Trustpilot provide the structured pros/cons data that LLMs use to build comparison tables.
2. Structured formatting (The “How”)
If an AI can’t parse your content, it won’t cite it.
- Semantic Chunking: Many in our industry suggest breaking content into distinct, self-contained sections. However, Google has explicitly advised against creating content purely to chase LLM rankings. Structure for human readability first.
- Tables & Lists: LLMs love structure. Using HTML tables for comparisons makes it easy for models to scrape and replicate that data.
- FAQs + Schema: Using distinct Q&A formatting helps models map specific questions to specific answers.
3. Digital PR & authority (The “Who”)
Getting cited by high-authority news outlets and industry publications signals to the model that your brand is a recognized entity in the space.
A practical tip we’re testing: AI share buttons
One tactic we’re actively experimenting with at Similarweb builds on this idea of guiding how content enters AI systems.
Next to the standard Share button on our blog articles, we’ve added a Summary option that lets readers send the article they’re reading directly to leading AI platforms, such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI, and Grok, and ask the model to summarize it.
This approach is inspired by research from Metehan Yesilyurt. The core idea is simple: instead of hoping AI systems discover and summarize your content organically, you make it easy for real users to introduce your content into AI conversations themselves.
When a reader clicks “Summarize in ChatGPT” or “Explore this article in Perplexity,” they’re not just sharing with other people, they’re sharing with machines. Over time, this creates more opportunities for:
- Your content to be summarized and cited by AI models
- Your brand to appear in users’ AI interaction histories
- Stronger brand–topic associations to form naturally
This doesn’t replace the need for high-quality content or traditional distribution. It complements them by adding a lightweight, user-driven way to seed content into AI workflows, right at the moment of engagement.
The challenge: Tactics without data are guesswork
These tactics are sound, but they only work when guided by data. Tables, forums, and reviews become effective when they are deployed deliberately, based on where models actually learn.
Most companies execute these blindly. They type 50 prompts into ChatGPT, see where competitors are mentioned, and then guess where to post.
This is fundamentally flawed for two reasons:
- Hallucinations: Asking an AI where it got its info often leads to fake citations.
- Scale: You cannot manually track the millions of prompt variations users ask.
To win, you need to stop acting like a user and start thinking like a data scientist. You need Gen AI Intelligence.
Step 1: Citation forensics (Finding the “High-Weight Nodes”)
Your competitors might be getting recommended by ChatGPT, but why?
In practice, this happens because they are cited on specific third‑party sources that the model repeatedly learns from. It’s because they are cited on a High-Weight Node, a third-party site the AI repeatedly trusts for a topic.
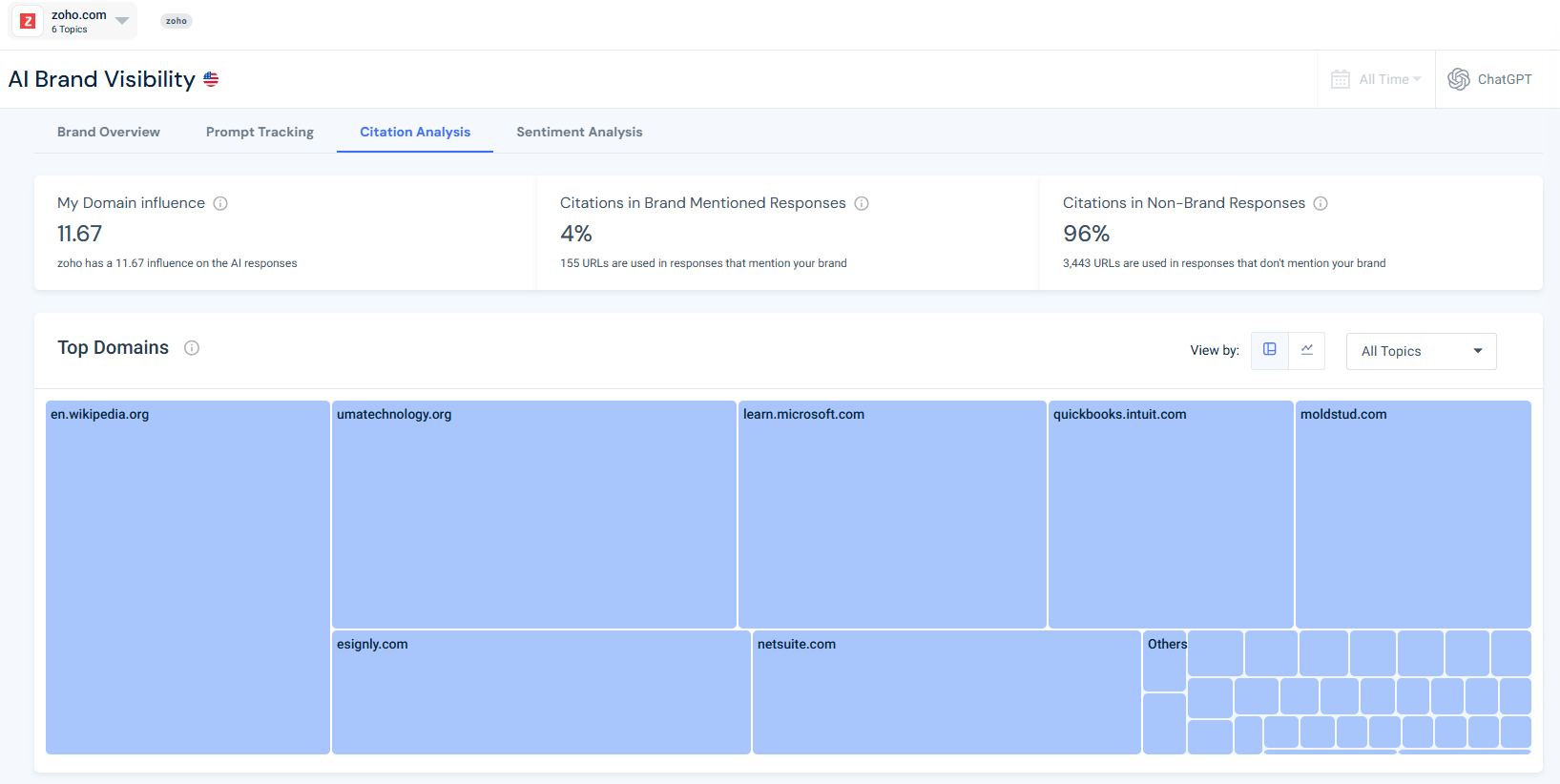
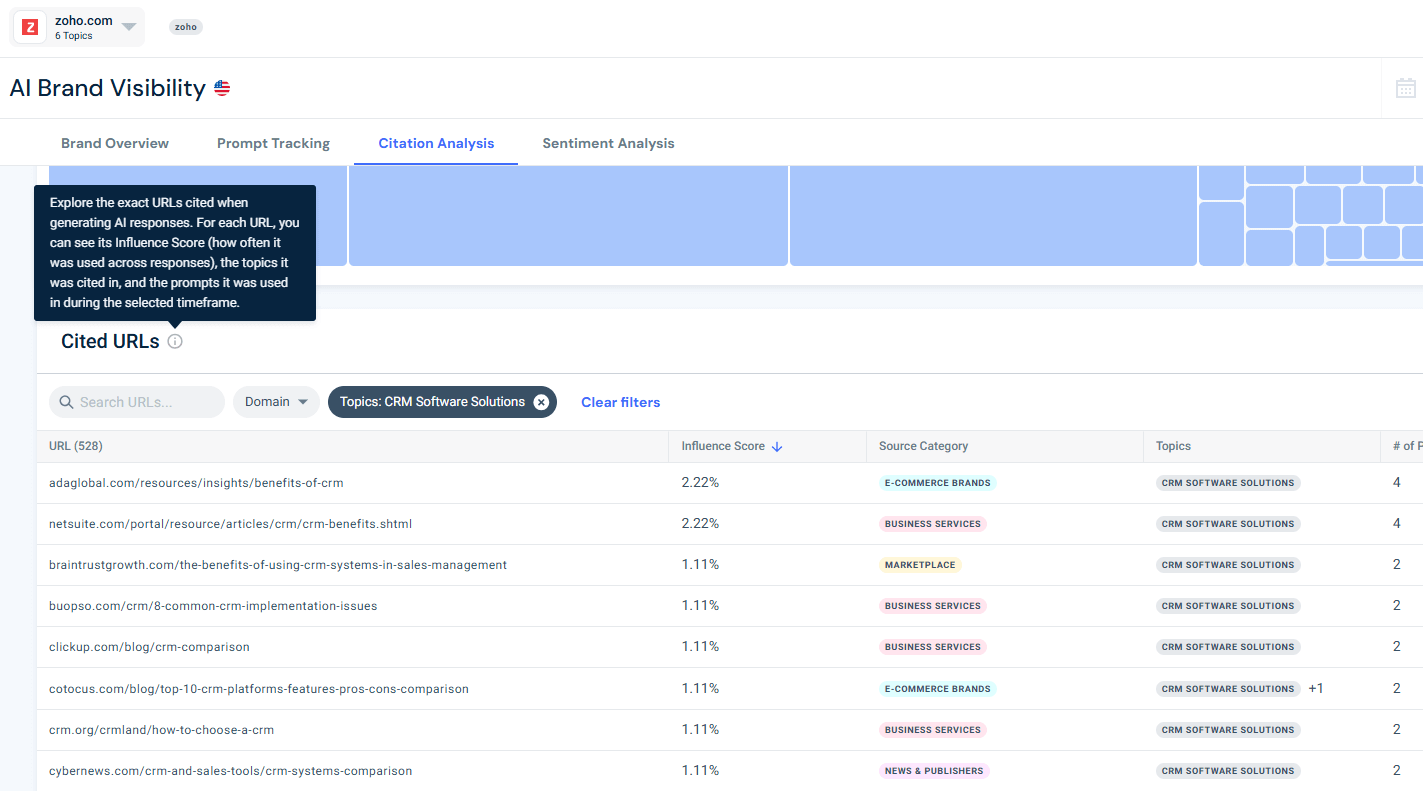
To demonstrate this, I opened an AI Brand Visibility campaign for Zoho, tracking the topic CRM Software Solutions.
Using Similarweb’s AI Citation Analysis tool, I didn’t guess, I looked at the data.
The insight
The data shows that AI visibility is driven primarily by third-party explainer and comparison content, not by brand-owned pages.
- 96% of cited URLs appear in responses that do not mention Zoho
- Only 4% of citations occur in brand-mentioning answers
- Zoho’s domain influence score is 11.67, meaning the model relies largely on external sources
The most influential domains are educational and comparison-focused, including Wikipedia, SaaS explainers, and neutral product guides.
This becomes even clearer when looking at the Cited URLs table for the CRM Software Solutions topic. The highest-influence URLs are not vendor landing pages. They are detailed articles such as “benefits of CRM”, CRM comparisons, and how-to guides published by third-party sites.
These pages share three defining traits:
- They explain a category, not a product
- They compare multiple solutions side-by-side
- They answer foundational questions that models repeatedly reuse
Key takeaway: LLMs don’t trust brands by default. They trust explanations.
Rather than spreading efforts across dozens of sites, brands should prioritize the small set of domains that consistently carry influence for a topic. Seeding these high-weight nodes produces exponentially higher returns than broad, unfocused outreach.
Step 2: Prompt-led content strategy
Once you know where to plant your seeds, you need to know what to plant.
Traditional keyword research shows what people type into Google. LLM seeding requires understanding prompts, the conversational questions users ask AI systems.
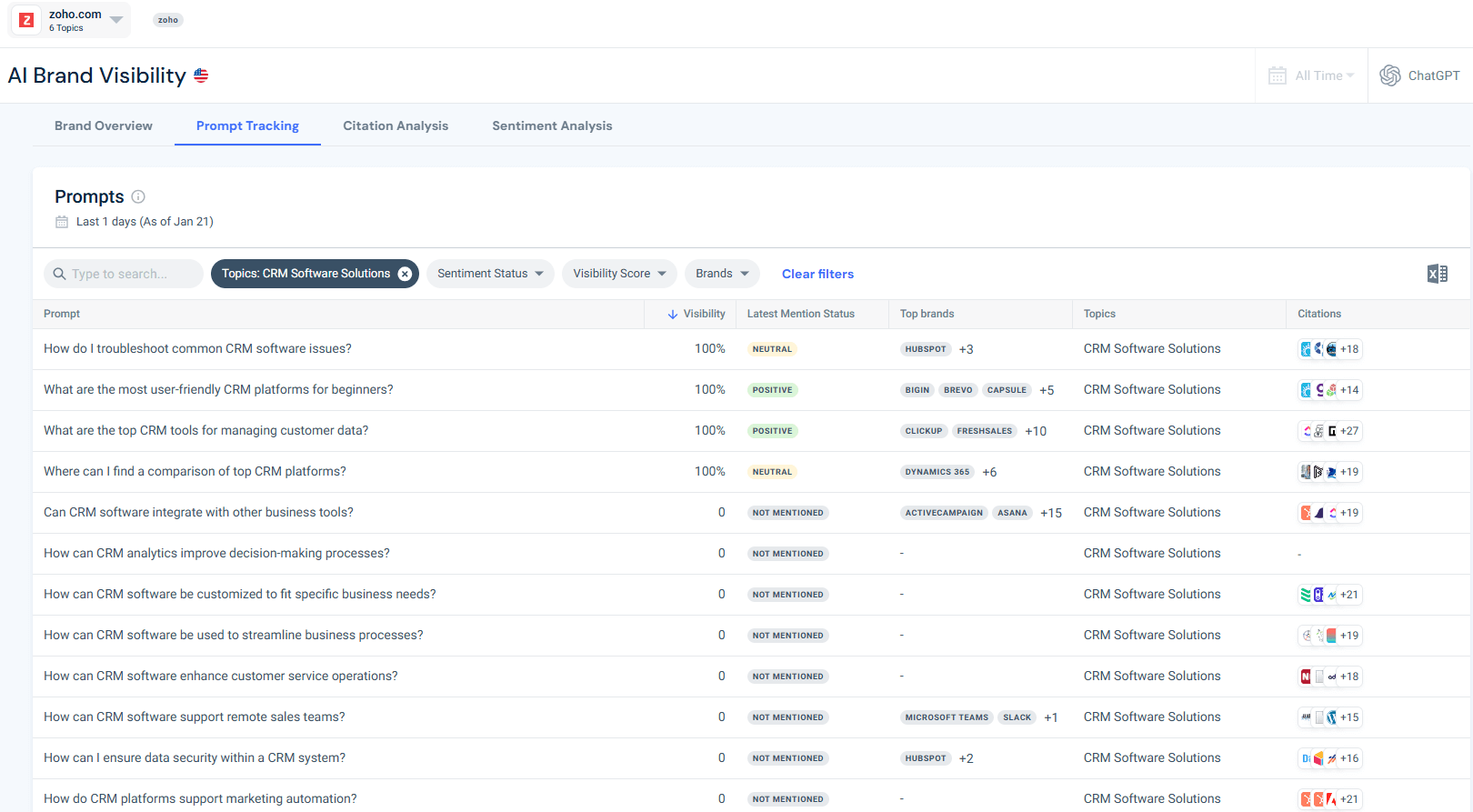
Using Similarweb’s AI Prompt Analysis tool, I analyzed CRM-related prompts sent to ChatGPT.
The insight
The data reveals uneven visibility:
- Some high-level CRM prompts show competitive coverage
- Many operational prompts (customization, integrations, analytics, customer service workflows) show zero Zoho mentions
- Competitors such as HubSpot, Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics, and ClickUp appear repeatedly
These gaps represent clear seeding opportunities. Each prompt where your brand is not mentioned becomes a precise content brief: create authoritative content answering that exact question and place it on the high-weight nodes identified in Step 1.
Step 3: Validating “Live Nodes”
Third‑party sites play different roles in the AI ecosystem. Some actively influence AI‑driven research journeys, while others function as passive content destinations.
Before investing in PR or guest content, validate the domain.
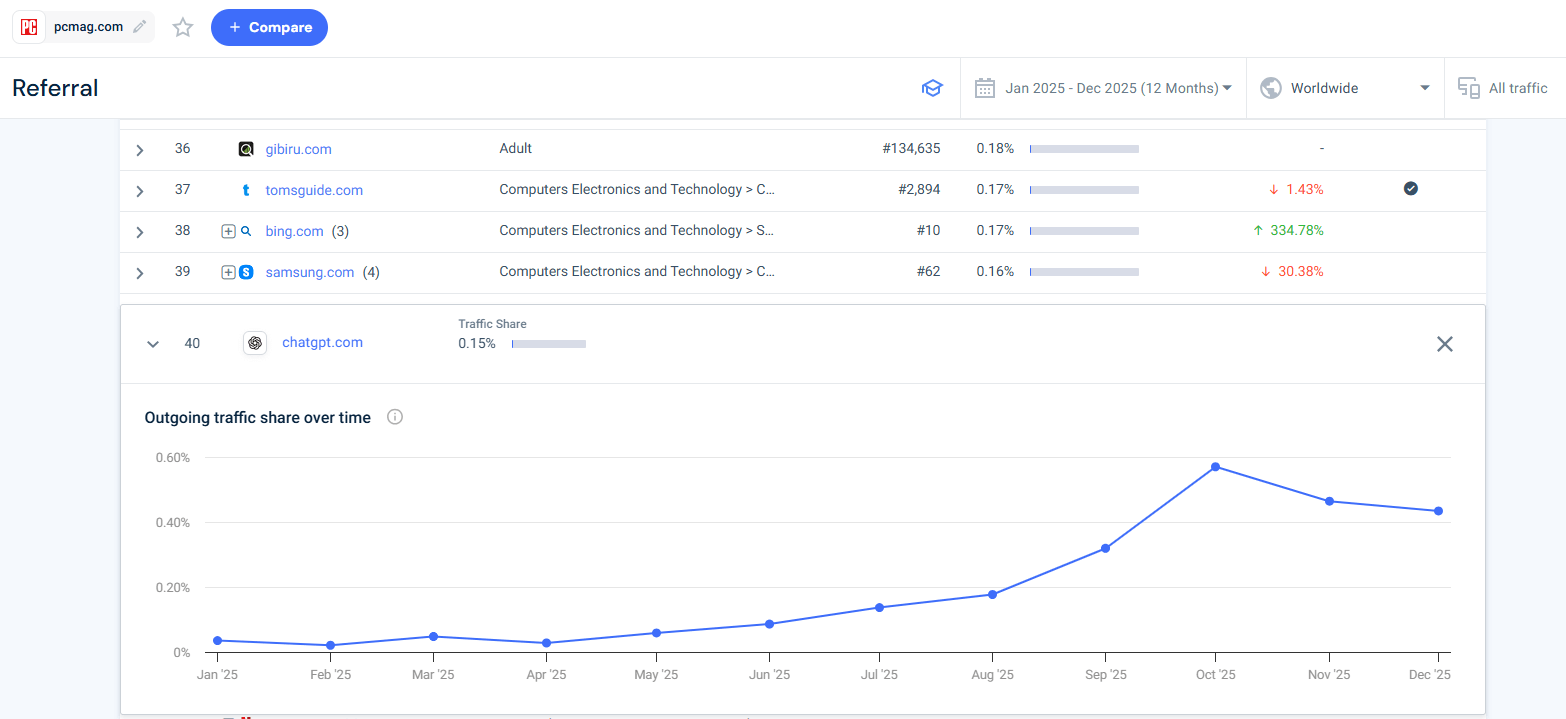
I use outgoing traffic behavior to identify which publishers actively participate in AI‑assisted research journeys.
The idea is simple: if users regularly move from a publisher’s content to an AI platform, that publisher is actively part of the AI-assisted research journey.
In Similarweb, this means looking at where a site sends its traffic after users consume its content. When a domain consistently sends users to destinations like ChatGPT or Perplexity, it’s a strong signal that readers are using AI to validate, compare, or expand on what they just read.
Why this matters
The pcmag.com example illustrates what a Live Node looks like in practice.
As the outgoing traffic trend shows, an increasing share of users move directly from PCMag content to ChatGPT. This indicates that readers treat PCMag as a trusted research source and then use AI to:
- Validate recommendations
- Compare alternatives
- Go deeper on product decisions
For LLM seeding, this is a powerful signal. Publishers like PCMag are not just authoritative, they actively sit inside the AI-assisted research loop.
Prioritizing content placements on domains that already send users to AI platforms increases the likelihood that:
- Your content is consumed by high-intent users
- The domain is repeatedly referenced during model training and inference
Step 4: Measuring ROI (Visibility & Traffic)
The hardest part of LLM seeding is proving value.
I track four metrics: AI Brand Visibility, Share of Model, Brand Mentions, and AI Traffic.
1. Competitive AI Brand Visibility Over Time
Beyond point-in-time visibility, LLM seeding performance needs to be evaluated relative to competitors and over time.
Using the AI Brand Visibility trend view, I track how my brand’s visibility changes week over week compared to other brands in the same topic.
For the CRM Software Solutions topic, this view shows that currently:
- HubSpot leads overall visibility
- Salesforce is following closely behind
- Zoho occupies a clear middle position
- A long tail of challengers with single-digit visibility
This metric answers a critical visibility ROI question – Are my LLM seeding efforts increasing my share of visibility faster than my competitors’?
Tracking this over time turns LLM seeding from a one-off optimization into a measurable competitive motion.
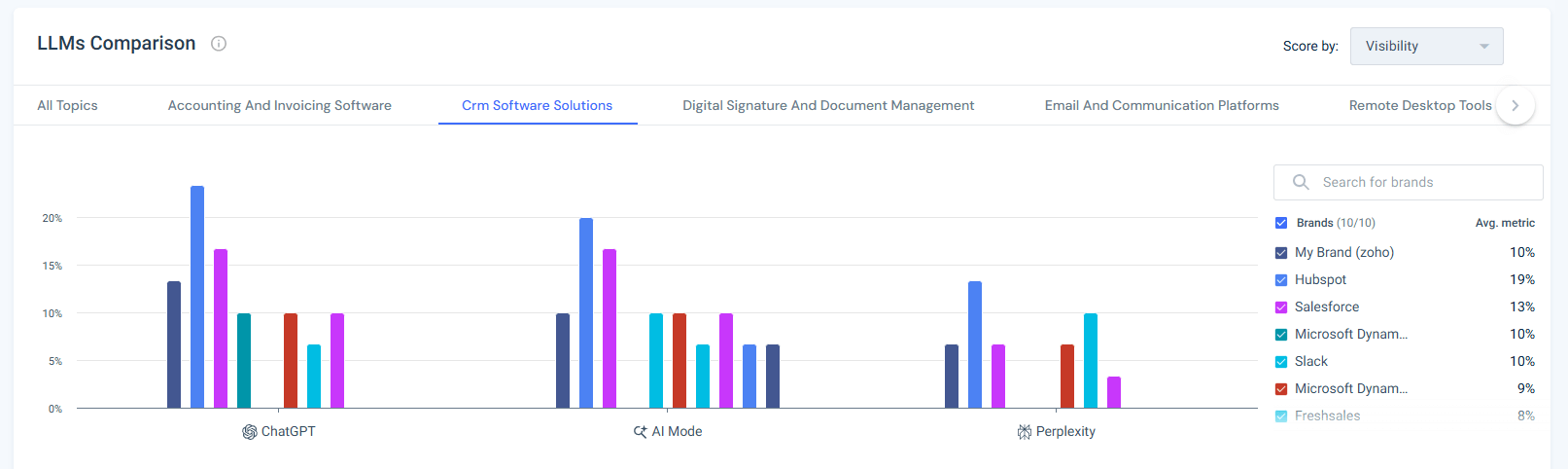
2. Share of Model
Share of Model measures how often a brand appears in AI-generated answers relative to competitors, broken down by model.
Looking at the LLMs Comparison view for the CRM Software Solutions topic, visibility is not evenly distributed across models:
- ChatGPT drives the highest overall visibility across brands, making it the dominant surface where CRM recommendations are formed
- AI Mode shows meaningful but lower visibility, with a similar competitive ordering
- Perplexity contributes a smaller share of visibility, but still plays a role in comparative and research-heavy prompts
At the brand level, Zoho’s visibility sits below HubSpot and Salesforce across all three models, with the largest gap appearing in ChatGPT, the most influential model in this category.
This breakdown makes the strategy clear: improving visibility in the dominant model produces disproportionate gains, while secondary models reinforce brand presence and competitive parity.
3. Brand Mention Volume
Brand Mention Volume measures how frequently your brand appears across AI-generated answers for a given topic.
This is where Prompt Analysis becomes essential. Instead of looking at aggregate sentiment or a single visibility score, I look at individual prompts and ask a simple question: Is my brand present in the answers users are actually asking for?
In the CRM Software Solutions topic, the Prompt Analysis view shows a clear split:
- Several high-visibility prompts where Zoho is mentioned alongside competitors
- A large set of common, high-intent prompts where Zoho is not mentioned at all
- Competitors consistently occupy those unanswered positions
This makes Brand Mention Volume actionable.
Rather than treating mentions as a vanity metric, I use this view to:
- Count how many prompts include my brand
- Identify which prompts exclude it
- Track how that balance changes over time
As AI brand mention volume increases, it signals that the model is learning to associate the brand with a wider set of questions and use cases, not just a narrow slice of the category.
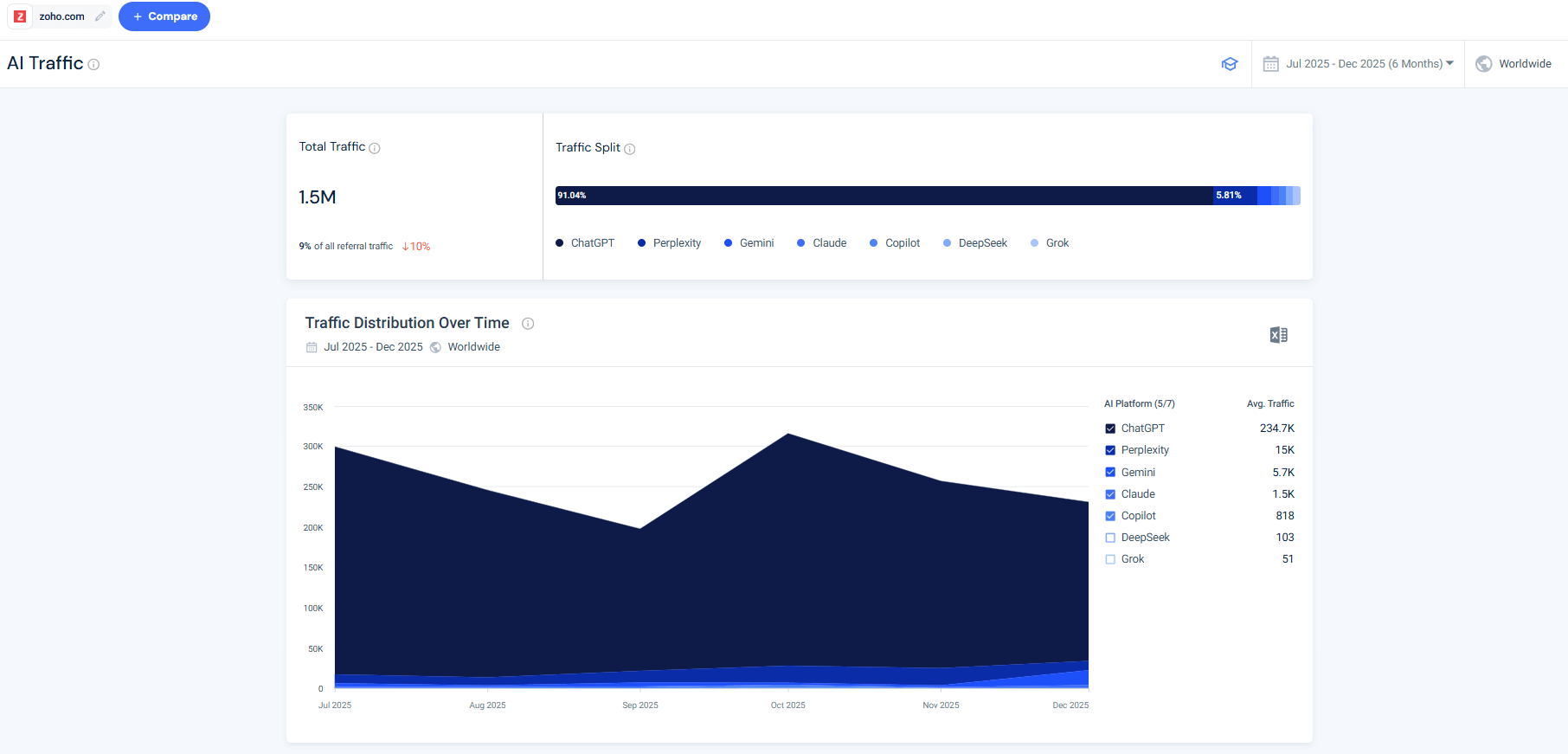
4. AI Traffic
Using Similarweb’s AI Traffic tool, we see that Zoho’s AI traffic shows clear ChatGPT dominance, with smaller contributions from other platforms such as Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude, and natural volatility over time.
This shows that AI interactions include a meaningful layer of high‑intent clicks, especially when users are validating pricing, features, and trust signals.
Conclusion: Stop Guessing, Start Measuring
The era of “spray and pray” content is over.
The winners in LLM seeding won’t be the brands producing the most content, they’ll be the ones with the best map of the AI information ecosystem.
By identifying high-influence citation nodes, analyzing real user prompts, and validating traffic flows, you turn guesswork into a repeatable system.
FAQs
What is LLM seeding, in simple terms?
LLM seeding is the practice of making sure your brand appears in the third-party content that AI models rely on when generating answers. Instead of optimizing only for search rankings, you optimize for where models learn.
How is LLM seeding different from SEO?
SEO focuses on ranking your own pages in search results. LLM seeding focuses on off-site influence, citations, explainers, comparisons, and reviews that models repeatedly reference when answering questions.
Is LLM seeding the same as GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
LLM seeding is a core input to GEO. GEO is the broader discipline of optimizing for AI-generated answers, while LLM seeding focuses specifically on placing your brand into the datasets and sources models cite.
Which types of sites matter most for LLM seeding?
The data consistently shows three high-impact categories:
- Educational explainers and how-to guides
- Comparison and “best tools” content
- Trusted review platforms and forums
These are the sources models reuse most often.
How do I know which sites AI models trust in my category?
Citation Analysis shows exactly which domains and URLs appear in AI responses for your topic. High influence scores and repeated citations identify High-Weight Nodes worth prioritizing.
Can LLM seeding drive traffic, or is it all zero-click?
LLM interactions include both zero-click answers and high-intent referral clicks. AI traffic tends to be smaller in volume but higher in intent, especially for pricing, feature comparison, and validation.
How long does it take to see results from LLM seeding?
LLM seeding compounds over time. Early progress appears as increased brand mentions and visibility across prompts, followed by stronger citation presence and downstream AI referral traffic.
How should I measure LLM seeding success?
Effective measurement combines:
- Share of model visibility
- Brand mention volume across prompts
- AI referral traffic
- Competitive visibility trends over time
Together, these metrics show whether your brand is gaining ground inside AI answers.
Do I need special content just for AI models?
No. The most effective LLM seeding content is human-first, explanatory content that already performs well for readers. AI models benefit from clarity and structure, but usefulness comes first.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!











![The Growth Leader's GEO Decision Framework [+Free Template]](https://www.similarweb.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/attachment-growth-leader-geo-decision-framework-768x429.png)