SEO vs GEO: 4 Key Differences and Building an Integrated Strategy
As online search evolves, so does the way users find information. Traditional search engines are no longer the only gateway; AI-driven platforms are changing how people ask questions and find answers. This has given rise to two parallel strategies: SEO and GEO.
Defining SEO and GEO
SEO and GEO are both strategies for improving visibility online. SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, focuses on optimizing websites and content for visibility in traditional search engines like Google. GEO, or Generative Engine Optimization, focuses on optimizing content for discoverability by generative AI engines that generate answers, summaries, or conversational results.
Key aspects of SEO (Search Engine Optimization) include:
- Focus: Driving organic traffic from search engines by improving a website’s ranking in search results.
- Goal: Attract users to click on a website’s link from a search engine results page (SERP).
- Methods: Perform keyword research, optimize website content, structure, and code to be more appealing to search engine algorithms, and build links to increase authority.
- Example: Improving the ranking of a blog post about “best hiking boots” on Google by using relevant keywords, optimizing the page title and description, adding relevant content, and building backlinks.
Key aspects of GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) include:
- Focus: Ensuring that content is easily found and cited by AI answer engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Google AI Mode.
- Goal: Making content discoverable and usable by AI to generate answers, summaries, or conversational responses, while basing AI responses on website owner objectives.
- Methods: Structuring and presenting information in a way that AI systems can easily understand and use, including using structured data, clear language, and answers to common questions, and achieving brand mentions in influential websites.
- Example: Building a product page with structured data, tables and FAQs to make it easier for AI to ingest its content, and building brand mentions to improve the chance AI engines recommend it to potential customers.
The following table summarizes the key differences:
| Aspect | SEO | GEO |
| Focus | Ranking in search engine results | Discoverability by AI systems and influencing AI responses |
| Goal | Drive organic traffic to website | Achieve citations and visibility in AI engines |
| User Intent | Click-through to website answering their query | Receive answers, summaries, or content within AI |
| Methods | Keyword research, content writing, technical optimization, link building | Structured data, adapting content to AI requirements, building brand mentions. |
How SEO Works: Optimizing for rank and traffic from search engines
SEO involves a range of techniques aimed at improving a website’s rankings on search engines like Google, resulting in increased organic traffic. This includes both on-page and off-page strategies.
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing content and site structure, ensuring that the website is easy to crawl and relevant to users’ queries. This involves keyword research, creating quality content, optimizing meta tags, and using internal linking strategies to improve relevance and user experience.
Off-page SEO involves building authority through backlinks from reputable sites, brand mentions, and social signals, which improve the trustworthiness of the website in the eyes of search engines.
Search engines rely on algorithms to assess hundreds of factors, including the quality, relevance, and authority of a website, to determine its ranking in search results. The goal is to match the website’s content and structure with what search engines consider important to meet user intent.
Optimizing for rank and traffic often requires consistent monitoring and adjustment, as search engine algorithms evolve and competition in the market changes. User experience elements like fast page load times, mobile-friendliness, and intuitive navigation improve SEO performance.
How GEO works: Optimizing for visibility in AI answer engines
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) changes the focus from driving traffic to a website toward being featured in the responses generated by AI-driven platforms, such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and Google AI Mode. GEO aims to ensure that content is visible and accurately represented in AI-generated responses, which may appear in AI answer boxes, chat interfaces, or summaries.
GEO involves tailoring content to meet the needs of AI systems. This includes structuring information in a clear, logical format, ensuring it is both accessible and understandable by generative AI models.
AI answer engines use multiple datasets, including training data and live web content. The key is to position content in a way that improves the likelihood of it being featured in an AI’s response to user queries. Unlike SEO, where rankings are often stable over time, visibility in generative AI responses are highly dynamic, and fluctuates based on the AI’s real-time processing and the query context. Optimization relies on monitoring the citations used by AI engines in relevant responses, and ensuring the cited sources contain information favorable to the organization.
To succeed in GEO, content creators need to think beyond traditional keyword strategies. The focus changes to creating content that educates the AI model, ensuring that the entity is referenced accurately by AI, and building brand mentions in sources cited by AI engines. A key focus is to ensure brands are recommended by AI answer engines when customers ask about relevant product categories.
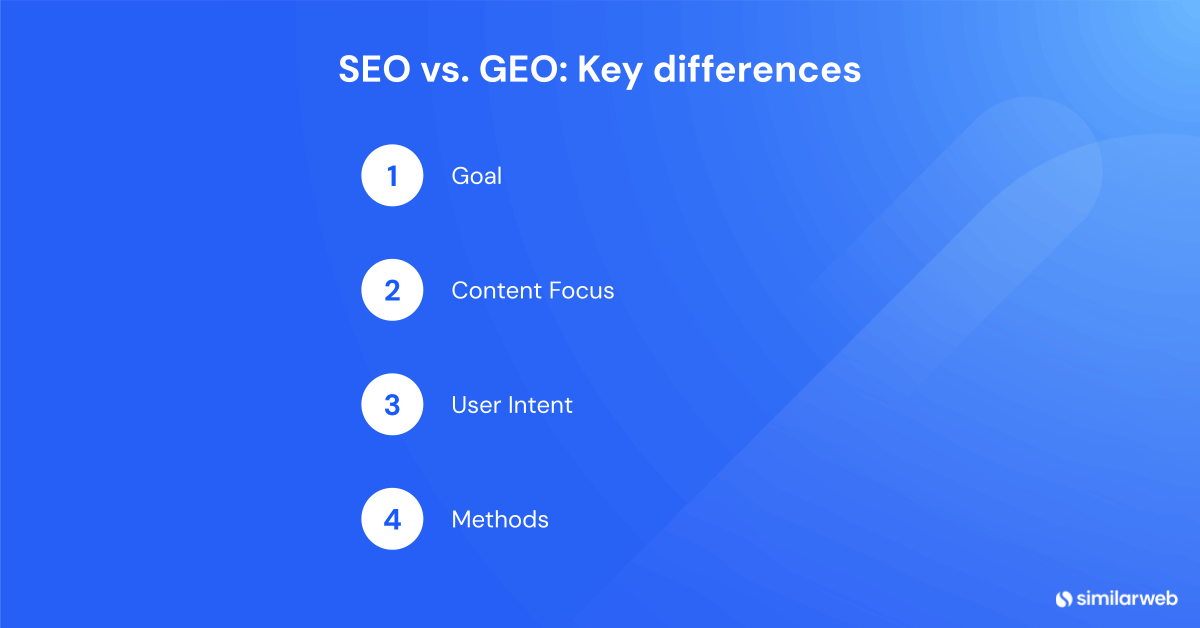
SEO vs. GEO: Key differences
1. Goal
SEO aims to drive users to a website by improving rankings in traditional search results. Success is measured in organic traffic and conversions originating from search engine results pages, typically on platforms like Google, Bing, or Yahoo.
GEO aims to gain visibility inside AI-generated answers. The focus is on influencing what AI engines say and cite, even when users never visit a website. Success is measured by inclusion and favorability in AI responses.
2. Content Focus
SEO content targets keywords and aims to match search intent with in-depth, readable material. Content is often longer and more detailed, designed to answer user queries. The structure supports both users and search engines, emphasizing engagement and ranking factors. Content optimization includes the use of header tags, meta tags, keyword integration, and internal linking.
GEO content prioritizes clarity, structure, and extractability. It’s optimized for AI interpretation, using structured data like tables, lists, and direct Q&A formats, to make it easier for AI engines to use in responses. Unlike SEO, which can rely on broader keyword targeting, GEO content is often optimized for highly specific information that is of interest to AI engines.
3. User Intent
SEO strategies are based on understanding user intent (the reason behind a search query). User intent is generally divided into three categories: informational (users looking for answers to questions), navigational (users looking for a website), and transactional (users looking to purchase a product or service).
GEO places a greater emphasis on user intent as understood by AI systems. Since generative AI platforms like ChatGPT don’t rely on traditional links, they must understand the intent behind a prompt and provide the most relevant content directly. GEO focuses on adapting content so that it can be seamlessly incorporated into AI-generated responses.
4. Methods
SEO uses several methods to improve a website’s position in search engine results:
- Keyword research: Identifying the terms and phrases users are searching for and optimizing content to include these keywords naturally.
- Technical SEO: Optimizing the site’s technical infrastructure to ensure it loads quickly, is mobile-friendly, and is easily crawled by search engine bots.
- Content creation: Writing detailed, high-quality content that meets user needs and meets SEO guidelines.
- Content optimization: Improving the content of a webpage by optimizing elements like headers, meta descriptions, internal linking, page structure, and topics covered to make it meet the search engine requirements and user intent.
- Backlink building: Gaining high-quality backlinks from reputable sites to boost domain authority and credibility.
- Analytics and monitoring: Tracking website performance, identifying problems, and optimizing for better results.
GEO employs strategies tailored to generative AI platforms:
- Citation research: Identifying what sources are commonly used by AI engines to answer relevant questions.
- Achieving citations and mentions: Ensuring the organization’s own content is cited by AI engines, and that its brand is favorably mentioned on other sources commonly cited by the targeted AI platforms.
- AI-optimized content creation: Creating content that can be easily understood and parsed by AI systems, using clear language and structured formats (bullet points, lists, concise paragraphs), and positioning brands in a way that encourages visibility in AI engines.
- Structured data and schema markup: Marking up content with schema (like FAQs, How-Tos, product information) to ensure AI engines can easily interpret it.
- Relevance to user intent: Matching content with the AI’s understanding of user intent. This may involve researching potential prompts and adapting content to possible AI responses.
- Ongoing research and adaptation: Regularly updating content and strategies based on how AI systems evolve and how they prioritize certain types of content.
Best practices to integrate GEO with SEO
GEO and SEO are commonly seen as separate initiatives, but in reality they are deeply related. Organizations integrating GEO with SEO can dramatically improve results in both areas. Here are the primary synergies between GEO and SEO activity, as proposed by SEO expert Lily Ray.
Use structured data
Structured data helps both search engines and AI systems make sense of content. While its role in LLMs is still evolving, using schema markup remains a recommended practice. It improves how content is understood, segmented, and potentially surfaced in AI-generated responses.
SEO teams already use schema to generate rich results and improve click-through rates. Extending this to GEO means ensuring markup is applied to content that AI engines might ingest: FAQs, how-tos, reviews, and product specs. This structured format provides a cleaner signal for AI models parsing the web for reliable information, reinforcing both traditional and generative visibility.
Focus on long-tail searches
Modern AI engines generate multiple variations of a query based on user intent, context, and personalization, which is known as query fan-out. Optimizing for these long-tail, conversational queries involves identifying how people naturally phrase questions and anticipating related subtopics. AI monitoring tools can provide visibility into common AI prompts. For example, our AI Traffic tool can help you see the top AI prompts for any website. SEO teams are already skilled at this due to years of experience optimizing for featured snippets, related questions, and the knowledge graph.
By applying long-tail keyword strategies and developing content that answers nuanced questions, organizations can meet both traditional SEO and AI engine needs. GEO success requires this same kind of granular intent matching, ensuring content can be extracted and cited when AI systems try to generate a response from fragmented user prompts.
Implement multi-modal search
AI search doesn’t limit itself to text.t pulls insights from video, audio, and images. For integrated SEO-GEO success, content teams need to think beyond blog posts and optimize across all media types. This includes adding alt text to images, transcribing videos, and tagging audio with metadata. These practices help AI models interpret and use non-text assets in responses, much like Google has long indexed podcasts or surfaced video results in SERPs.
SEOs have already been doing this through image SEO, YouTube optimization, and content repurposing strategies. A multi-modal approach ensures visibility across AI engines that ingest diverse formats, making it easier for AI tools to pull in relevant segments regardless of the content’s original medium.
Capitalize on digital PR
Digital PR plays a central role in boosting AI visibility, just as it has long supported SEO efforts. AI engines prioritize sources that are credible and well-cited, which increases the importance of earning brand mentions, citations, and links on authoritative third-party websites.
SEO teams already do this through link building and media outreach. By adapting these efforts to GEO goals (targeting publications and domains commonly cited by LLMs) organizations can boost the chances that their content is referenced in AI-generated responses, improving authority and visibility without relying on traditional rankings.
Optimize content holistically
Core SEO principles like clear writing, direct answers, and structured formatting are even more critical for GEO. AI systems favor content that is broken into logical sections, uses bullet points, and directly addresses common questions; exactly the kind of structure SEO teams use to target featured snippets or FAQs.
This overlap makes it natural for SEO teams to optimize content that performs well in both search engines and AI tools. Leveraging practices like chunking content into indexable passages and using headers to signal topic changes helps LLMs extract useful fragments, increasing the likelihood of inclusion in AI answers.
Ensure cross-platform visibility
AI engines collect information from a range of platforms: Forums, social media, cloud documents, and content aggregators. SEO professionals have long optimized for these platforms, from Amazon listings to app store pages to YouTube videos.
To integrate GEO with SEO, teams must ensure brand visibility across these digital ecosystems. This means optimizing for content syndication, monitoring brand mentions on Reddit and Quora, and maintaining active presences on channels AI tools frequently pull from. The more platforms a brand appears on, the more likely it is to be recognized and cited by generative engines.
Tools like our AI Brand Visibility can help you find how your brand appears in AI engines for specific topics, benchmark visibility against top competitors, identify common sources AI tools rely on, and analyze relevant prompts to see if your brand appears in them.
Powering SEO and GEO with Similarweb
The rise of generative AI has changed the way users search, making it necessary to go beyond traditional SEO. While SEO remains essential for driving traffic through search engines, GEO ensures your content is present in AI-generated responses, even when users never visit your website. Together, they form a holistic visibility strategy.
Robust data about user behavior and intent is a critical foundation of both SEO and GEO. Similarweb is a veteran provider of real user data about search keywords, web traffic and competitor behavior, and is now pioneering research tools that shed light into prompts in AI answer engines.
In addition, Similarweb provides unique tools that help teams integrate GEO with SEO (for example, identify relevant keywords and prompts on both search engines and AI engines for the same strategic topics), positioning it as the leading data provider for modern digital visibility strategies.
FAQs
What is the main difference between SEO and GEO?
SEO focuses on improving a website’s visibility in traditional search engines like Google, aiming to drive clicks and organic traffic. GEO, on the other hand, focuses on making content discoverable and usable by AI answer engines, and improving brand visibility in AI responses.
Why is GEO becoming important?
With the rise of generative AI, users increasingly get direct answers without visiting websites. GEO ensures your content is referenced and cited in these AI-generated responses, helping maintain visibility even when traditional search traffic drops.
Can you do SEO and GEO at the same time?
Yes. Many best practices overlap, and there is great benefit to integrating SEO and GEO practices. However, GEO requires additional focus on structured data, content formats that are easily parsed by AI systems, and brand mentions. Combining both strengthens your digital strategy.
How do you optimize content for GEO?
Use structured data (like schema markup), clear language, bullet points, and Q&A formats. Ensure that key facts and answers are presented in a way that generative AI can extract and reuse accurately in responses. Ensure brands are positioned in a way that encourages visibility and favorable treatment in AI responses.
Will GEO replace SEO in the future?
Probably not. SEO will remain vital for web traffic and visibility in search engines for a long time to come. GEO complements SEO by expanding your reach into AI-driven platforms. As search behavior changes, using both will be essential to staying relevant.
Wondering what Similarweb can do for your business?
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!









![The Growth Leader's GEO Decision Framework [+Free Template]](https://www.similarweb.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/attachment-growth-leader-geo-decision-framework-768x429.png)