Top 100 Most Asked Questions About GEO in 2025, Answered
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is no longer a fringe idea: it’s the only way to make sure your brand shows up in AI‑generated answers. As zero‑click searches grow and AI assistants and Google’s AI Mode synthesize information from across the web, brands must adapt.
How do they adapt? They start learning, testing, and asking questions. Our industry forums and social channels have been buzzing with questions and discussions from everyone trying to learn as much as possible, as quickly as possible.
So, isn’t it a good idea to put it all in one place where everyone can get an answer for every GEO question? I think it is.
This article collects 100 of the most common questions about GEO, including many questions raised by real Similarweb customers.
Each question is organized into a clear category and followed by an expanded answer explaining the logic behind the guidance, why it matters, and how you can use Similarweb tools to put the advice into practice.
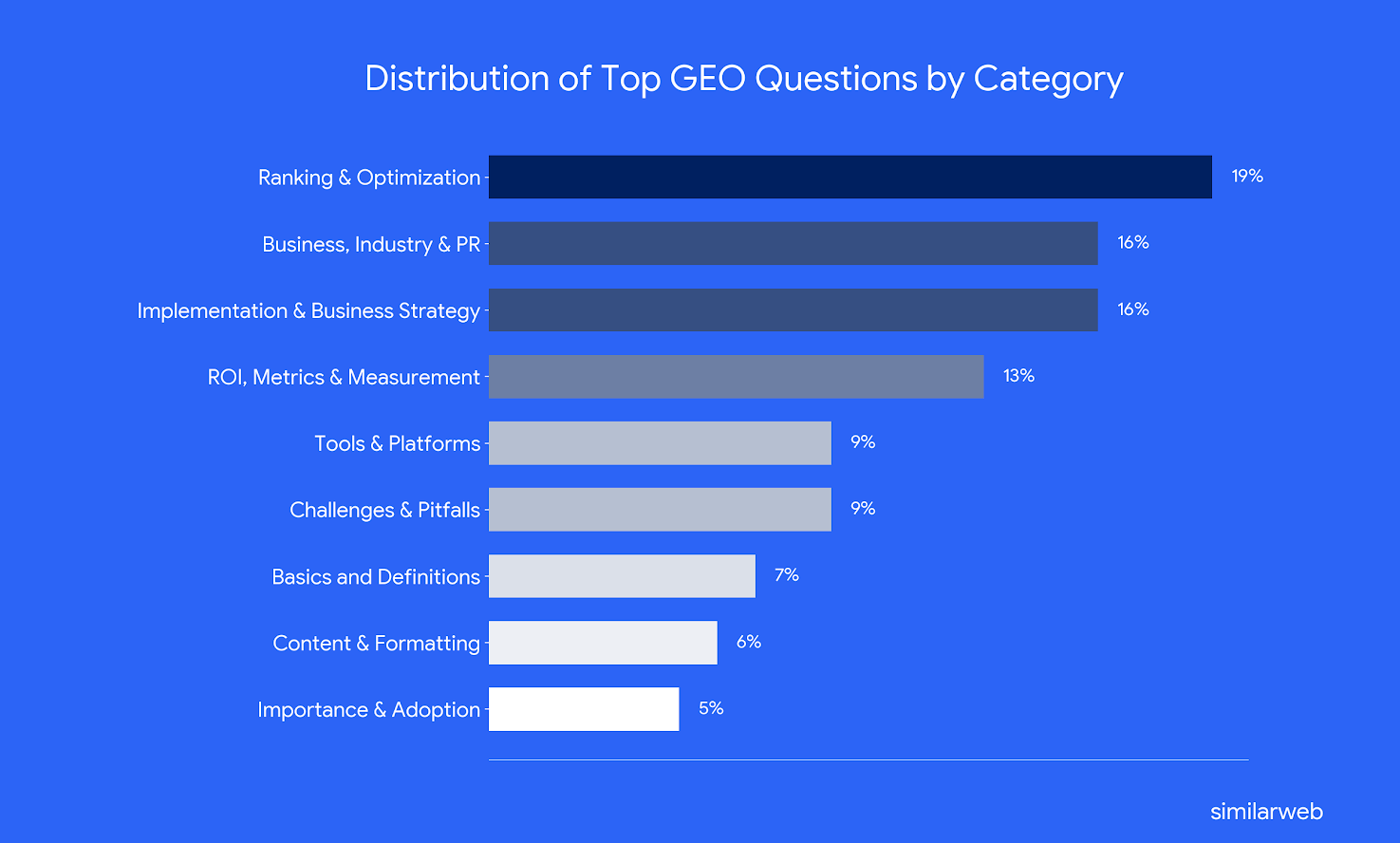
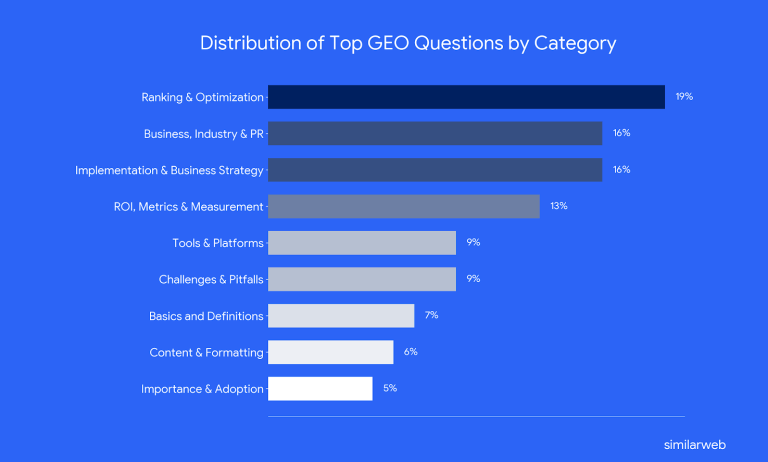
The topic distribution below can already tell you a few things regarding the main things SEO and business are currently curious or worried about when it comes to GEO:
I’ve listed my own insights at the bottom of this article. Let me know if you agree.
You can use this as a go-to reference for any questions about Generative Engine Optimization you might have.
To jump directly to a specific category, click on it below:
- Basics & Definitions
- Importance & Adoption
- Content & Formatting
- Ranking & Optimization
- Implementation & Business Strategy
- ROI, Metrics & Measurement
- Business, Industry & PR
- Challenges & Pitfalls
- Tools & Platforms
Questions about GEO basics & definitions
What is a generative engine?
A generative engine is a system that responds to user queries by synthesizing text (or images, code, and other outputs) using pre‑trained models and real‑time retrieval. They break the user’s question into sub‑queries, fetch information from multiple sources, and compose an answer.
Generative engines use retrieval‑augmented generation (RAG): they access live web documents and their internal knowledge. Because they blend structured data, web pages, reviews, and social posts, brands must ensure their information is accessible, trustworthy, and machine‑readable to be included in the output.
Is generative AI different from traditional AI?
Yes. Traditional AI systems typically classify or predict outcomes based on structured data (for example, predicting customer churn or classifying images). Generative AI models like GPT‑5 and Gemini, however, create new content by learning patterns from vast corpora.
They generate paragraphs, code, charts, and images. Because they operate in a free‑form way, they need comprehensive, well‑structured content to ground their answers. GEO focuses on making your content discoverable and trustworthy within these generative contexts.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
GEO is the discipline of making your content easy for generative AI engines to discover, understand, and cite. It concentrates on AI answer visibility: if AI models do not use your content in their responses, your brand effectively disappears from the conversation.
GEO involves structuring information around the questions your audience asks, supplying concise answers, and using schema markup so machines can extract the key facts.
It also extends beyond your own site: it includes building authority through citations on high‑trust domains and ensuring that product descriptions, reviews, and press coverage are findable.
By aligning content with the way large language models break down and reconstruct questions (a process known as query fan‑out, where the AI splits a complex query into multiple sub‑queries and synthesizes the results), you help ensure your brand’s expertise is part of the final answer.
How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?
SEO remains the foundation of digital marketing: it optimizes pages for keywords, earns backlinks, and fixes technical issues to help you rank in search results. GEO sits on top of these basics but shifts the focus from rankings to citations.
Search engines measure relevance while generative engines measure trust. AI models scan content to answer questions directly, so they need concise facts, structured lists, tables, and explicit answers to common questions.
GEO also emphasizes cross‑site authority more than SEO: your own pages matter, but generative engines frequently cite third‑party sources. That means earning coverage on trusted sites, encouraging user reviews, and building a presence on platforms AI engines trust.
How is GEO different from Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)?
AEO and GEO are related but distinct. AEO is meant to optimize content for featured snippets, voice assistants, and zero‑click search results. It focuses on creating succinct answers that fit into search engine answer boxes.
GEO takes those practices and broadens them to all generative platforms: ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Google’s AI Mode, and others. In GEO vs AEO, you don’t just optimize for a single snippet but build a comprehensive question inventory so your brand can answer many related questions.
You also track how often your content is cited, which topics you dominate, and where you’re absent. The output is measured through metrics like brand visibility score, brand mention share, and citation share, which are absent in AEO.
What’s the difference between SEO, SGE, and GEO?
- SEO optimizes content to rank on traditional search engine results pages.
- SGE (Search Generative Experience) refers specifically to Google’s AI‑generated answer summaries and the underlying generative module.
- GEO applies to all generative systems and focuses on making your content the easiest to retrieve and cite across multiple AI platforms.
In practice, GEO takes the best of SEO (technical hygiene and authority) and AEO (answer‑ready content) and layers on cross‑platform monitoring and citation analysis. Successful GEO ensures your brand is referenced whether the user interacts with Google, ChatGPT, Perplexity, or a voice assistant.
What is LLM SEO or AI search optimization?
LLM SEO (also called AI search optimization) refers to techniques that help large language models (LLMs) retrieve and understand your content more effectively.
It complements GEO by focusing on semantic clarity and entity relationships. For example, clarifying the names of products, people, and organizations through structured data (schema) and consistent wording helps AI models link concepts correctly.
LLM SEO also encourages you to provide context (e.g., definitions and related topics) because models use that context to disambiguate terms. While GEO aims for citations, LLM SEO ensures your pages are included in the retrieval step.
Questions about GEO importance & adoption
Why should my organization care about GEO?
Generative search has changed user behavior. In traditional search, users clicked through to multiple links, but today, they often accept the AI’s first answer and leave. Pew Research shows that only about 18% of Google queries display AI summaries, but those summaries attract close attention and cite multiple sources.
Similarweb’s data reveals that ChatGPT receives billions of visits each month, and Google’s AI Mode serves more than 100 million monthly active users. Because generative answers compile information from a handful of sources, you must be in the answer to get noticed.
GEO ensures your brand is cited so that even if no one clicks, you maintain visibility and trust. Without GEO, zero‑click behavior effectively erases you from AI‑driven discovery.
Is GEO replacing SEO?
No. GEO builds on SEO. You still need optimized pages, mobile‑friendly designs and quality backlinks. However, GEO focuses on answer‑first structure, question coverage, schema markup, and cross‑platform citation analysis, with the goal of increasing brand visibility rather than ranking.
SEO and GEO are complementary: strong SEO improves crawlability and authority, which helps AI engines trust your content, while GEO ensures that the engines interpret and cite your pages properly.
Is GEO just a passing trend?
Generative search adoption is explosive: Similarweb reports that ChatGPT reached 7 billion monthly visits and over 570 million monthly active users on its mobile app. These numbers show that generative interfaces are mainstream.
Because GEO builds on timeless principles like structuring content and building authority, it is expected to become a long‑term element of digital marketing rather than a fleeting fad.
Do clients actually care about GEO yet?
Interest is growing but not universal. Early adopters, including many Similarweb customers, are already building GEO dashboards, tracking brand visibility and citation share across AI engines. Other organizations are waiting to see a clear ROI before allocating budgets.
As generative platforms become a primary way people search for answers, ignoring GEO will mean surrendering share of voice to competitors. Early movers are discovering competitive advantages by appearing in AI answers across multiple engines.
Is anyone actually doing GEO or is it just SEO rebranded?
Despite having a lot of overlap, many leading agencies, SaaS platforms and in‑house teams are actively practicing GEO. It’s not simply “SEO with a different name,” since GEO focuses on several tasks that hardly mattered in modern SEO, such as analyzing unlinked mentions and identifying sentiment distribution across multiple AI engines.
Similarweb’s Gen‑AI suite offers dedicated tools that track GEO metrics like brand visibility share, prompt gaps and citation overlap, which are not found in classic SEO dashboards.
Questions about GEO content & formatting
What types of content or formats work best for GEO?
Generative engines process vast amounts of content quickly, so structure is your friend. FAQs, how‑to guides, listicles, comparison tables, glossaries and case studies give AI models clearly segmented pieces of information.
Begin each section with a summary or direct answer, followed by supporting details. Use bullet points, numbered lists and tables to summarize data. Provide definitions of industry terms and cross‑link related questions to help models understand context.
For product pages, include technical specifications, benefits and user reviews. For how‑to guides, break steps into simple tasks.
By offering multiple content types (text, images, charts, even downloadable templates), you increase the likelihood that generative engines will find and cite at least one asset.
What are GEO techniques and best practices?
Key techniques include:
- Question inventory and answer‑first structure: Build a list of the exact questions your audience asks and turn each into a section or page. Start with a concise, 40–60 word answer, then expand with details, examples and related questions. This approach aligns with the query fan‑out mechanism that generative engines use to break down user queries.
- Schema markup: Use structured data types (FAQPage, HowTo, Product, Review, QAPage) to mark up your content so AI can parse it quickly. Schema clarifies entities (product names, organizations, people) and relationships (features, benefits), which improves retrieval and citation. Without schema, AI models might misinterpret context or skip your page entirely.
- Comprehensive coverage and content hubs: Cover topics broadly and deeply. Answer common questions, edge cases and comparisons. Create content hubs around core themes to signal authority and provide the variety generative engines seek. Avoid duplicate Q&As across multiple pages to prevent dilution.
- E‑E‑A‑T signals: Demonstrate Expertise, Experience, Authority and Trust by providing author bios, linking to professional credentials and citing credible sources. In regulated industries, ensure all claims are accurate and include regulatory statements. Provide user testimonials, case studies and reviews to enhance trust.
- Regular updates: AI engines favor fresh information. Update high‑value pages at least quarterly and more frequently for rapidly changing topics. Add new sub‑questions as user needs evolve and update statistics and references.
- Multimodal assets: Include images, charts and videos where appropriate. Generative engines sometimes include visuals in their answers or rely on visual cues to understand complex processes. For example, a step‑by‑step diagram of an installation process can make your content more valuable to AI.
- Internal and external linking: Link related questions within your site to create a web of context and provide AI models with pathways to additional information. Earn links from authoritative sites to boost domain influence and trust.
Is E‑E‑A‑T part of GEO?
Absolutely. Generative engines evaluate whether your content comes from a credible source.
- Expertise means you cover your subject deeply and accurately
- Experience shows you have first‑hand knowledge (e.g., case studies, personal stories)
- Authority is backed by citations from other trusted sites and signals like domain influence
- Trust means transparency (e.g., clear policies, contact information) and positive sentiment.
Without these signals, your content may be overlooked in favor of more authoritative pages. Similarweb’s Citation Analysis tool can show you whether high‑authority domains link to you and whether you need to build relationships with influential publishers.
Are duplicate Q&A sections harmful?
Yes. Repetition across pages dilutes relevance and can confuse AI models. Generative engines look for unique passages. If two pages contain the same Q&A, the engine might choose one at random, or worse, ignore both (i.e., cannibalization).
Consolidate your FAQs into authoritative hub pages and link to them from related articles. When referencing the same question in multiple contexts, summarize it and link to the detailed answer rather than duplicating the text.
How should regulated claims be handled?
In regulated industries (healthcare, finance, legal), you must provide accurate, compliant statements and citations. Clearly state the regulatory guidelines you follow and avoid unsubstantiated health or financial claims.
Provide citations to government websites, peer‑reviewed journals or official product documentation. Structured data can clarify that your content is informational, not advisory.
In all industries, but especially regulated ones, working with legal and compliance teams ensures your GEO efforts build trust rather than risk penalties.
Are GEO and AEO the same thing?
They overlap but differ. AEO focuses on optimizing for answer boxes within search engines (like featured snippets or voice answers). GEO requires you to track prompts across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, AI Mode and other engines, monitor citations and fill content gaps across platforms.
You can look at AEO as a subset of GEO (which is a subset of SEO), so think of GEO as the broader strategy that includes AEO tactics but adds cross‑platform measurement, sentiment analysis and domain influence.
Questions about GEO ranking & optimization
How do AI engines choose which content to cite?
Generative engines use a combination of retrieval and ranking. When a user asks a question, the engine breaks it into sub‑queries and searches for passages that answer each part. It considers signals such as domain authority, topical relevance, passage structure, and freshness.
Models trained on documents assign scores to candidate passages. Those with clear structure and explicit answers score higher. Content with schema markup and clear section headings is easier to parse. External authority signals (backlinks and citations from high authority websites) increase your chances of being selected.
The engine also balances sources: for example, ChatGPT tends to cite retail and marketplace sites while AI Mode prefers brand and OEM domains. Therefore, your strategy must include both on‑site optimization and off‑site reputation building.
What factors influence brand visibility in generative search results?
Brand visibility is determined by several metrics: topical authority, domain influence, structured content, prompt coverage, citation share, and sentiment.
Topical authority measures how comprehensively you cover each subject, and domain influence captures how often your site is cited relative to all sources. Structured content and schema make your information easy to extract.
Prompt coverage assesses whether your content answers the exact questions users ask, and citation share indicates how often your site is used as evidence in AI answers. Sentiment shows whether the AI portrays your brand positively or negatively.
Improving visibility means publishing comprehensive, well‑structured content, earning citations, closing prompt gaps and managing brand perception.
How can I appear in AI search results?
Start by listening to your audience: use keyword research tools, community forums and social media to collect the questions people ask about your product or industry. Then create content that explicitly answers those questions.
Use headings that mirror the question, write a concise answer, and expand with explanations, examples and citations. Add FAQPage or HowTo schema so AI engines can parse your content. Next, earn backlinks and media coverage to build domain authority.
Finally, monitor your progress: Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility and Prompt Analysis tools show which prompts cite your brand and where you’re absent. Identify gaps and create new content or strengthen existing pages accordingly.
How do I rank in ChatGPT or Perplexity?
ChatGPT doesn’t display ranked lists, and the default model draws from its pre‑training rather than live data. However, ChatGPT can cite sources when browsing is enabled, and Perplexity uses live retrieval.
To appear in ChatGPT’s answers, ensure your site is included in the model’s training or browsing data. This means being linked from authoritative sites, being part of widely referenced sources like Wikipedia, and using robust metadata.
Perplexity emphasises citations and uses retrieval augmented generation, so you need fresh, structured content, high domain authority and a presence on various sources (brand site, reviews, press, blogs).
The algorithms also aim to balance different perspectives: Perplexity may show multiple citations in its answer, so diversifying where your brand is mentioned increases your chances.
How do AI search engines rank content?
Generative engines do not produce a list of links, but create an integrated answer. They rank passages internally during retrieval.
Factors include:
- Domain‑level authority (how trusted your site is).
- Page‑level signals (schema markup, headings, structured layout).
- Passage‑level signals (clarity of the answer, presence of keywords, and context), and freshness.
Additionally, AI engines may penalize duplicate or low‑quality content and favor pages that include descriptive context (e.g., definitions, examples and code snippets). Because ranking is hidden, you measure success by metrics like brand visibility and citation share rather than ranking positions.
What are the key differences between traditional SEO and AI search optimization?
SEO emphasizes keyword placement, link building and technical health. AI search optimization (LLM SEO) adds semantic understanding, entity relationships and prompt coverage.
AI engines try to understand meaning rather than matching exact keywords. They also evaluate whether the content is written in an answer‑first style, whether it has the right structured data and whether it’s up to date.
Success is measured by visibility metrics (brand visibility score, brand mention share, citation share) rather than traffic and positions in the SERP. AI search optimization also demands cross‑platform strategy: ChatGPT, Gemini and Perplexity all behave differently.
How should brands prepare for the future of GEO?
- Audit your current content: Identify existing pages that answer relevant questions and evaluate their structure and authority.
- Develop a comprehensive question inventory covering different intents (informational, comparative, transactional).
- Use Similarweb’s Prompt Analysis tool to find high‑volume prompts and competitor gaps.
- Plan a content hub for each major topic and update or create pages to cover all sub‑questions. Implement schema markup across all content types.
- Build off‑site authority by pitching expert articles to industry publications and securing citations from high‑trust domains.
- Monitor GEO metrics (brand visibility, prompt coverage, sentiment) regularly and adjust your strategy as AI models evolve.
- Educate your team: GEO requires coordination between SEO, content, PR, social, and analytics.
What are the first steps to optimize for GEO?
Begin by understanding what people ask. Compile queries from keyword research tools, support tickets, social media and internal data. For each question, determine if your existing content answers it, and if not, create new pages. Use FAQPage and HowTo schema for clear question‑answer pairs.
Check whether your pages are crawlable and accessible (no major login gates or paywalls). Structure your answers with a summary followed by details and citations. Then use Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool, Prompt Analytics, and Citation Analytics to measure your baseline visibility and find missing prompts.
Address content gaps, improve authority by earning citations from trusted domains and track improvements over time. Many brands start by focusing on a single topic or product line to prove the concept before scaling.
Do we need to optimize differently for each AI tool?
Yes.
- Google’s AI Mode pulls from a live index, Knowledge Graph and Shopping Graph, and its citations appear under the answer. It favors brand and OEM sites and balances commercial and informational sources.
- ChatGPT is a stand‑alone chatbot that primarily relies on pre‑training: it cites sources only when browsing is enabled and tends to favor retailer domains and marketplace reviews.
- Perplexity is retrieval‑heavy: it shows citations from various sources including news articles, official documentation and community posts.
Because each platform uses different data and citation preferences, you must tailor content distribution: invest in brand sites, official documentation and knowledge bases for AI Mode, ensure your products are well represented on major retailers for ChatGPT, and secure references from news and community sites for Perplexity.
How often should I revisit my AI platform priorities as the market evolves?
The generative‑AI landscape changes quickly. This volatility means you should reassess your platform focus at least quarterly and after major updates.
Track where your audience spends time: ChatGPT currently commands nearly 80% of global Gen‑AI visits, but engines like Gemini and Perplexity are gaining momentum. Use AI visibility reports to see where you’re cited most and adjust your content strategy accordingly.
What criteria should I use to decide when to expand my GEO efforts to a new AI engine?
- First, gauge audience adoption: some engines (like ChatGPT) dominate AI search traffic, while others serve niche users.
- Check citation overlap to see if a separate strategy is warranted (only about 11% of domains overlap between ChatGPT and Perplexity).
- Analyze each engine’s citation preferences (publishers vs. review sites vs. community forums), and examine how often the engine updates its data.
- Finally, ensure you can measure your presence. if you can’t track visibility, it may be premature to invest in that platform.
What tools can help with GEO?
Similarweb’s Gen‑AI Intelligence suite provides an all-in-one solution for GEO research, strategy and monitoring how often your brand appears in AI answers, which topics you dominate, competitor performance, and the sentiment of your mentions.
- The AI Brand Visibility tool shows metrics such as brand visibility share, brand mention share, domain influence and citation share.
- The Prompt Analysis tool lists individual prompts, visibility scores and sentiment to identify gaps.
- The Citation Analysis tool reveals which domains and URLs generative engines cite, including competitor citations. With this tool, you can analyze your domain’s influence relative to competitors and other AI sources, pinpointing the sources with the most impact on your topics.
- The AI Sentiment Analysis tool gives you visibility into your audience’s pain points and opinions about your brand and your competitors’ brands. With this tool, you will be able to not only optimize where you appear, but also how you appear in AI answers.
AI‑writing assistants (e.g., Balzac, WordCraft) can generate drafts and question structures. Schema generators and the schema validator help add structured data.
Do I need special tools for GEO?
You can perform basic GEO manually, but specialized tools save time and provide deeper insights. Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool offers dashboards for brand visibility and competitor benchmarking.
The prompt analysis tool surfaces the exact questions AI engines ask, the citation analysis tool identifies influential domains, and the sentiment analysis tool tracks brand perception across topics. The AI Traffic Analytics measures visits from AI engines and conversions.
Without these tools, you might miss opportunities or misinterpret the impact of your efforts.
What is llms.txt and should I add it to my site?
llms.txt is a proposed standard, similar to robots.txt, that tells large language models how to access your content. It allows webmasters to specify which sections of a site may be crawled or used by AI models.
Its’ adoption is still limited, and most AI engines don’t yet enforce it. Adding an llms.txt file can help express your preferences, but it shouldn’t replace other steps like adding schema or focusing on authoritative content.
As the standard evolves, monitor adoption and adjust your llms.txt directives to balance content protection with visibility.
Can we block AI tools from using our content?
You can request that AI crawlers respect your preferences via robots.txt or llms.txt (for example, disallowing certain directories or file types). However, compliance is voluntary, and many models use public data scraped prior to your directive.
Blocking AI models may protect proprietary information but also reduces your chances of being cited, harming visibility. If you have sensitive data, consider gating it behind authentication, but for public marketing and product pages, it’s usually better to allow AI access and optimize them for citations.
Do AI tools honor authenticated or paywalled content?
Most AI engines rely on publicly accessible pages. Google’s AI Mode may index pages behind soft paywalls (as long as they can be previewed), but ChatGPT and Perplexity generally cannot access gated or authenticated content. They work from publicly available data and optional browsing.
If you want your content cited, ensure it’s available without login barriers. For paywalled content, publish free abstracts or summaries to provide AI models with citation opportunities.
What tools help measure GEO performance?
To measure success, use comprehensive analytics suites. Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility suite provides many GEO metrics like brand visibility share, brand mention share, topical coverage, domain influence, citation share and sentiment distribution.
Using Similarweb’s Gen AI tools allows you to benchmark AI performance, identify gaps and prioritize improvements. For example, if your brand visibility is high but domain influence is low, you know to build more high‑authority content or secure citations from trusted publishers.
What are the key tactics involved in GEO?
Effective GEO involves multiple well-known SEO actions, with higher focus on Gen AI digestion:
- Content creation: Produce comprehensive, answer‑first content using a question inventory. Cover definitions, comparisons, how‑tos and transactional queries. Use structured formats and schema.
- Technical optimization: Ensure pages are accessible and indexable. Provide fast loading times, mobile responsiveness and proper status codes. Implement schema and llms.txt as appropriate.
- Authority building: Earn citations from trustworthy domains via PR, guest posts and partnerships. Develop relationships with journalists and industry influencers. Being cited by third‑party sources increases domain influence and trust.
- Sentiment management: Track sentiment through Similarweb’s Sentiment Analysis tool. Identify topics with negative sentiment and address underlying issues through product improvements, clearer messaging or community engagement.
- Measurement and iteration: Establish baseline metrics (brand visibility, citation share, etc.), monitor performance and iterate. Use frameworks like DEEP (Define, Explore, Evaluate, Plan) to structure your workflow. Adjust your strategy when prompts or citation patterns shift.
Why is citation overlap so low between ChatGPT and Perplexity, and how should I adapt my strategy?
Citation sets differ dramatically because each generative engine has its own retrieval and ranking pipeline. Research found that only about 11% of domains overlap between ChatGPT and Perplexity, and roughly 50% of cited domains change month to month.
ChatGPT often favors authoritative publishers, review sites and community forums, while Perplexity relies more on news publishers and Q&A sources. As a result, content that earns citations in one engine may be ignored by another.
Adapt by monitoring each platform separately using Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility and Citation Analysis tools, which show you which prompts cite your brand and which sources are used. Then produce tailored content: ensure your site answers questions comprehensively for Perplexity, and engage with user‑generated platforms and authoritative publishers to influence ChatGPT.
Regularly updating your content and off‑page signals helps you stay visible across platforms as citation sets evolve.
Questions about GEO implementation & business strategy
Who should own GEO strategy inside an enterprise?
GEO is inherently cross‑functional. SEO teams typically lead because they understand technical optimization and content structure. However, success sometimes requires collaboration with content writers, PR teams (to secure citations and manage sentiment), data analysts, and product experts (to provide subject matter expertise).
GEO initiatives should be championed at the leadership level because they touch brand perception and competitive positioning. Assign clear roles: SEO leads strategy & optimization, content teams own question inventory and answer writing, PR handles outreach execution, and analysts manage dashboards and measurement.
How often should we refresh prompts and content?
Generative search evolves quickly. New topics emerge, and existing topics shift in importance. At Similarweb, we recommend reviewing your question inventory every 90 days and refreshing content at least quarterly. In fast‑moving industries, monthly updates may be needed.
Use Prompt Analysis to identify new prompts gaining traction and to monitor whether your brand is being cited. Refresh high‑value pages whenever you see a decline in visibility or a spike in competitor citations.
Updating doesn’t always mean rewriting: sometimes a simple statistic update, a new paragraph or a fresh citation is enough to maintain freshness.
Can GEO hurt traditional SEO performance?
No. GEO practices support SEO. Creating thorough, answer‑focused content with clear structure improves user engagement and dwell time signals, which benefit SEO rankings. Schema markup can enhance rich results. Earning citations from credible sites also yields backlinks, boosting domain authority.
The only caution is to avoid sacrificing readability for AI: content should remain useful to human readers. In general, GEO and SEO reinforce each other.
What budget range should we allocate to GEO initiatives?
Budgets vary depending on your goals and scale. Small businesses can start with a few thousand dollars per month to fund content creation and tools. Larger enterprises may invest tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars when combining content teams, PR outreach, specialized tools, and measurement frameworks.
Consider a phased approach: begin with a pilot project to prove value (e.g., optimize one product category or business line), measure results and then expand. Remember to allocate resources for ongoing monitoring and updates. GEO (just like SEO) is not a one‑time exercise.
What criteria should I use to evaluate new AI platforms before investing in GEO?
Choose your priority engines based on reach and relevance.
Google’s AI Mode and ChatGPT have large audiences and broad adoption, so they’re good starting points. If you’re in a technical or developer‑focused field, Gemini (Google’s open model) or Anthropic’s Claude may be important. Perplexity is popular among researchers and early adopters.
Use Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool to compare your brand’s visibility across engines and identify where you’re weak. Align your efforts with the platforms where your customers are most active.
What kinds of content should SEO agencies create and optimize for clients?
SEO agencies should optimize for a wide range of content types: blog posts, research papers, whitepapers, product pages, press releases, video scripts and webinars (multimodal).
It’s recommended for agencies to also develop a structured framework that aligns with AI retrieval and can be rolled out for all clients. Content pieces should include a clear question, a concise answer, supporting evidence and references.
Agencies should complement on‑site content with off‑site efforts (backlinks) to build domain influence, and perform regular audits to ensure content remains up to date and aligned with the latest AI engine behaviors.
How does an agency measure GEO performance?
Agencies use Similarweb’s Gen‑AI Intelligence dashboards to monitor core GEO performance metrics like brand visibility share, brand mention share, topic coverage, prompt coverage, domain influence, citation share, sentiment distribution and AI traffic. They also compare these metrics against competitors.
Creating monitoring dashboards helps streamline reporting and analysis for a large number of clients (brands), making them highly useful for agencies.
Agencies also track organic traffic, conversions and leads generated through AI referrals. Reporting includes recommendations on content updates, outreach targets and resource allocation. Agencies may also create custom KPIs based on business goals, such as increasing citation share in a specific topic by a given percentage within three months.
How do I get started with GEO services?
Start by performing an AI visibility audit: use Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility and Prompt Analysis to see how often your brand is mentioned, which topics you dominate and where you’re absent. Build a question inventory covering top prompts and topics.
Create structured content for high‑priority questions, implement schema and secure citations from authoritative domains.
Set baseline metrics (brand visibility, domain influence, sentiment) and define goals, and launch a pilot project on a small set of topics. Then monitor results and refine your approach before scaling.
How does GEO influence PR strategy?
Generative engines rely heavily on off‑site sources. PR teams therefore play a crucial role in GEO: they craft AI‑friendly press releases with clear headlines, bullet points and key statistics that AI models can quote.
PR must collaborate with SEO and content teams to ensure that press releases include structured summaries and links back to authoritative pages. Media coverage from high‑authority domains (industry journals, mainstream media) is especially valuable because these sources heavily influence AI engines.
PR can also support sentiment management by addressing negative stories and highlighting positive user experiences.
How do I measure if PR efforts impact GEO results?
To evaluate PR’s impact, track changes in citation share and brand visibility after press campaigns.
- Use Similarweb’s AI Citation Analysis tool to see whether press articles and interviews appear in AI answers and whether your domain influence score grows.
- Monitor sentiment to ensure new coverage improves perception.
- Evaluate changes in AI‑driven traffic using AI Traffic Analytics.
If visibility and sentiment improve after a campaign, PR is contributing to GEO success.
How do user‑generated reviews and community posts influence GEO citations?
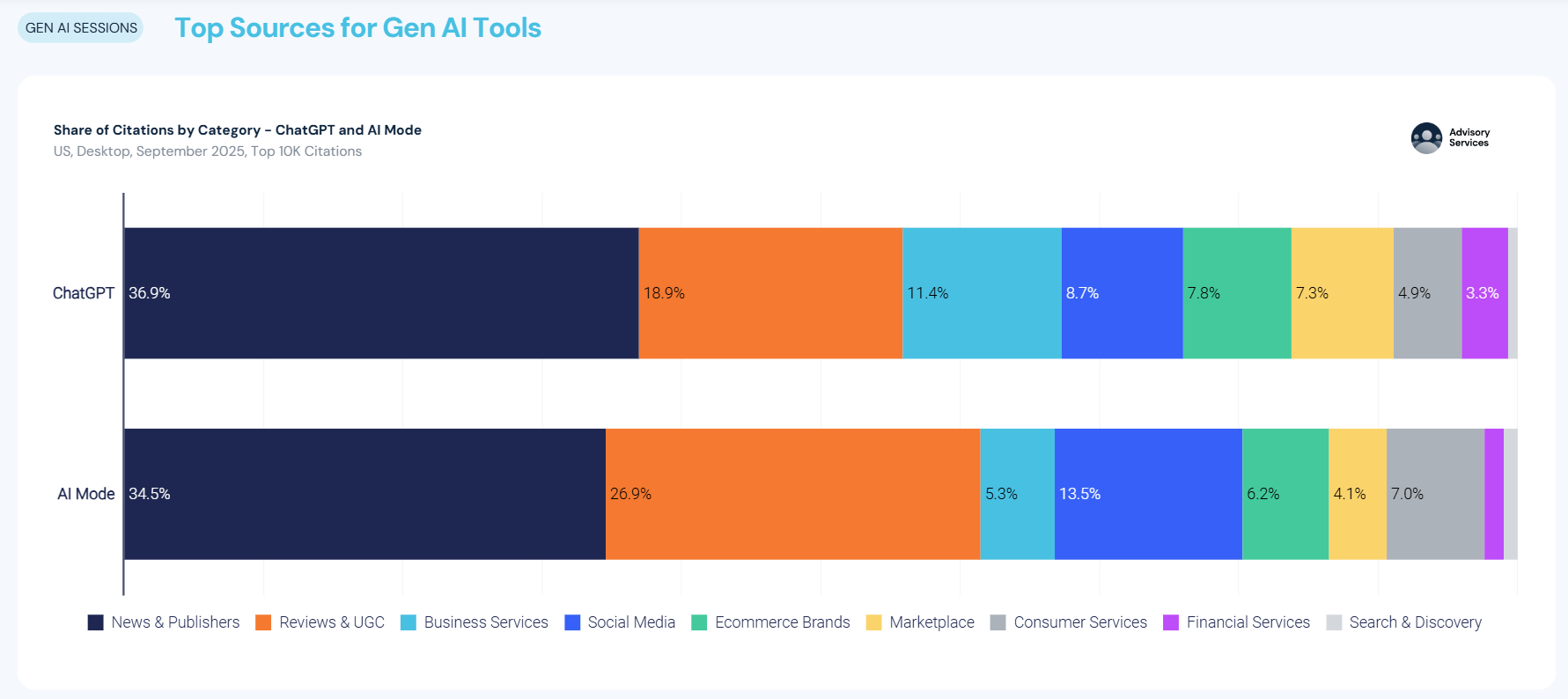
Generative engines pull information from more than just brand and news sites. Similarweb’s analysis of ChatGPT’s citations showed that the model references external sources such as review sites and community platforms like Reddit, and that AI Mode tends to cite news outlets and other authoritative sources, resulting in a different citation mix.
Because user reviews and forum discussions signal real‑world experience and authenticity, they can increase your chances of appearing in AI answers, particularly for product and service queries.
Encourage customers to leave thoughtful reviews on trusted platforms, participate in relevant community discussions, and ensure your reputation is positive and consistent. Also monitor these channels using Similarweb’s tools to see how often they contribute to citations for your brand.
A robust UGC presence complements traditional PR and improves your visibility in generative answers across multiple engines.
What factors influence how quickly GEO efforts show results?
There is no single timeframe for GEO success, but most brands begin to see meaningful improvements within three to six months. Several factors affect the pace:
- AI engine update cycles: Generative models refresh their data at varying intervals. Some platforms update monthly and even change half their cited domains in a single month, while others incorporate new information more slowly.
- Authority and content quality: High‑quality, well‑cited content earns citations faster than thin or promotional pages.
- Topic demand: Hot or emerging topics are indexed and cited more quickly than niche subjects.
- Off‑page signals: Strong backlinks, media coverage and user reviews accelerate recognition by AI engines.
- Tool monitoring: Using Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tools helps you identify when and where you start gaining citations, allowing you to adjust your strategy sooner.
By addressing these factors (creating authoritative content, earning trusted citations and monitoring progress) you can shorten the timeline to tangible GEO impact.
How does GEO influence local and e‑commerce search?
For local businesses, optimize your Google Business Profile, include local schema (address, phone, opening hours) and create content that answers local “near me” queries. Encourage reviews on platforms like Yelp, TripAdvisor and Google Maps because AI engines use these signals to determine local relevance.
For e‑commerce, implement Product schema, include detailed specifications, address FAQs and encourage customer reviews. Recent BrightEdge research shows that AI engines often cite retail domains in shopping responses, so ensure your product pages are comprehensive and trustworthy.
How can niche or emerging industries use GEO to gain early traction?
For a nascent sector, the key is to become the authoritative source before larger competitors enter the space.
Publish answer‑first, long‑tail content that addresses the exact questions your potential customers are asking, adding structured data like FAQPage and HowTo schema helps AI engines pull your information.
Engage beyond your own site by encouraging reviews and participating in trusted industry forums: ChatGPT cites review sites and community platforms alongside publishers, while AI Mode prefers authoritative articles.
Finally, monitor progress using Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility metrics: a rising brand visibility score and brand mention share signal you’re gaining recognition
Can small businesses compete in GEO?
Yes. Generative engines prioritize relevance and authority over brand size. A small business can compete by focusing on niche questions, producing expert content, earning quality backlinks and leveraging local signals.
Because AI engines often cite only a few sources, high‑quality, authoritative content can outrank bigger brands that lack specificity.
Can local businesses benefit from GEO?
Absolutely. Many AI queries have a local intent (“restaurants near me,” “best plumber in town”). AI engines use structured data from Google Business Profiles, local directories and reviews to answer these questions.
Ensure your local listings are complete and updated. Include schema markup for location and service areas. Create content that answers local questions (e.g., “What are the best book stores in Manahttan?”). Encouraging positive reviews and responding to negative ones improves sentiment and increases the likelihood of being cited.
Questions about GEO ROI, metrics & measurement
How is GEO impacting my site’s analytics and organic traffic?
Generative answers reduce clicks from traditional SERPs, so your web analytics may show declining organic traffic even as AI visibility grows. When AI engines provide complete answers, users often don’t click through.
However, citations build brand awareness and trust, which can lead to direct visits, brand searches and conversions later.
For example, Similarweb’s AI Traffic Analytics can reveal that AI‑originated sessions convert at higher rates (Similarweb 2025 Gen AI Landscape Report found that while AI traffic usually accounted for less than 10% of a brand site’s visits, it converted better than other channels).
Therefore, you need to look beyond traffic volume and monitor citation share, brand visibility, and conversions to assess GEO’s impact.
How do you measure GEO success and track AI citations?
Measure success with a suite of metrics:
- Brand visibility score: The percentage of AI answers that mention your brand. In the AI Brand Visibility dashboard, you’ll see the number of mentions and total answers during your chosen timeframe. A high score means the model often uses your brand in its responses, and a low score indicates poor visibility.
- Brand mention share (AI share of voice): Your share of all brand mentions across AI answers. This shows how prominently you compete against others. A low share may be acceptable for a niche brand, but make sure to track changes to gauge momentum.
- Topical visibility: Visibility within individual topics, used to spot strengths and gaps. If you’re strong in social media marketing but weak in analytics, plan content accordingly.
- Prompt‑level visibility and query gap analysis: How often your brand appears in responses to specific prompts. Prompts reveal user intent and highlight where you need more content. Group prompts by type (definitions, how‑tos, comparisons) and intent (informational, transactional, creative) to prioritize.
- Domain influence and citation share: The frequency of your domain’s citations relative to all sources. A high domain influence means AI engines regard your site as authoritative. Citation share distinguishes between citations in answers that mention your brand and those that don’t.
- Sentiment distribution: The percentage of positive, neutral and negative mentions. High positivity suggests trust, while high negativity signals issues to address.
- AI traffic: Visits from AI engines, measured via Similarweb’s AI Traffic Analytics. Combine traffic data with conversions (e.g., sign‑ups, purchases) to gauge ROI.
Track improvements over time: if brand visibility rises from 15% to 25% after a content update, you know your efforts are paying off. Monitor prompt‑level visibility to identify specific questions where you’re missing. Combine this data with AI traffic and conversions to determine business impact.
How do I set up a dashboard to track AI citation metrics, and what’s the difference between brand visibility score and brand mention share?
To monitor GEO performance effectively, you need to track multiple metrics and understand their nuances. A good starting point is to create a dashboard using Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool.
In this tool, the brand visibility score shows how often your brand appears in AI answers relative to all answers within your chosen topics. The brand mention share measures your share of citations compared to competitors and reflects brand popularity across AI responses.
To set up your dashboard:
- Define topics and prompts relevant to your business.
- Track brand visibility and mention share to understand overall presence and competitive standing.
- Monitor topical visibility and prompt-level coverage to see which specific questions trigger citations.
- Monitor domain influence and citation share, which show the authority of your domain versus others.
- Track sentiment distribution and AI traffic metrics to gauge whether citations are positive and whether they drive visits.
Combining these metrics in a single dashboard provides a comprehensive view of your GEO performance and highlights where to focus your optimization efforts.
What is the ROI of GEO?
ROI stems from increased visibility, trust and eventual conversions. Although AI answers may reduce clicks, being cited makes your brand top‑of‑mind, leading to direct visits, brand searches and conversions later.
To calculate ROI, compare the cost of content creation, schema implementation and citation outreach with gains in brand visibility, citation share, AI traffic and conversions. If brand visibility and conversion rates rise after a campaign, your GEO investment is paying off.
What ethical considerations should I keep in mind when implementing GEO?
Ethics matter in AI optimization. Here are some simple steps you can take to make sure ethical standards are kept in your organization:
- Respect user autonomy by avoiding manipulative tactics and ensuring your content doesn’t mislead or coerce.
- Protect user privacy and secure any data you collect.
- Be transparent about AI use: disclose when generative tools create content and verify facts to minimize misinformation.
- Strive for fairness and inclusivity, avoid bias in language and ensure content serves diverse audiences.
- Audit your GEO strategies periodically to prevent unintended harm and maintain public trust.
How much does GEO cost to implement?
Costs vary widely by scale. A DIY program might involve a few thousand dollars per month for content writers, schema tools and one or two monitoring subscriptions. Enterprise‑level programs covering multiple product lines, languages and markets can cost tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars (when including content costs, and backlinks and PR outreach costs).
Consider your competitive landscape and potential ROI when setting budgets. Start small and prove value before expanding.
How do you track AI citations?
Use citation‑tracking platforms like Similarweb’s Citation Analysis tool, which lists the prompts that cite your brand and which domains are referenced. You can see how many citations you receive across engines (ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity), identify which pages generate citations, spot citation gaps, and track changes over time.
Manual testing (typing prompts into AI engines and noting citations) can complement Similarweb’s tools but is not scalable.
What is citation share and why does it matter?
Citation share measures the percentage of citations pointing to your domain relative to all citations used by AI engines. For example, if 10% of all citations in “best project management tools” answers come from your site, your citation share is 10%.
A high citation share indicates that AI engines trust your content and can drive more brand recognition, while a low share shows missed opportunities.
Citation share is particularly important because AI engines may cite only a handful of sources, which means that being one of them provides very high visibility. Monitoring citation share helps you decide where to focus outreach and content efforts.
How often should we update content for GEO?
Refresh high‑value pages at least quarterly to maintain relevance and ensure AI engines revisit them. In fast‑moving industries or time sensitive content, monthly updates may be necessary.
Use the prompt Analysis tool to monitor whether your visibility declines: if you drop out of citations or sentiment worsens, update the page with new information, examples or references. Regular updates also signal freshness to AI engines, increasing retrieval likelihood.
How often should brands check their LLM visibility?
Review visibility metrics monthly or after significant updates to AI engines or search behaviors. Because AI citation sets are volatile, frequent monitoring helps you react quickly.
Use dashboards to track brand visibility, prompt coverage and sentiment across engines. Adjust your content and outreach strategy when you see dips or competitor surges.
How do you track visibility in LLM results, boost ranking or get cited?
Use Similarweb’s AI prompt analysis tool see which prompts cite your brand and where you’re absent. To increase citations, improve the quality and structure of your content, expand coverage of related questions, earn external citations from trusted domains and manage sentiment.
Focus on filling prompt gaps: create content specifically targeting those questions. Also, consider partnerships or guest posts on high‑authority sites that generative engines trust.
What milestones indicate that GEO efforts are starting to work?
Progress isn’t measured by rankings but by visibility and authority.
- You know you’re gaining traction when your brand visibility score rises in Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool.
- A growing brand mention share shows you’re gaining a larger share of total mentions.
- Improved topical visibility and prompt coverage indicate you’re filling more question gaps.
- Increases in domain influence and citation share mean AI engines see your domain as a trusted source.
- A more positive sentiment distribution (more positive mentions versus negative) signals that AI platforms are portraying your brand favorably.
Together, these upward trends over several months show that your GEO strategy is working.
What are the biggest misconceptions about GEO?
Many clients and stakeholders misunderstand what Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) entails. A few key myths stand out:
- GEO is just SEO with AI content: Traditional SEO focuses on keywords, crawlability and backlinks, while GEO shifts the goal to making your content understandable and citable by AI models. Generative engines don’t scan every indexed page, but rely on structured data and semantic clarity, so you can’t simply recycle SEO techniques and expect to succeed.
- GEO is overhyped or irrelevant: AI usage is exploding: Perplexity tripled its monthly queries in less than a year, ChatGPT handles billions of prompts per week, and Google’s AI Overviews reaches billions of users monthly. Even if AI currently drives a smaller share of traffic than Google search, the conversion potential is high, meaning GEO is already an important channel, not a passing fad.
- GEO will hurt SEO: In fact, GEO and SEO complement each other. Strong SEO pages form the foundation that AI engines use to find your content, and adding structured answers for GEO often improves rankings by clarifying content for search engines.
- You can’t optimize for AI because you don’t know the prompts: GEO isn’t about stuffing long prompts into your pages, it’s about anticipating user intent and signaling answers clearly. Using descriptive headings, FAQs and other structured elements helps large language models map your content to a wide range of questions.
- AI traffic isn’t worth it: Measuring AI-driven traffic is harder than measuring clicks from traditional search, but conversions tell a different story. In one case study, adding a “Where did you hear about us?” field revealed that 15% of sign‑ups came from people who first discovered the brand on ChatGPT. That suggests AI visibility can drive valuable leads even if traffic appears small.
By dispelling these misconceptions, you can set realistic expectations and build GEO strategies that leverage both AI and traditional search effectively.
Questions about GEO for business, industry & PR
Does GEO work for e‑commerce and product pages?
Yes. Generative engines frequently answer shopping questions by citing product specifications, reviews and how‑to guides. If you want to get your products recommended by AI engines, here are a few steps you can take:
- Use Product schema to mark up your product name, description, price, availability, manufacturer and key features.
- Provide a Q&A section on product pages to answer common questions.
- Include high‑quality images and videos.
- Encourage customers to leave reviews and respond to them.
These signals help AI models gather the information needed for buying guides and comparison queries. Also, ensure your products are listed on major retailers and marketplace sites because ChatGPT heavily cites Amazon, Target and Walmart.
How does GEO differ for B2B versus B2C strategies?
Yes. Both sectors use answer‑focused content and schema markup, but they diverge in tone and depth.
B2C brands should optimize product pages, comparison articles and user reviews because AI models send significant traffic to transactional sites and cite user‑generated content frequently.
B2B buyers seek technical specifications, ROI analyses and integration information. Pages with structured technical data receive 3.2x more AI citations in business‑focused queries.
In short, B2C content should be concise and emotionally resonant, while B2B content should be comprehensive and expert‑driven.
What industries benefit most from GEO?
Retail, technology, travel, finance, healthcare and education benefit particularly because they have high information demand and consumer queries. These industries generate many long‑tail questions, comparisons and how‑tos, which provide ample opportunities for citation.
However, any industry can leverage GEO: a niche SaaS company or local service provider can dominate AI answers if it provides unique, authoritative information and earns trusted citations.
What budget considerations should small businesses keep in mind for GEO?
You don’t need a large budget to start. The biggest expense is creating high‑quality content, thorough FAQs, guides and local pages. Begin by optimizing free or low‑cost assets: update your Google Business Profile, add FAQPage and LocalBusiness schema and encourage customer reviews.
Allocate a modest portion (10–20%) of your broader search budget to AI‑search tools and monitoring. Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility offers free trial and 99$ packages to track citations and visibility without a huge investment.
As results improve, you can scale spending on advanced analysis or PR outreach.
How does a small website rank in ChatGPT, Gemini or other AI?
Start by creating authoritative, comprehensive pages for each of your core topics. Use answer‑first structures, schema markup and internal linking to guide AI models. Earn backlinks from reputable sites in your niche (guest posts, partnerships and local press can help). Engage in communities (forums, social media) to build brand signals. Ensure your site is technically sound
Because AI engines weigh domain authority, even small sites can rank if they become go‑to resources.
What specific steps should a single‑location business take to implement GEO effectively?
Absolutely. Local businesses can thrive with GEO, but the strategy must emphasize local signals.
According to Similarweb’s GEO guide, Google Business Profile (GBP) completeness, customer reviews and consistent Name‑Address‑Phone (NAP) data across directories are crucial signals for AI search. To optimize:
- Claim and optimize your GBP: Ensure hours, services and photos are up to date. Answer common questions and add local keywords.
- Encourage reviews on Google, Yelp and industry‑specific platforms. Reviews signal trust and are often cited by AI engines.
- Maintain NAP consistency across your website and third‑party directories so AI crawlers can match your business accurately.
- Implement local schema markup: Use LocalBusiness schema and include your address, phone number and service area so AI models can easily extract location data.
- Create locally focused content: Write blog posts or FAQs about neighborhood events, local needs and “near me” queries.
- Monitor local citations using Similarweb’s tools to see which prompts mention your business and where improvements are needed.
Taking these steps helps a single‑location business appear in AI answers for nearby searches and reinforces your authority in local contexts.
Why is being cited more important than ranking #1?
In generative search, the concept of “ranking” is replaced by citation. AI engines produce a single answer and often cite only a handful of sources. If your brand is cited, you gain visibility and implicit endorsement, and if not, you’re invisible, even if you rank highly in traditional search.
Being cited not only builds trust but also influences users’ perceptions of expertise and authority. Citations are the new ranking signals in AI search because they are the only links users see.
What types of media coverage are most valuable for GEO?
Earned media from high‑authority publications matters the most. These sources carry significant influence in AI models. User reviews and community posts are more valuable in AI Mode than in ChatGPT, but they still matter because generative engines weigh social proof.
Coverage on product comparison sites, authoritative blogs and knowledge bases (Wikipedia, Stack Overflow) is also beneficial. Evaluate your competitor’s citation sources using the citation analysis tool and prioritize similar outlets for your outreach.
How is GEO influencing the PR industry?
PR teams now must consider AI readability when crafting stories. Press releases should include succinct bullet points, clear statistics and structured summaries that AI engines can parse. PR outreach should target publications with high AI influence.
Collaboration between PR and SEO is more critical than ever: PR secures third‑party mentions, while SEO ensures those mentions are technically optimized for AI ingestion.
What does GEO mean for PR teams?
PR professionals need to think like content strategists. They must produce AI‑friendly assets (press releases, interviews, thought‑leadership articles) with structured data and clear key points.
They should monitor AI visibility dashboards to see if press coverage is being cited. When sentiment is negative, PR should coordinate with product and support teams to address underlying issues.
PR teams should also build relationships with industry experts and community managers because citations often come from third‑party reviews and social content.
Does GEO improve Google rankings?
GEO primarily affects AI answer visibility. However, the same practices are also a part of SEO and can indirectly improve Google rankings.
For example, adding FAQPage schema can enhance your chances of appearing in both AI answers and rich snippets. Earning citations often involves earning backlinks, which boosts domain authority and can improve organic rankings.
So while GEO doesn’t target SERP positions directly, its tactics often produce SEO benefits.
What are zero‑click searches and how does GEO solve them?
Zero‑click searches occur when users get the answer directly in the search interface or chat, without clicking any result. After the launch of Google’s AI Overviews, zero‑click rates jumped from 56% to 69%.
Zero‑click behavior means traditional SEO traffic declines, but GEO ensures your brand appears within those AI answers. By structuring content around questions and earning citations, you maintain visibility even when users don’t click through.
Can GEO help with local search visibility and audience targeting?
Yes. AI engines use local signals to answer location‑based queries. Optimizing your local listings and creating location‑specific content increases the chances of being cited for “near me” questions. Additionally, by analyzing prompt data for local intent, you can tailor content and outreach to target audiences more effectively.
Does GEO help brands appear in platforms like ChatGPT and AI Mode?
Yes. Structured data, authoritative content and comprehensive topical coverage increase your chances of being cited across AI engines.
However, each platform has unique retrieval and citation patterns:
- ChatGPT relies on its training data and may favor retail and marketplace sources.
- AI Mode uses live web data and favors brand and OEM sites.
- Perplexity cites a mix of news, official documents and community content.
Therefore, your content and outreach strategy should be tailored to each platform.
What signals do LLMs use when selecting sources?
LLMs evaluate authority (citations, backlinks), freshness, semantic relevance, user engagement (reviews and ratings) and structured data. They also consider the type of question: definitions may lead to encyclopedias, how‑tos to tutorials, comparisons to reviews.
Similarweb research notes that AI Mode and ChatGPT favor brand and OEM sites but balance commercial and informational sources, while Perplexity tends to include news and blog content. Align your content with these citation patterns by publishing authoritative guides, encouraging reviews and engaging with community discussions.
What’s the difference between live web retrieval and training data?
Live web retrieval (used by AI Mode and Perplexity) means the model actively searches the web for up‑to‑date content when generating answers, whereas training‑data systems (like default ChatGPT) rely on static data snapshots until the next model update.
Live retrieval allows your fresh content to be cited quickly, but it also means citations can change as new pages appear.
In training‑data systems, you need to get your content into widely referenced sources and pre‑training datasets (e.g., Wikipedia, reputable blogs) for it to be included.
Because each system updates differently, maintain evergreen content for training data and publish timely articles for live retrieval.
Questions about GEO challenges & pitfalls
What are the key challenges when integrating GEO with existing SEO strategies?
Major challenges include:
- New metrics.
- Cross‑functional coordination.
- Content quality at scale.
- AI volatility.
You must track metrics like brand visibility and citation share, which aren’t part of traditional SEO dashboards.
SEO teams must work with PR and content teams to produce AI‑friendly assets and secure citations. Maintaining high‑quality content across hundreds of questions requires resources and editorial rigor.
Finally, AI citation sets change rapidly: 50% of cited domains change every month, so you need ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
What are the most common GEO mistakes?
Common GEO mistakes include relying solely on keyword lists instead of building a robust question inventory, ignoring structured data, neglecting off‑site authority signals, failing to update content regularly and over‑automating content creation.
Some marketers publish dozens of AI‑generated posts every day, but generative engines value quality over quantity. Another mistake is focusing exclusively on ChatGPT: because citation sets differ across platforms, you need to optimize for each engine.
Could rapid AI‑generated content harm credibility or trigger quality flags?
Yes. Flooding your site with low‑quality AI content can harm your reputation and cause AI engines to ignore you. AI models and search engines increasingly detect and penalize auto‑generated spam.
Use AI as a drafting tool but always edit, fact‑check and add unique insights. Focus on adding value rather than scaling content for its own sake. High‑quality, expert‑written or expert‑reviewed content builds trust and authority.
Should I publish fewer, carefully crafted posts or a hybrid of AI drafts and human editing?
A hybrid approach usually works best. AI tools can speed up research and initial drafts, but human editors should refine the language, verify facts and provide context.
Carefully crafted posts that solve real problems and demonstrate expertise are more likely to be cited than generic, repetitive articles. Use AI to generate bullet points or outlines, then expand on them with examples, case studies and expert commentary.
Do daily automated posts sustainably improve visibility, or will AI discount repetitive patterns?
AI engines evaluate content quality and authority rather than volume. Publishing repetitive, thin or machine‑generated posts may reduce trust and cause your site to be ignored. Instead, focus on answering specific questions thoroughly and updating content regularly.
A consistent, high‑quality publishing cadence is more effective than daily automation.
Does simplifying language and using domain‑specific jargon contradict each other?
Use clear, plain language so AI models can easily interpret your content, but include necessary technical terms for accuracy. Provide definitions and context for specialized jargon.
For example, if you mention “retrieval‑augmented generation,” define it in a sentence and link to a deeper explanation. This balance ensures that both novice users and AI models understand your content.
Any data on click‑through rates, impressions, or rankings from GEO experiments?
Early data showd that CTR’s are decreasing and zero-click searches are rising, but also suggested that appearing in AI answers increases visibility even if clicks decline.
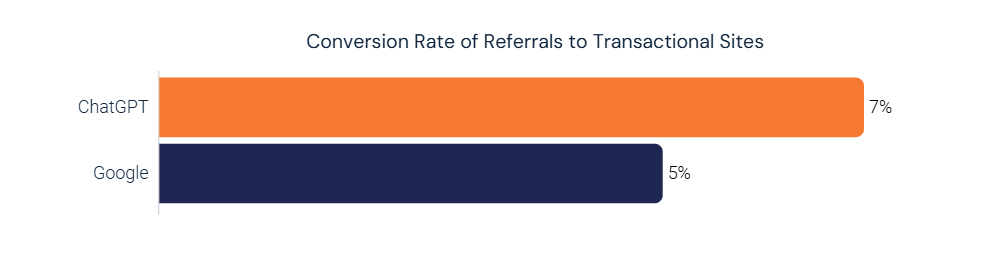
Similarweb’s latest research shows that generative AI engines sent 233 million USA visits to other websites during September 2025, and that referral rate per AI visit has increased from 0.17 to 0.2. AI‑mode traffic accounted for less than 10% of a retailer’s traffic but converted at 7%, better than other channels.
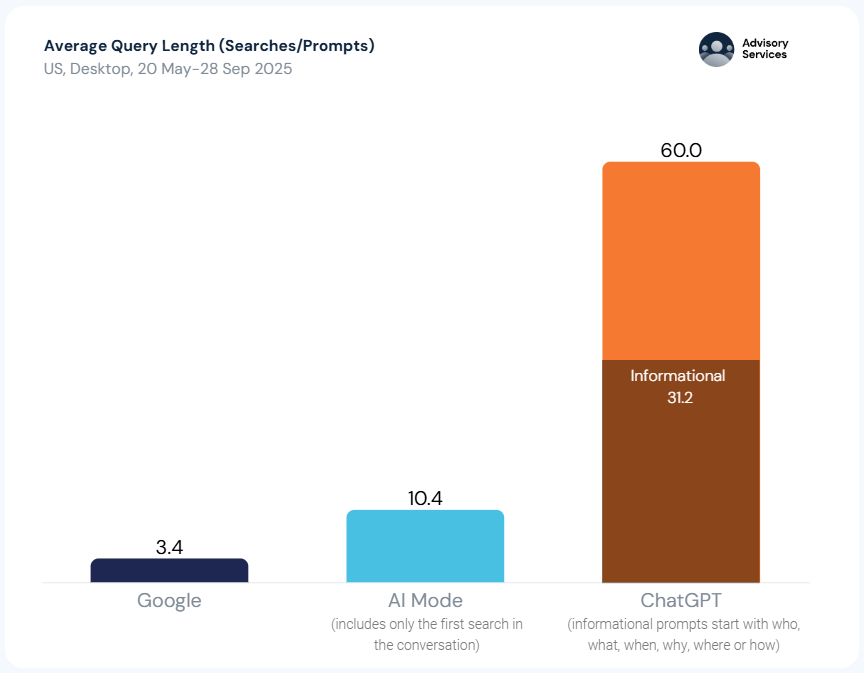
Our data also shows that there’s a 95% overlap between Google and ChatGPT users (meaning almost all of ChatGPT users search Google as well), and that the average ChatGPT query length is x6 than AI Mode’s (implying much higher complexity and personalization in the prompts).
To download the fully detailed report, click here.
Does SEO influence GEO?
Yes. Technical SEO makes your pages easier for AI crawlers to access and parse. High‑quality backlinks improve domain authority and increase the likelihood of being cited. However, GEO adds a focus layer on answer‑first content, citation outreach and cross‑platform monitoring.
Think of GEO as building on SEO foundations but requiring some re-prioritization and a few additional tactics.
What’s the best way to correct misattributed or inaccurate AI citations across platforms?
Misattributed or “hallucinated” citations can harm your credibility, but there are proactive steps you can take. In a previous article about fixing negative sentiment in AI, I recommended creating a corrections page on your site that clearly states the facts and references the queries or answers where errors occur.
This provides a source for AI engines to reference and helps correct future answers. You should also use platform feedback tools to flag inaccuracies. Engaging in relevant communities (e.g., forums, social networks) to clarify misinformation can further improve your reputation.
Finally, ensure your own content is well‑structured and supported by authoritative sources. Accurate information from trusted pages reduces the likelihood of hallucinations and helps AI models associate the right facts with your brand.
Questions about GEO tools & platforms
How should I adapt my GEO strategy for direct‑to‑consumer vs. marketplace business models?
Direct‑to‑consumer brands thrive when product pages, comparison guides and customer reviews are optimized for AI (generative engines cite transactional content and user reviews frequently).
Marketplace operators need to focus on category pages, seller profiles and trust signals like seller ratings. These elements function like B2B content, where structured detail drives citations.
DTC strategies should emphasize emotional benefits and social proof, while marketplaces should highlight breadth of selection, unbiased comparisons and clear seller reputations.
How should I prioritize AI platforms based on my industry and audience?
Instead of trying to optimize for every generative AI platform at once, focus first on those that align with your audience and industry.
ChatGPT and Google’s AI Mode serve the largest user bases so most brands start there. Next evaluate other engines like Perplexity and Gemini based on where your audience consumes information.
Each platform has its own citation patterns, meaning you must tailor content and outreach for each.
Use Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility and Citation Analysis tools to see which engines cite you most and which prompts drive those citations. Prioritize content development where your competitors are outperforming you.
This targeted approach conserves resources and maximizes impact.
What role does structured data play in improving AI citations?
Generative engines rely on structured signals to identify and extract authoritative answers. Adding schema markup helps AI systems understand which sections answer specific questions. Logical heading hierarchy and concise bullet points further improve machine comprehension.
Without structured data, even accurate content may be overlooked. Implementing markup and clear structure tells AI models that your site is a reliable source, increasing citation likelihood.
How does Similarweb’s Gen‑AI Intelligence suite support GEO?
Similarweb’s Gen‑AI suite is a comprehensive monitoring platform. It measures how often your brand appears in generative answers, tracks prompt coverage and sentiment, benchmarks competitor performance and identifies citation gaps.
The suite includes:
- AI Brand Visibility (for visibility and mention share).
- Prompt Analysis (for prompt‑level insights and gap analysis).
- Citation Analysis (for domain influence and source diversity).
- Sentiment Analysis (for perception tracking).
- AI Traffic Analytics (for referral visits and conversions).
Using these tools, you can prioritize content updates, outreach and resource allocation based on data rather than guesswork.
How does the Similarweb AI Brand Visibility tracker work?
The AI Brand Visibility tracker monitors how often your brand appears in generative AI answers across tracked topics. It consolidates data from multiple engines and shows your brand’s visibility share, mention share and domain influence.
It also lists the prompts that trigger each mention so you can see which questions drive visibility and where you have opportunities to improve.
AI Competitive analysis and benchmarking is built in: you can compare your visibility against other brands in your sector.
What data can I get from the AI Brand Visibility tracker?
The tracker provides several data layers: (1) Brand visibility share and brand mention share for each topic, (2) a list of prompts and whether your brand is mentioned, (3) the number of citations and their sources, (4) a breakdown of sources by type (brand pages, publishers, UGC).
By slicing the data by engine, topic or date range, you can see where you’re succeeding and where you need improvement. This granularity helps you allocate resources to topics and prompts that matter most.
Can I compare my performance to competitors in Gen AI?
Yes. Similarweb’s dashboard ranks the top 30 brands for each topic and displays their visibility over time. You can see competitor share of voice, brand mention share, and domain influence.
By watching competitor trends, you can identify emerging rivals, learn from their content strategies, and adjust your own efforts. Benchmarking also reveals topics where your competitors are absent, presenting opportunities to dominate.
What prompts lead to citations in ChatGPT vs. Perplexity, and how can I identify them?
Each engine breaks a query into sub‑prompts differently. ChatGPT tends to cite publishers, review sites, and community platforms like Reddit, while Perplexity leans toward news publishers.
To discover the prompts that matter for your brand, use Similarweb’s Prompt Analysis tool, which lists individual prompts, shows whether your brand is mentioned, and highlights gaps.
In general, ChatGPT prompts are long and conversational, averaging around 60 words, whereas Perplexity users ask shorter, more fact‑focused questions.
Analyze each engine’s intent and craft content that directly answers the high‑impact prompts (e.g., product comparisons and user reviews for ChatGPT, and concise expert summaries for Perplexity).
How can I educate my team about preventing and fixing misattributed AI citations?
Start by teaching your team how generative search engines assemble answers and why citations matter.
Encourage them to monitor AI‑generated answers and flag inaccuracies using Similarweb’s AI Brand Visibility tool to see when your brand is misattributed.
Train them to publish “AI answer corrections” pages on your site and optimize those pages for relevant queries. These pages give AI models a reliable reference.
Finally, instruct them to use feedback mechanisms in each platform to report errors and to engage with relevant communities to correct misinformation.
Maintaining transparency and factual accuracy across all content builds trust and reduces misattributions.
What can we learn from the top GEO questions?
- Tactical visibility dominates: Almost 20% of the most asked questions fall under “Ranking & Optimization.” Many ask how AI engines pick citations, how to rank in specific platforms, and how to structure content. This shows practitioners want actionable guidance to appear in AI answers, not just theory.
- Strong interest in business strategy: 16% of questions fall under “Implementation & Business Strategy”. These ask about budgets, ownership, and whether GEO works for small businesses or niche sectors. The high volume indicates that organizations view GEO as a cross‑functional initiative requiring dedicated resources and strategic integration with marketing and communications.
- Metrics and ROI are a major concern: The “ROI, Metrics & Measurement” category is the third‑largest (13% of questions). Questions probe definitions of brand visibility score, brand mention share, domain influence, and reporting dashboards. This signals that marketers need clear KPIs to justify investment in GEO and to track performance over time.
- Relatively few ask for definitions or adoption stats (12%): This suggests that readers essentially understand what GEO is and are more concerned with execution than with introductory concepts.
The distribution of questions shows that SEOs are treating GEO less as a buzzword and more as a legit discipline.
With nearly 20% of all questions focused on ranking and optimization, another 29% on business strategies & KPIs, and only 12% on what GEO is or how to get started, indicating the field has moved beyond introductory theory.
Taken together, these patterns signal a decisive shift for SEOs: to stay competitive, you need to treat generative search as part of your standard playbook, allocate resources accordingly, and adopt new KPIs. As AI engines become ever more integrated into search experiences, those who embrace GEO today will be the ones who dominate tomorrow’s search results.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!