What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Practical Guide and 7 Winning Tactics
Generative search is changing how users find and consume information. Instead of scanning search results, people now receive complete answers from AI systems. This trend requires a new approach: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). GEO focuses on making content understandable and attractive to AI models so brands remain visible when answers are generated, not just when links are ranked.
What is GEO?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) refers to optimizing content for AI chatbots and search engines that respond to queries using generative AI. It focuses on creating high-quality, contextually relevant content that directly answers user queries and is compatible with the way AI models train, retrieve up-to-date data, and synthesize information.
Generative engine optimization involves:
- AI answer engines: Generative engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude use large language models (LLMs) to understand user intent and generate conversational answers.
- AI-powered search engines: Google now shows AI Overviews at the top of the search results page (SERP) for many search queries (according to a recent study, 30% of general queries and 74% of problem-solving queries). In June 2025, Google launched AI Mode, which provides a full generative interface integrated into its search engine. Bing and other search engines also integrate generative AI responses.
- Influencing AI responses: GEO aims to influence what information AI models include in their responses, ensuring your brand, content, and message are represented accurately and favorably.
Why is Generative Engine Optimization important?
The growth of AI-driven search has begun to cannibalize the traffic websites traditionally earned through SEO. Instead of clicking through search results, users are increasingly satisfied with AI-generated answers at the top of Google and Bing or by asking tools like ChatGPT directly. This change means fewer visits to brand websites, even when their content informs the AI’s response.
For example, the Wall Street Journal reports that Mailchimp, a leading email marketing provider, saw a steep drop in traffic as consumers rely more on AI summaries. To adapt, they have optimized their sites for AI crawlers, prioritizing technical elements like load speed and structured code, which are important for content discoverability by AI engines.
This trend is reinforced by the rise of zero-click search, where a significant share of queries are resolved without any link clicks. A Similarweb report, quoted in Search Engine Land, showed that the number of search queries resolved without a click to a website increased from 56% in May 2024 to 69% in May 2025. A report by the University of Virginia School of Business showed over 60% of consumers use AI for shopping, underscoring how quickly purchasing behavior is shifting.
While AI-driven referral traffic currently accounts for a very small fraction of traffic, under 1% according to a Cloudflare study of 25 million websites, it is growing rapidly, especially in the retail sector. Modern Retail reported that ChatGPT now accounts for 20% of Walmart’s referral traffic.
This evolution requires marketers to rethink their strategies. Traditional SEO metrics (rankings, click-through rates, and positions) are less applicable for AI models, which use different mechanisms to decide what information to display. GEO does not replace SEO, mainly because Google continues to be the world’s biggest referrer of traffic to websites, and also because the practices are quite similar. However, it adds new metrics and best practices to help organizations achieve visibility in AI engines alongside search rankings.
How Generative AI search engines work
Generative AI search engines pull information from two primary sources: pre-trained knowledge and real-time web searches. Pre-trained knowledge comes from the data used to train the model, which has a fixed cutoff date and does not update regularly. Real-time searches allow these systems to retrieve the latest information when answering queries.
When a user asks a timely question such as “what tools do experts recommend for generative engine optimization?” an AI like ChatGPT typically does not rely on training data, which may provide outdated information. It performs a live web search, processes the top results, and composes its answer based on their content. This means the sources and rankings in the search engines these AIs use directly affect what gets included in their responses. The technical mechanism AI engines use to retrieve up-to-date data and use it in their responses is called Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
Different platforms rely on different search engines for this process. ChatGPT is thought to primarily use Bing due to its partnership with Microsoft. However, recent reports by The Information and other sources indicate that it also uses Google search results. Perplexity combines results from multiple engines, while Google’s AI systems draw exclusively on Google’s search index. In many cases, AI engines directly crawl web pages without relying on a search index.
To appear in AI-generated answers, brands must optimize for the underlying search engine that the AI platform queries, and ensure their pages are directly accessible and crawlable by AI bots. This makes search optimization, especially for Google and Bing, a critical element for AI visibility.
GEO vs. SEO
How is GEO similar to SEO?
Many of the things that improve visibility in AI answers are similar to traditional SEO techniques. The same practices still matter: Clear content that answers questions, scannable structure with headings, FAQs, and passages, entity-focused writing, and citing sources. Digital PR, links, and brand mentions remain key because LLMs favor credible, well-referenced sources.
Familiar channels also carry over. Long-tail, conversational queries (fan-out questions), multi-modal assets (text, images, video, audio), cross-platform presence (sites, social, forums), local signals (GBP, reviews, NAP consistency), and structured data are all longstanding SEO tactics that map directly to AI search needs.
How is GEO different from SEO?
GEO adds a layer of activity specific to AI platforms. Teams must track citations, mentions, and share of voice across multiple LLMs (e.g., ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews/AI Mode, Perplexity) and analyze how responses reflect brand perception. GEO also pushes practitioners to learn AI-adjacent skills like prompt design, embeddings and similarity, NLP/semantic search, and workflow automation.
RAG systems used by modern AI engines tighten the link between traditional rankings and AI answers, because LLMs pull from search results and re-rank passages. That raises the bar on passage-level relevance and clarity, while making spammy shortcuts risky. While AI engines don’t currently have advanced spam protections and penalties like search engines do, spamming can cause websites to be penalized by search engines, which will also hurt their visibility in AI engines.
Integrating GEO with SEO
When building your GEO program, it’s critical to maintain SEO fundamentals: information architecture, high-quality content, digital PR, technical hygiene, and pragmatic structured data that matches documented use. Then layer GEO on top:
- Implement tracking for LLM citations, coverage, and sentiment across key AI surfaces.
- Optimize for fan-out questions with concise, answerable passages, FAQs, and entity clarity.
- Expand multi-modal coverage and cross-platform presence by seeding text, images, and rich media where LLMs source information.
- Build team capability in AI literacy, embeddings/NLP, and automation to speed research and reporting.
Treat GEO as incremental to SEO, not a replacement. Strong performance in traditional search feeds AI retrieval, while GEO metrics and workflows ensure your brand is findable, quotable, and accurate inside AI-generated answers.
Best practices and strategies for Generative Engine Optimization
Here are some of the ways organizations can build a winning GEO strategy.
1. Generative AI research and analysis
Effective GEO begins with a structured research process that reveals how AI-driven platforms view your brand, your competitors, and the topics that matter to your audience. This research covers four main areas:
- GEO prompt research: Identify conversational, long-tail, and semantically related terms that AI platforms favor. Use our Gen-AI tools to see real prompts searched by users in your industry across informational, navigational, commercial, and transactional (or Asking, Doing, and Expressing) prompt intents.
- AI Overview response analysis: Our rank tracker can identify which queries trigger AI Overviews; study their structure and adapt your content to match preferred formats such as lists, tables, or mixed media. Monitor your content’s placement in AI Overview citations and optimize to improve your rank.
- AI Competitor analysis: Identify who is being cited in AI answer engines and AI Overviews for your target queries. Study their formats, coverage depth, and use of multimedia, then improve upon them while maintaining your own brand voice.
- Brand perception intelligence: Using our Gen-AI Intelligence Toolkit, you can assess how AI platforms and user-generated content portray your brand. Monitor sentiment, adjust messaging, and ensure your positioning matches authority and trust signals that AI systems value.
We’ll dive into our Gen-AI tools at the bottom.
2. Technical optimization for AI crawlers
AI crawlers don’t browse like humans. They scan pages quickly, looking for clear, well-defined snippets they can quote in responses. To increase inclusion in generative answers, sites must be fast, clear, and easy to parse. Key practices include:
- Don’t block AI bots: Many organizations, and CDNs like Cloudflare, block AI bots by default to prevent them from training on their content. While this might be a valid business decision, it is not compatible with generative engine optimization. To maximize GEO, allow AI bots to access your public-facing content without restriction.
- Design for skimmability: Use clear headings (H2/H3), short paragraphs, bullet lists, and tables. Add FAQ blocks and comparison charts so AIs can lift precise snippets.
- Apply structured data: Implement schema markup (faq, howto, product) where relevant. Keep HTML clean and semantic with real headings, lists, and alt text for images.
- Optimize for speed: AI systems often operate with a timeout of under 2 seconds. Improve Core Web Vitals and load speed so pages are fully retrievable when directly accessed by AI bots.
- Cover related queries: Include concise answers to many related questions on one page (e.g., “X vs Y,” pros/cons, common use cases) to boost passage-level relevance.
- Expand language reach: Most AI citations skew to English. Publish English versions of high-value content alongside local-language pages to maximize inclusion across queries.
3. Structure content for AI readability
AI-driven platforms prefer content that is easy to parse, contextually clear, and directly aligned with user intent. This means:
- Using schema markup and structured data to make relationships between concepts explicit.
- Organizing content with clear headings, bullet points, and concise paragraphs so AI can extract relevant segments without ambiguity.
- Covering the full spectrum of search intents (informational, commercial investigation, navigational, and transactional) so your content matches a wider variety of prompts.
- Including authoritative references, statistics, and industry terminology to signal credibility.
- Posting and republishing content on social platforms like Reddit, Quora, LinkedIn, and Medium, which generative models often cite in responses.
4. Brand mentions on high-ranking lists and reputable sites
Since many AI-generated answers draw directly from high-ranking Google results, especially list-based content, earning placement in these articles is one of the fastest ways to improve your visibility. This requires comprehensive coverage of your target topic, which means creating multiple variations for different audience segments and use cases.
For example, if you’re targeting “finance software,” you might develop dedicated pieces for “best finance software,” “best finance software for small businesses,” “best finance software for personal budgeting,” and “top finance software tools for enterprises.” Maintaining these lists over time is just as important as creating them, because AI engines place a special emphasis on fresh and timely content.
In addition to creating your own lists, it is critical to identify lists on authoritative websites that are frequently cited by AI engines. Reach out to these websites to get yourself included in the lists, in the highest position possible. If ranking organically is not realistic, negotiating inclusion with reputable publishers can be an effective alternative. Some will accept paid placement, while others will require strong evidence of your credibility before adding you.
5. Ensure presence in trusted directories and databases
Generative engines often reference data from authoritative directories and databases, either directly, as with Claude, or indirectly, through indexed search results, as with ChatGPT and Gemini. Securing a presence in these sources reinforces your credibility and boosts your chances of being cited.
The most valuable sources typically fall into three categories: Tier 1 high-authority research hubs like Statista, McKinsey, and Pew Research Center; Tier 2 general directories and review sites like Wikipedia, Bloomberg, and Clutch; and Tier 3 industry-specific aggregators relevant to your field.
Each category has a different influence weight depending on the generative engine. For example, Claude leans heavily on high-authority research hubs, while Perplexity and Gemini distribute weight more evenly between research and review platforms. In all cases, the more reputable and established the directory, the more beneficial the listing.
6. Publish unique, data-driven insights
Original research and proprietary data remain one of the most reliable ways to secure citations from AI platforms. Generative systems prefer to draw from content that offers something beyond what’s already widely available, meaning data-backed insights, benchmarks, and new metrics carry more weight than generic overviews.
For example, publishing an annual industry benchmark report, producing original survey results, or releasing in-depth case studies positions your content as a primary source. This type of material also attracts backlinks, which indirectly improves your GEO performance by increasing domain authority.
Thought leadership articles that challenge conventional wisdom or introduce new frameworks can also gain traction, as can comparison pieces that guide decision-making with detailed evaluation criteria. The more your content demonstrates unique expertise, the more likely AI is to cite it as an authoritative reference.
7. Implement digital PR activities
Building a reputation as an industry authority requires putting expertise in front of the right audiences. Digital PR remains one of the most effective ways to earn authoritative mentions that AI systems recognize. Contributing expert quotes to news stories and industry reports, appearing on niche podcasts, securing positive media coverage, and being cited in white papers or analyst reports all increase the number of trusted references tied to your brand.
Each activity strengthens your authority footprint across the web. Generative models scanning for credible sources are more likely to include your brand when they find it consistently referenced in multiple high-quality publications. Over time, a strong digital PR presence also supports your inclusion in trusted directories and high-ranking lists, making it an integral part of a sustainable GEO strategy.
How to Use Similarweb’s Gen-AI Tools
Generative Engine Optimization relies on understanding how AI platforms find and cite your content. Similarweb’s Gen-AI Intelligence toolkit provides two complementary modules: AI Traffic and AI Brand Visibility, which show where traffic comes from and how brands are mentioned in generative answers. The example below shows how to use these tools to evaluate a real brand (Mailchimp) and illustrates how the data can inform your GEO strategy.
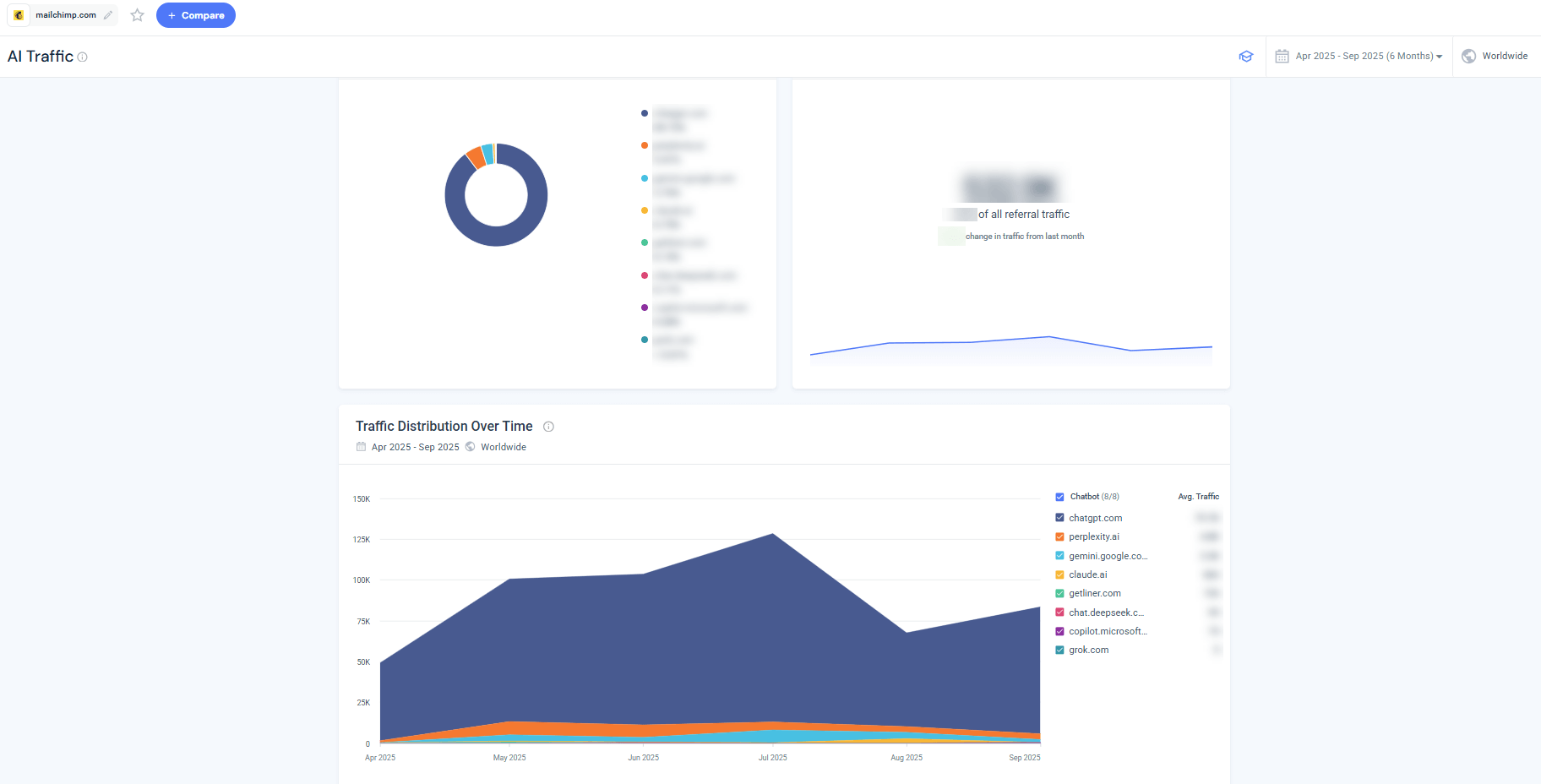
Step-by-step: AI Traffic
- Open the AI Traffic module. After logging in, go to Gen-AI Intelligence, AI Traffic. A search box appears asking for a domain.
- Enter your website. Type the domain you want to analyze (e.g., mailchimp.com) and select it. The page loads charts summarizing AI-generated referrals.
- Review traffic split by AI platform. The doughnut chart shows the percentage of referral traffic from each AI engine.
- Check website traffic and trends. A separate panel shows the total number of visits driven by chatbots and how this metric is trending.
- Explore traffic distribution over time. A stacked area chart plots monthly traffic from each AI source.
- Identify top landing pages. The tool lists landing pages that receive the most AI-generated traffic.
How this helps GEO: The AI Traffic report shows which generative platforms (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, etc.) matter most for your brand. If ChatGPT accounts for almost all AI-driven visits, focusing on optimizing content for OpenAI’s retrieval and ranking algorithms may deliver the highest return. Identifying landing pages with strong or weak AI-referral performance guides future content improvements and helps you measure whether GEO tactics are increasing AI-driven traffic.
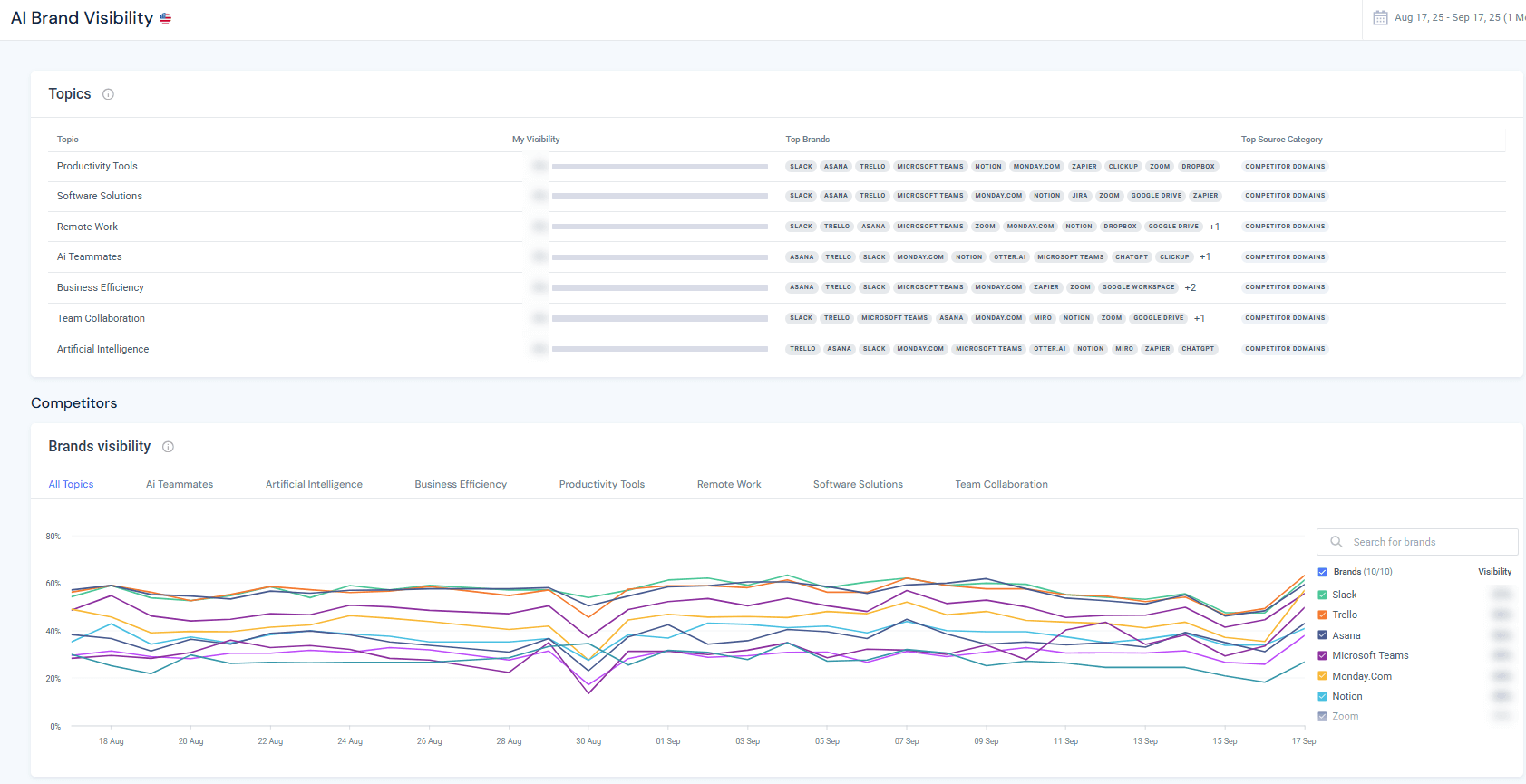
Step-by-step: AI Brand Visibility
- Navigate to AI Brand Visibility. From Gen-AI Intelligence, select AI Brand Visibility. A dashboard appears showing existing campaigns and a form to create a new campaign.
- Create a new campaign. In the Create a new campaign area, enter your company’s website (e.g., mailchimp.com) and click Get Started. A modal opens asking for more details.
- Configure campaign settings. You are prompted to confirm the brand name, select the region where you want to monitor AI responses, and choose topics relevant to your brand (e.g., “Email Marketing,” “Marketing Automation,” “E-commerce Integration”). This targeting ensures that Similarweb tracks the right generative prompts and citations.
- Create the campaign. After configuring, click Create Now. Similarweb will then monitor AI-generated answers across the selected topics and locations, reporting where and how the brand is cited.
- Analyze AI mentions. Once the campaign runs, the dashboard will show the number of citations across ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexit,y and other engines, the prompts that triggered mentions, and sentiment distribution. These insights help you identify which topics and AI models already recognize your brand and where gaps exist.
How this helps GEO: The AI Brand Visibility module is essentially a brand-share-of-voice monitor for generative answers. It highlights prompts where your brand appears (or is missing), the tone of AI-generated mentions, and competitor comparisons. By understanding which AI engines cite your brand and under what contexts, you can tailor content and digital PR efforts to influence generative models. For instance, if your brand isn’t cited for “marketing automation platforms” in ChatGPT’s answers, you may need to publish more authoritative content or secure mentions in high-ranking comparison lists so AI models have high-quality material to draw from.
Key takeaways
-
- Start with AI Traffic to understand the landscape. Identify which chatbots drive visits and which landing pages resonate most.
- Use AI Brand Visibility to monitor and expand your share of voice. Track topics, locations, and prompts where your brand is mentioned, and adjust your GEO strategy accordingly.
- Combine insights from both tools. High traffic from ChatGPT, but few brand mentions in competitor topics indicate an opportunity to create authoritative, structured content that AI can cite. Conversely, strong brand visibility but low traffic may mean optimizing technical elements (speed, structured data) to improve AI crawlers’ ability to fetch your pages.
Integrating Similarweb’s Gen-AI tools into your GEO workflow provides concrete data on how AI engines interact with your content. By regularly monitoring AI referral traffic and brand visibility, you can refine both SEO and GEO tactics to remain visible in traditional search results and AI-generated answers alike.
Get ahead of the GEO curve with Similarweb
Generative search is changing the rules of visibility. While SEO focuses on rankings and clicks, GEO requires influencing how the top AI platforms interpret and present information. Success depends on ensuring that your content is accessible, authoritative, and consistently cited in AI-generated responses.
Organizations that integrate GEO with traditional SEO will be better positioned as user behavior shifts. Strong SEO fundamentals keep content discoverable in search engines, while GEO practices extend visibility into AI-driven answers where users increasingly get information.
While many organizations struggle to adapt to the new reality, you can get ahead of the curve. Using Similarweb’s integrated SEO and GEO toolset to gain competitive intelligence, perform GEO research, and build content strategies will build authority that compounds as generative platforms take center stage.
FAQs
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization is the process of optimizing content so it appears in AI-generated answers from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google AI Overviews. It emphasizes structured, authoritative content that AI models can parse and cite.
How is GEO different from traditional SEO?
SEO focuses on rankings and clicks in search results, while GEO targets how AI systems generate and present answers. GEO involves tracking AI citations, optimizing passages for readability, and ensuring content is machine-friendly as well as user-friendly.
Why is GEO important now?
As more users rely on AI tools for information, fewer clicks go to websites. GEO ensures that your brand is still visible and accurately represented in AI answers, even when users don’t visit your site directly.
What are the key GEO best practices?
Best practices include optimizing content for structured readability, using schema markup, publishing original research, securing placement in high-authority lists and directories, and monitoring how AI tools cite your brand.
What are the most common mistakes in generative engine optimization?
Common GEO mistakes include focusing on keyword density instead of covering related entities and conversational queries, neglecting schema markup and structured data, letting content grow stale, and failing to establish trust signals. Poor mobile-friendly UX, not tracking AI citations, and treating GEO separately from core SEO further hurt AI visibility.
What metrics should I track for generative engine optimization success?
For generative engine optimization, track visibility metrics (citation frequency, share of voice, brand mentions, and sentiment), AI traffic growth, conversion rates, and AI overview presence. Don’t lose sight of traditional SEO metrics like impressions and CTR, as they can also indicate your visibility in Google AI search.
How can tools like Similarweb help with GEO?
Similarweb’s Gen-AI Intelligence toolkit tracks brand mentions, citations, and traffic from AI platforms. It helps marketers understand where they appear in generative answers, measure AI-driven visits, and adapt strategies to increase share of voice across platforms.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!






![The Growth Leader's GEO Decision Framework [+Free Template]](https://www.similarweb.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/attachment-growth-leader-geo-decision-framework-768x429.png)