Guide to AI Agents: How They Work, Uses, and Best Practices
What are AI agents?
AI agents are autonomous software entities designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and act to achieve objectives. AI agents are based on large language models (LLMs), but unlike traditional AI assistants, they do more than answer questions. They can adapt their behavior based on new information, use tools to carry out relevant actions, and operate independently within a given set of constraints.
AI agents are found across many domains, from simple scripts that manage tasks in an operating system to complex systems that can perform complex business analysis, drive cars, and trade stocks autonomously. These agents usually follow an iterative process: analyze their environment, make sense of the inputs, decide on an appropriate action, and carry it out. The cycle repeats as the agent interacts with dynamic environments, adjusting its strategies based on feedback and outcomes.
Summarize with ChatGPT | Google AI | Perplexity | Grok
The following table illustrates the difference between AI agents, AI assistants, and traditional bots that enable simple, deterministic automation.
| Feature | Traditional Bots | AI Assistants | AI Agents |
| Autonomy | Low: follow predefined rules | Medium: respond based on input | High: act independently to achieve goals |
| Learning Ability | None | Limited: Fine-tuning possible | High: adapt through feedback and experience |
| Tool Integration | Minimal | Moderate: Search, calendar, etc. | Extensive: use APIs, databases, other agents |
| Reasoning | None | Basic pattern matching | Advanced: plan, reason, and strategize |
| Interaction Mode | Rule-based conversations | Natural language dialog | Multistep, iterative task execution |
| Environment Awareness | None | Limited to inputs from the user | Perceives dynamic environments |
| Typical Use Cases | FAQ bots, simple automation | Virtual assistants (e.g., Siri) | Autonomous workflows, simulations, DevOps |
7 capabilities that define AI agents, and the 7 benefits they deliver
AI agents usually follow an iterative process: sense their environment, make sense of the inputs, decide on an appropriate action, and carry it out. The cycle repeats as the agent interacts with dynamic environments, adjusting its strategies based on feedback and outcomes.
Core capabilities of AI agents
- Reasoning and autonomous decision making: AI agents use logic and contextual data to conclude, solve problems, and make informed decisions.
- Acting: They perform tasks or execute decisions through digital or physical actions to fulfill goals.
- Observing: Agents perceive and interpret their environment through data inputs like text, images, or sensor signals.
- Planning: They strategize by evaluating possible actions and outcomes to choose optimal steps toward their objectives.
- Collaborating: Agents coordinate with other agents or humans to accomplish tasks that require joint effort or information sharing.
- Self-refining: Through learning and feedback, they adapt and improve their behavior and performance over time.
- Multimodal processing: They can handle various data types – text, voice, images, code, all simultaneously to make richer decisions.
Why AI agents matter for organizations
- Automation of repetitive tasks: AI agents handle routine and time-consuming activities such as data entry, monitoring, and scheduling.
- Faster decision-making: By processing data in real time and executing predefined actions, agents can make and act on decisions more quickly than human operators.
- Scalability: AI agents can manage increasing workloads without proportional increases in human resources, enabling systems to grow efficiently.
- 24/7 operation: Agents function continuously without fatigue, making them suitable for environments requiring constant monitoring or support.
- Personalization at scale: Agents can tailor interactions and services to individual users by learning from data, improving user experience and satisfaction.
- Cost reduction: By automating tasks and improving efficiency, organizations can reduce labor costs and minimize losses from downtime or human error.
- Adaptability to change: Learning agents can adjust their behavior in response to new data or changes in their environment, maintaining performance even under shifting conditions.
How do AI agents work?
AI agents operate through a sequence of interconnected stages: goal initialization, reasoning using tools, and learning through feedback. At the foundation of most AI agents are LLMs, which serve as the reasoning engine.
However, LLMs alone are limited to their training data. To overcome this, agents use tool calling to access external resources such as APIs, databases, or even other agents, allowing them to retrieve current information and execute tasks more effectively.
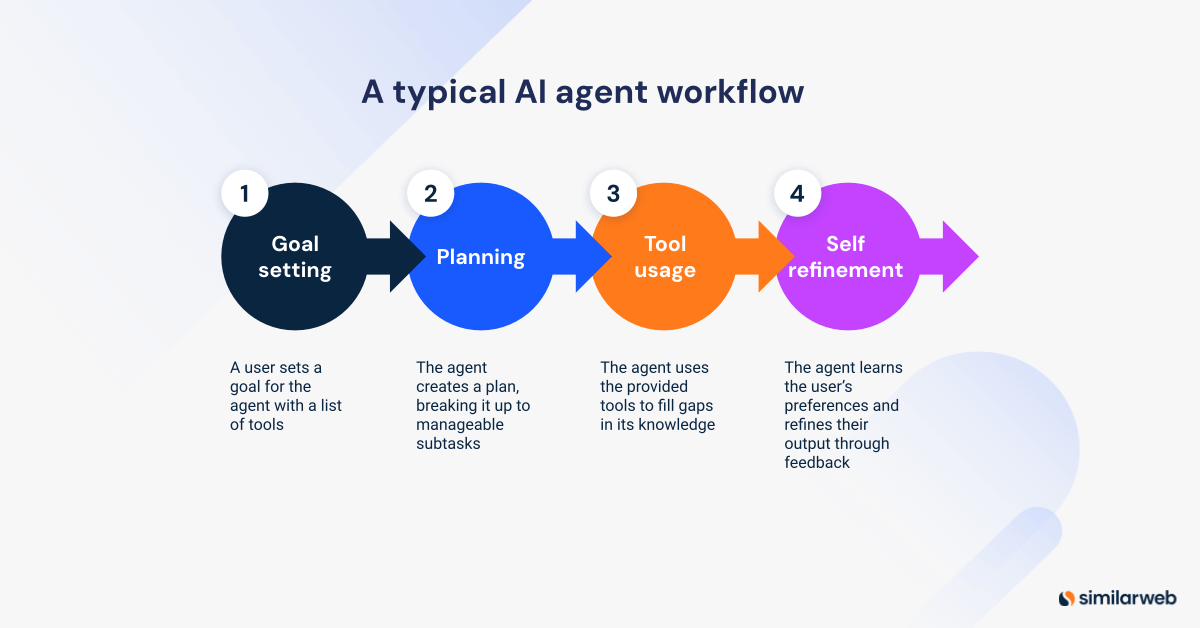
Here is a typical AI agent workflow:
- Goal setting: The process begins when a user or developer sets a goal for the agent, along with a list of tools it can use.
- Planning: The agent creates a plan, breaking the goal into smaller, manageable subtasks when needed. For straightforward tasks, it may skip detailed planning and instead improve through self-reflection on its outputs.
- Tool usage: As it acts, the agent uses available tools to fill gaps in its knowledge. For example, suppose the agent is asked to plan a surfing trip. In that case, it can consult a weather database for up-to-date weather forecasts, or a dataset with specialized knowledge about surfing.
- Self-refinement: Agents also learn and refine their performance through feedback from users, other agents, or built-in mechanisms that track outcomes.
Common use cases and applications of AI agents
Digital marketing
AI agents are increasingly used in digital marketing to simplify processes and improve targeting strategies. They can generate content for blogs, social media, and advertisements, with multi-stage processes that include research, outlining, editing, and optimization.
AI agents can also analyze keyword trends, optimizing search engine optimization (SEO) efforts, and adjusting pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns for maximum performance.
Read more: How To Use AI For Keyword Research
Product research and development
AI agents assist in product research and development by efficiently processing large volumes of market data and user feedback. They sift through reviews, surveys, and customer support tickets to identify pain points, preferences, and potential product improvements.
These agents can also track market trends, helping teams anticipate consumer needs and develop products that align with emerging demands.
Competitive and market intelligence
AI agents support competitive analysis and market intelligence by monitoring digital signals, such as social media mentions, online reviews, and competitor pricing strategies. They can track shifts in market demand, new entrants in the industry, and other significant changes that impact business strategy.
Additionally, AI agents can continuously monitor market signals and send alerts when potential threats or opportunities arise, allowing businesses to respond proactively.
Read more: How To Analyze Your Competitors’ AI Traffic
Data analysis and reporting
AI agents excel in data analysis and reporting by summarizing complex datasets and extracting actionable insights. They can automatically generate complex reports based on predefined criteria, reviewing and summarizing relevant sources while consulting relevant tools.
These agents can analyze both internal and external data, identifying trends, anomalies, and correlations that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Customer service and marketing automation
AI agents in customer service and marketing automation are transforming the way businesses engage with customers. Conversational agents can autonomously handle a wide range of customer inquiries, routing complex issues to human agents, escalating requests based on urgency, and cross-selling or re-engaging customers through personalized recommendations.
In marketing, AI agents can hyper-personalize content and interactions, automating communication and providing tailored offers that improve customer satisfaction and drive sales.
HR and recruiting
AI agents simplify HR and recruiting processes by automating tasks such as resume screening and candidate matching. By analyzing resumes and job descriptions, they can identify the most qualified candidates based on complex criteria.
These agents also assist in organizing interviews, sending out communications, and tracking candidates throughout the hiring process. This reduces the manual effort required in recruitment, ensuring quicker, data-driven hiring decisions.
Software development and DevOps
In software development and DevOps, AI agents enable automation across multiple stages of the development lifecycle. They can generate code based on given requirements, conduct automated testing, and manage release orchestration to ensure smooth software deployments.
AI agents also aid in infrastructure diagnostics and optimization, identifying system inefficiencies or vulnerabilities that need addressing. By automating these repetitive tasks, they improve productivity, reduce errors, and improve the software development cycle.
Types of AI agents
Here are a few types of AI agents, distinguished by the methods they use to learn and interact with their environment.
1. Simple reflex agents
Simple reflex agents respond to environmental inputs using predefined condition-action rules. They do not store any history or context, meaning their responses are solely based on the current input from their sensors. This simplicity makes them fast and reliable in controlled, predictable environments where the possible states and required actions are limited.
2. Model-based reflex agents
Model-based reflex agents introduce an internal representation of the world to improve decision-making in partially observable environments. Instead of reacting only to immediate sensor inputs, these agents maintain a model that tracks how the environment evolves and how actions influence it. This allows the agent to infer the current state with incomplete information.
3. Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents are designed to achieve outcomes by evaluating potential future states and planning action sequences. They assess whether each possible action will bring them closer to a defined goal, using this analysis to select the most effective path forward. This planning ability lets them navigate more complex and dynamic environments.
4. Utility-based agents
Utility-based agents extend the concept of goal-based agents by considering multiple possible outcomes and assigning utility values to them. These values measure how “happy” the operator will be with each outcome. This allows the agent to weigh tradeoffs and choose actions that maximize overall benefit, not just reach a goal. These agents operate using a utility function that quantifies the desirability of different states.
5. Learning agents
Learning agents differ from other types by their ability to improve over time based on experience. They include components that evaluate their performance, learn from outcomes, and propose exploratory actions to refine future behavior. This allows them to adapt to new situations and improve without requiring explicit reprogramming.
6. Hierarchical agents
Hierarchical agents are structured with multiple levels, where higher-tier agents assign goals and coordinate the actions of lower-tier agents. This layered approach enables the handling of complex tasks by breaking them down into manageable subtasks, each handled by a specialized agent or system-level component.
7. Multi-agent system (MAS)
A multi-agent system involves multiple independent agents that interact within a shared environment. These agents may work cooperatively to achieve shared goals, competitively to optimize individual performance, or in a hybrid model combining both dynamics. MAS are governed by defined communication protocols and coordination rules.
Risks and limitations of AI agents
Limited emotional intelligence and social understanding
AI agents often lack the emotional depth and contextual awareness needed for tasks that require empathy, intuition, or complex human interaction. In domains like therapy, conflict resolution, or social work, they may misinterpret emotional cues, overlook nonverbal communication, or respond insensitively. These limitations can lead to misunderstandings or ineffective outcomes in emotionally nuanced situations where human rapport is critical.
Inadequate for high-stakes ethical decision-making
While AI agents can process large volumes of data to make decisions, they do not possess moral reasoning or a human sense of ethics. This makes them ill-suited for tasks that involve ethically charged decisions, such as law enforcement actions, medical diagnoses and treatments, or judicial rulings. Relying on agents in such contexts risks outcomes that may be technically rational but socially or morally unacceptable.
Poor adaptability in unstructured physical environments
AI agents can struggle in unpredictable physical environments that require real-time decision-making, manual dexterity, or rapid adaptation. Tasks like surgery, certain construction operations, or disaster response involve a level of situational awareness and fine motor control that current AI systems cannot match. Physical risks and uncontrolled variables make such domains less suitable for agent deployment without substantial human oversight.
High computational and resource demands
Advanced AI agents require substantial computational power, storage, and memory, especially for multimodal processing or continuous learning. These resource demands can drive up infrastructure costs and limit accessibility for small organizations or resource-constrained projects. In some cases, the performance gains offered by agents may not justify the overhead, making traditional automation or human execution more viable alternatives.
Best practices for AI agents
Here are a few best practices that can help your organization make the most of AI agents.
1. Define clear goals and scope of autonomy
Before deploying an AI agent, define a clear objective or set of objectives that it is responsible for achieving. Goals should be specific, measurable, and aligned with broader system requirements. For example, an agent tasked with managing IT incidents should have a well-defined success metric (e.g., time to resolution, number of resolved tickets) and operate within the domain of support automation only.
Constraints must also be articulated, including operational limits like which APIs the agent can access, data boundaries, and allowable action types. This limits the scope of behavior and reduces the risk of misaligned actions or system drift. In addition to goal specification, autonomy boundaries must be codified explicitly. These define when the agent may act independently versus when it must escalate to human oversight or seek additional input.
This could involve permission thresholds (e.g., spending limits), domain boundaries (e.g., read-only access to sensitive data), or conditions for human override. Clearly enforced constraints prevent agents from taking unintended or high-risk actions and make behavior more predictable. Scope control also simplifies monitoring and compliance, especially in regulated environments.
2. Use modular, tool-integrated architectures
Design agents using a modular architecture where core components, input processing, planning, reasoning, memory, and action are encapsulated into separate units with well-defined interfaces. Each module should function independently and be replaceable without impacting the rest of the system.
For instance, a planning module might generate task sequences based on goals, while a separate tool execution module handles API calls. This design enables rapid testing, debugging, and iterative improvements of individual capabilities without the complexity of modifying a monolithic codebase.
Tool integration should be explicit and managed through structured interfaces. Tools should be wrapped in functions or services that expose parameters, expected outputs, and error-handling protocols. All tool interactions must support fail-safes such as retries, timeouts, and fallback responses. Logging at the interface level should capture tool inputs and results to support traceability.
3. Implement robust monitoring and feedback loops
To ensure reliability and continuous improvement, deploy robust monitoring systems that track every stage of an agent’s decision cycle. This includes input data, intermediate reasoning steps, tool outputs, final decisions, and post-action outcomes. Each event should be logged with metadata such as execution time, resource usage, and error messages.
Logging systems should support both live observability (for real-time debugging and alerting) and historical analysis (for diagnostics and optimization). This level of visibility helps detect issues early and provides the data needed to refine agent logic or behavior.
Feedback loops are critical for improving agent performance. These can be automated, where the agent evaluates its own performance using heuristics or scoring functions, or manual, involving human review and annotation of agent outputs. Feedback should feed into agent memory or learning modules that support behavior refinement over time. For example, if a tool call fails frequently under certain conditions, the agent should learn to choose alternatives or adjust its call strategy.
4. Establish Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) oversight
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) oversight should be used at critical points where incorrect actions could have significant consequences. This includes actions involving legal compliance, safety, financial transactions, or irreversible system changes. The agent should flag these situations and pause for human validation before proceeding.
For example, an agent generating legal documents may be allowed to draft but not to submit without review. HITL workflows can be managed through approval queues, policy engines, or interrupt-based user prompts that insert human decision points into the execution pipeline. For oversight to be effective, humans must have visibility into the agent’s decision context.
This means exposing the internal state, inputs, and reasoning chain that led to a proposed action. User interfaces should allow for inspection, modification, or rejection of planned agent behavior, with clear options for feedback submission. All manual interventions should be logged and used to retrain or adjust agent parameters.
5. Manage multi-agent systems carefully
When deploying multiple agents in a shared environment, define clear roles, responsibilities, and boundaries to avoid redundant work, conflicting actions, or decision deadlocks. Each agent should be assigned a domain of control and know what tasks it owns versus those handled by others. Use coordination mechanisms like task registries or agent directories to centralize role assignments and prevent duplication.
For example, one agent may handle real-time alerts while another focuses on report generation, with shared data streams managed through access-controlled interfaces. Communication between agents must follow strict protocols to ensure message integrity, synchronization, and fault tolerance. This includes implementing timeouts, retries, and conflict resolution policies, especially when agents interact asynchronously.
When agents have shared goals or interdependencies, use shared state stores or consensus algorithms to synchronize plans and decisions. In failure scenarios, agents should detect upstream errors, isolate impacted tasks, and trigger fallback routines or escalations. A well-orchestrated multi-agent system maximizes reliability, reduces latency, and enables coordinated responses to complex problems.
Meet Similarweb’s AI agents
AI Trend Analyzer Agent
Similarweb’s AI Trend Analyzer agent helps organizations stay ahead of shifting consumer behavior by identifying real-time demand spikes. It analyzes unexpected search trends, clusters rising keywords, and uncovers the drivers behind these changes, whether they’re seasonal patterns or linked to broader market events.
By connecting search behavior to real-world developments, the agent enables teams to act quickly on emerging opportunities before competitors do. It provides clear insights into what’s trending and why, helping organizations make smarter, data-driven decisions for marketing, product development, and strategy.
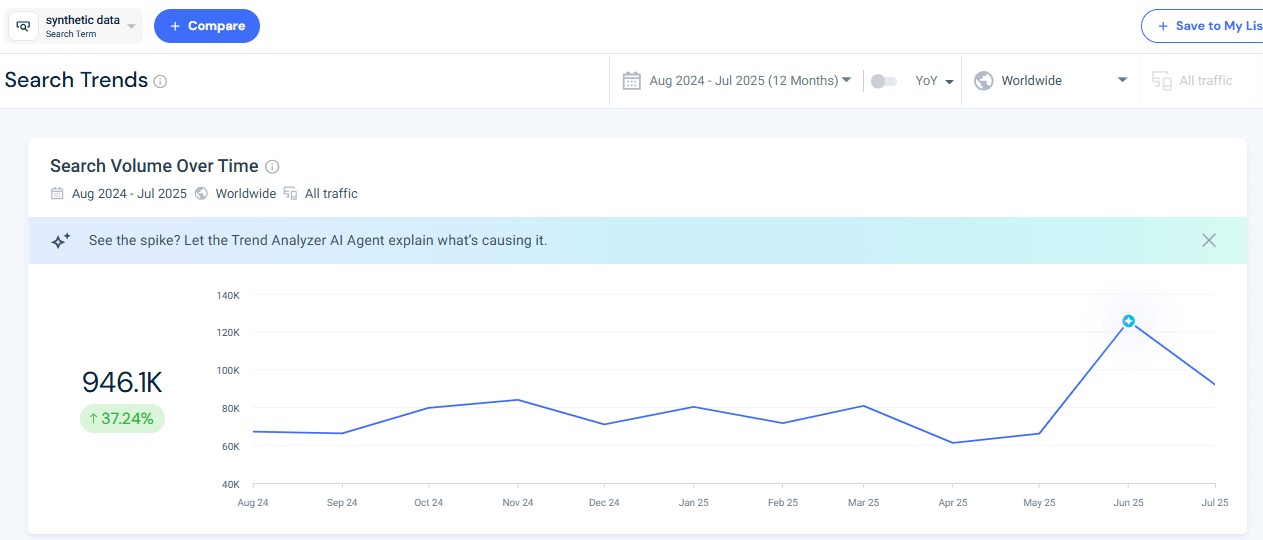
For example, when analyzing the keyword “synthetic data” in Similarweb’s Demand Analysis tool, the AI Trend Analyzer agent detected a sharp spike in June 2025.
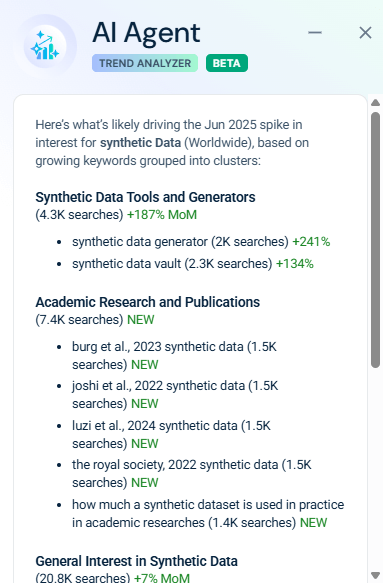
It revealed that searches surged around terms like “synthetic data generator” and “synthetic data vault”, alongside new academic publications on the topic.
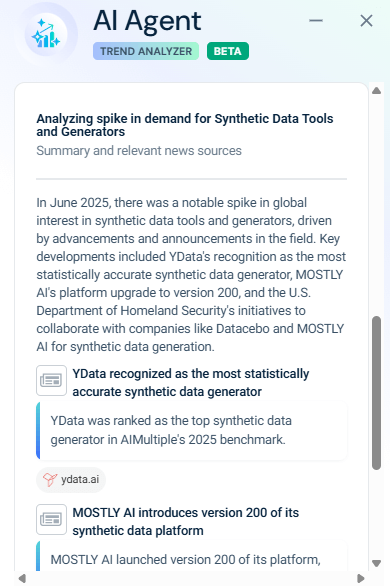
When asked to explain why, the agent attributed the spike to several real-world developments: YData being recognized as the most statistically accurate synthetic data generator, MOSTLY AI launching version 200 of its platform, and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security partnering with Datacebo and MOSTLY AI on synthetic data initiatives.
This kind of context transforms raw search data into actionable insights, allowing businesses to understand not just what is trending, but why.
AI SEO Strategist
The Similarweb AI SEO Strategist agent transforms keyword lists into full-scale, actionable SEO plans. It analyzes competitive landscapes, performs keyword gap analysis, and suggests topic clusters prioritized by intent and value. This allows teams to focus on high-impact areas that drive traffic and boost search rankings.
The agent also recommends optimal content formats, structures, and on-page elements by analyzing top-performing pages. Combined with offsite strategy suggestions, it equips marketers with a comprehensive SEO roadmap to outperform competitors and dominate the SERPs, without the hours of manual research typically required.
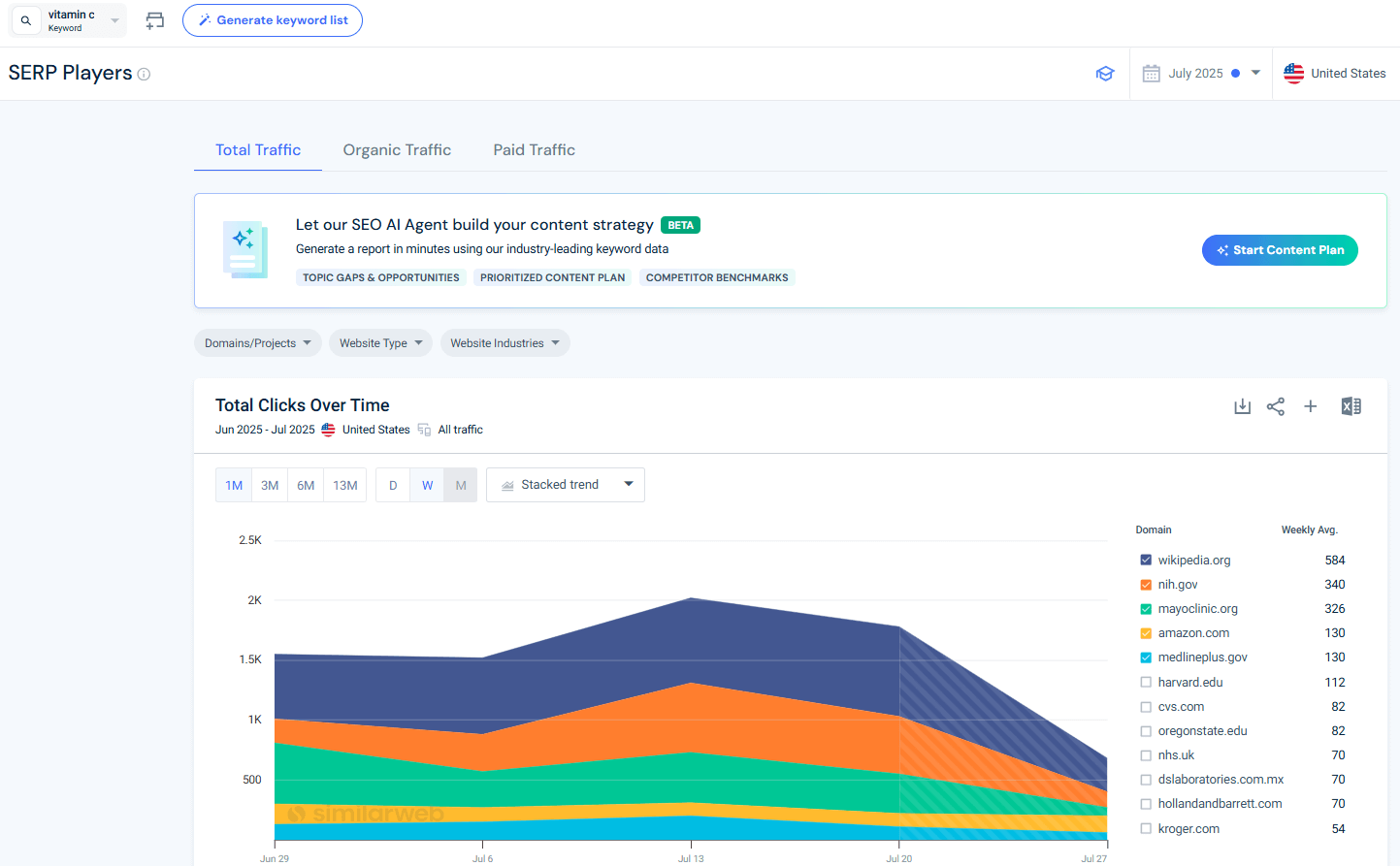
For example, I selected the keyword “vitamin C” and chose mayoclinic.org as the domain I wanted to optimize for.
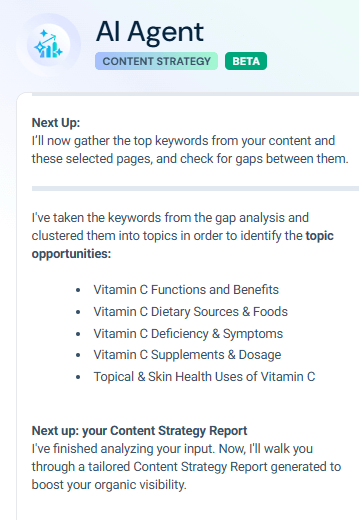
The agent first mapped out the competitive landscape, showing that sites like Wikipedia, NIH.gov, and MedlinePlus were dominating search clicks. It then ran a keyword gap analysis, clustering underutilized opportunities into key topic areas such as “Vitamin C Supplements & Dosage” and “Vitamin C Deficiency & Symptoms”.
Finally, the agent generated a complete SEO strategy document. The report included an executive summary highlighting significant SEO gaps, topic opportunities where Mayo Clinic could gain share, and coverage weaknesses compared to competitors. It also recommended prioritized actions, from creating robust topical authority content and FAQs to targeting Featured Snippets, building offsite engagement through expert partnerships, and strengthening internal navigation.
This example shows how the AI SEO Strategist agent transforms keyword data into an actionable content plan, helping marketing teams not just see where they’re falling behind, but also understand exactly how to close the gap.
AI Meeting Prep
The Similarweb AI Meeting Prep agent enables sales teams to enter every meeting fully prepared. By analyzing real-time company data, market trends, and digital signals, it generates tailored meeting briefs that highlight a prospect’s business needs, performance, and key challenges.
These briefs include actionable talking points that connect the company’s pain points to your product’s capabilities, along with competitor insights and growth opportunities. With an intuitive, chat-like interface, users can refine their briefs on the fly, adding new data points or adjusting focus areas to craft a winning plan in minutes instead of hours.
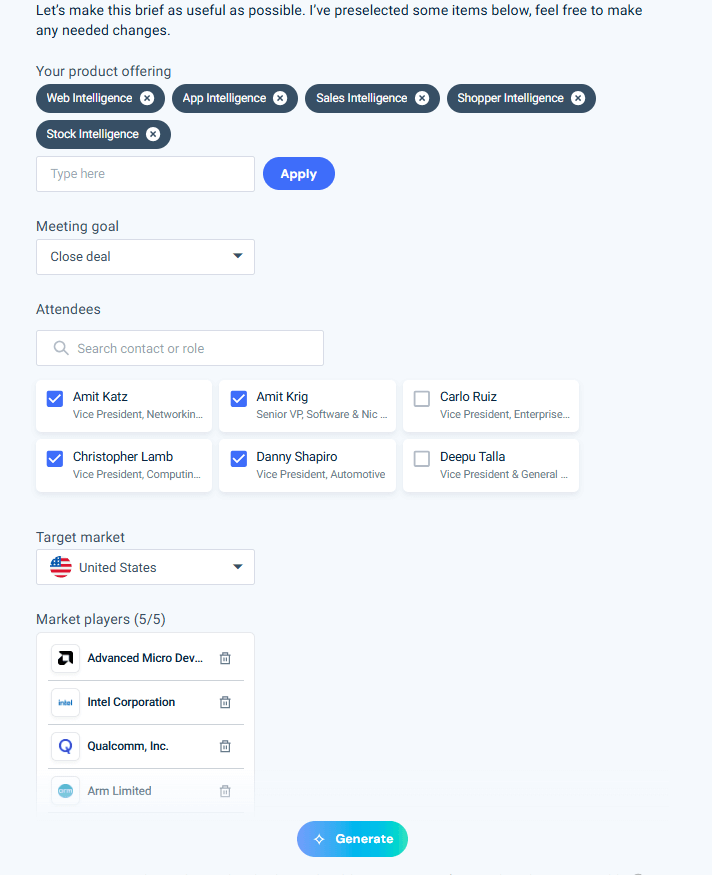
For example, I prepared for a meeting with NVIDIA using the AI Meeting Prep agent. After selecting my meeting goal (close deal), attendees, target market, and top competitors (AMD, Intel, Qualcomm, and Arm), the agent generated a comprehensive brief in minutes.
The brief included, among other things:
- Meeting Objective – framing the goal of showcasing value across Similarweb solutions, tied directly to NVIDIA’s challenges and opportunities.
- Company Overview – a snapshot of NVIDIA’s rapid growth, strategic partnerships, and recent product launches, highlighting both strengths and vulnerabilities in its AI and data center businesses.
- Market Trends Analysis – competitor comparisons, keyword and traffic insights, and signals from recent news, such as AMD’s push with paid ads on driver-related searches and NVIDIA’s expansions in AI chips.
- Strategic Talking Points – actionable ways to connect NVIDIA’s pain points (e.g., pressure to benchmark against AMD and Intel, demand for channel intelligence) with Similarweb’s capabilities.
In just a few clicks, I had a tailored, strategic briefing pack, something that would normally take hours to research and assemble manually. This shows how the AI Meeting Prep agent helps sales teams walk into high-stakes conversations informed, credible, and ready to win.
AI Sales Outreach
The AI Sales Outreach agent simplifies prospecting by generating tailored outreach messages that resonate with buyers. Using intent signals and account-specific insights, it crafts high-impact message copy designed to engage prospects effectively. This enables sales teams to connect with accounts more efficiently and close deals faster, based on accurate data about millions of organizations.
Beyond messaging, the agent performs rapid research on each prospect, equipping sales development representatives (SDRs) and account executives (AEs) with actionable insights for meetings and calls. It also identifies opportunities and risks across accounts, delivering data-driven talking points to support timely and informed actions.
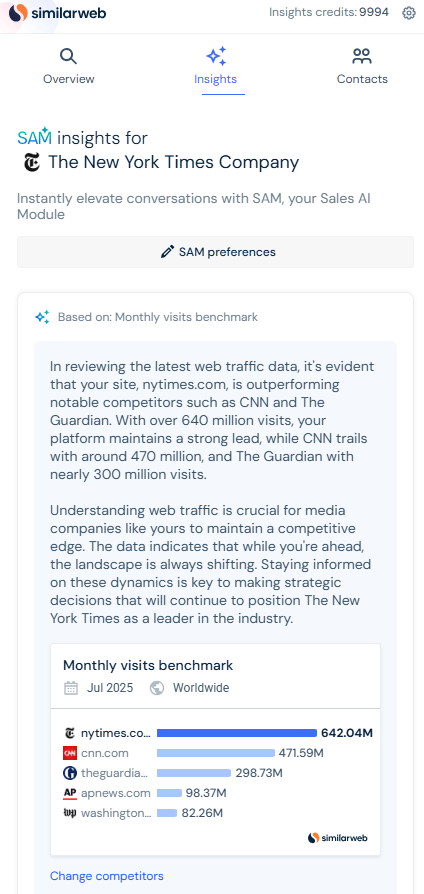
For example, after installing the Similarweb Sales Extension, I navigated to nytimes.com and opened the “Insights” tab. The agent asked me about the prospect’s challenges and automatically generated a set of tailored insights.
In this case, it highlighted that The New York Times is outperforming competitors like CNN and The Guardian in monthly visits, but also emphasized the need to stay agile in a shifting media landscape.
These insights were paired with a suggested outreach message that directly connected Similarweb’s value proposition to the prospect’s goals, giving me both the data and the copy I needed to start a compelling conversation.
Future of AI agents
From assistants to autonomy
AI agents are evolving from passive assistants into goal-driven, multi-step executors. Instead of waiting for instructions, next-gen agents will plan and carry out tasks across tools (e.g., finding a lead, writing an email, and logging it in CRM), all without human prompts.
This shift toward autonomous workflows will reshape productivity and decision-making. AI agents will no longer be confined to narrow, predefined tasks. As they become more self-sufficient, they will revolutionize how businesses operate, reducing bottlenecks and simplifying processes.
Why it matters: Expect AI to move beyond suggestions and into real business operations, reducing workloads and freeing staff for more strategic activities.
Collaboration between agents
We’re entering the era of multi-agent ecosystems, where specialized AI agents work together, one might gather data, another analyze it, and a third generate a recommendation. These AI “teams” can tackle complex business problems faster than a single agent can.
By pooling their strengths and collaborating seamlessly, agents will be able to tackle broader, more intricate tasks, creating smarter solutions that drive business growth. This synergy will extend beyond traditional workflows, combining agents with complementary skills to deliver powerful, holistic outcomes.
Why it matters: Multi-agent systems can achieve more complex and nuanced outcomes than single agents, and take the capabilities of agentic AI to a new level.
Seamless integration across business tools
AI agents will increasingly live inside your daily software stack, your CRM, analytics tools, ad platforms, or CMS. With deeper APIs and better context awareness, they’ll take action automatically, not just analyze. These agents will make decisions and execute tasks directly within the tools you already use, reducing friction between software platforms.
Whether handling routine maintenance or driving real-time optimization, AI will work in the background, seamlessly supporting the overall user experience across all business functions.
Why it matters: AI agents won’t be a separate app, they’ll be part of how every tool works. They will eventually become the glue that connects your entire stack together.
What to expect from Similarweb
Similarweb is the world’s leading AI-powered digital data company, providing insights to help businesses understand market dynamics and make informed decisions. Our robust datasets enable you to track and analyze your competitors, customers, and industry trends in real time.
Moving forward, we are integrating more AI agents into our offerings. These future agents will continue to support every area of your business, from market research to competitive intelligence, ensuring you stay ahead in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
FAQs
What is an AI agent?
An AI agent is an autonomous software system that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific objectives without constant human intervention.
How are AI agents different from regular software?
Unlike traditional software, AI agents can adapt to changes in their environment, learn from experience, and operate independently. This makes them more flexible and capable of handling dynamic, complex tasks.
Where are AI agents commonly used?
AI agents are used in industries like marketing, customer service, logistics, healthcare, and software development. They automate tasks, analyze data, and assist with decision-making.
What are the main benefits of AI agents?
AI agents improve efficiency, reduce operational costs, work 24/7 without fatigue, and provide personalized user experiences at scale. They also enable faster and more consistent decision-making.
What risks do AI agents pose?
Potential risks include data privacy concerns, biased decision-making, technical complexity, and coordination issues in multi-agent systems. Human oversight and preventive design practices help mitigate these challenges.
Can AI agents work together?
Yes, multi-agent systems allow different AI agents to collaborate, share information, and achieve complex goals that would be difficult for a single agent to handle.
What is the future of AI agents?
AI agents are moving toward greater autonomy and collaboration. They will increasingly handle multi-step tasks, integrate seamlessly with business tools, and work alongside human teams to deliver smarter solutions.
Maximize your growth potential
Harness the power of data with Similarweb’s APIs to drive smarter business decisions