How To Perform an SEO Site Audit: A Complete Guide

When starting work on a site, you must start with a comprehensive site audit. This will help you uncover strengths to leverage and issues limiting the site’s traffic potential. With these insights in hand, you’ll have strong foundations that will enable you to scale your SEO efforts moving forward.
In this post, you’ll discover:
- What you are looking for in an SEO site audit, and why
- How to get started with minimal resources
What is a website audit?
An SEO site audit is a comprehensive analysis of all of the technical elements of a site in order to find errors standing in the way of its ability to rank pages on search engines. Your site audit should include site-wide factors, URL and website structure, and individual pages and errors.
What are the benefits of an SEO site audit?
Done correctly, an SEO site audit will help you:
- Find and nullify technical issues
- Improve how search engines crawl your site and navigate your content
- Rank higher and beat your competition
1. Finding and nullifying technical issues
Technical issues could hurt your site’s performance in more ways than you realize. Issues like broken pages (404) or poor site structure can eat away at your conversion rates as well as kill your rankings. Long load times could affect key user metrics like Bounce Rate.
What’s more, working on the technical side of your website, AKA Technical SEO, could open up many opportunities you didn’t even know existed.
2. Helping search engines and users navigate your content
If your users can’t easily find what they are looking for on your site, they are likely to find it on your competitors’ sites. And, if navigation is difficult for your users, it’s just as difficult for search engines. Because search engines analyze your navigation to understand how important pages are, they also look at your site structure to understand what your content is about.
This means auditing your navigation could potentially increase your conversion rates as well as your SERP rankings.
3. Beating your competitors with higher rankings
Let’s face it. SEO is, by nature, a competitive discipline. Sites in similar niches compete to rank on limited sets of keywords. This means that as an SEO, you should be constantly looking for leverage against your competitors.
The good news is that your website audit can help you find that leverage.
Since ranking in Google is about optimizing several factors, a thorough site audit might uncover several fixes that make your site more likely to rank than your competitors’.
Getting started on the right foot early on will help you scale your SEO in the future.
Now that you understand the why, let’s get into the how of the website audit process.
How to audit a website: Your 10-step website audit checklist
In this section, we’ll cover the key steps for assessing a website’s traffic potential during an audit. You’ll learn how to identify and address issues that may be hindering your site’s performance and discover structural enhancements to increase your organic traffic for the future.
Here’s a quick checklist of all the steps you need to understand for a thorough website audit:
- Assess your current SEO status and rankings
- Examine the robots.txt file and sitemaps
- Identify issues and opportunities using a site crawler
- Resolve indexing problems through Google Search Console
- Optimize your website’s speed
- Evaluate your site’s structure.
- Review internal linking
- Review your blog content
- Examine your site’s backlinks
- Analyze competitors to uncover gaps in your digital strategy
1. Assess your current SEO status and rankings
Evaluating your current traffic will help you understand what traffic potential is locked away in your site. But rather than tell you, we’ll show you how to do this by analyzing gardendesign.com through the lens of the Similarweb Website Performance report.
The first thing we see is the site got 6.484M visits in the last year.
Where is that traffic coming from?
Breaking down your traffic channels
Examining the Channels Overview, gardendesign.com primarily relies on Organic Search and Direct Traffic for its traffic, as shown below. While there are other active channels driving traffic, Organic Search stands out as their primary traffic source.
Looking at their organic search traffic, we see that 94% is coming from non-branded search terms.
This means that, strategically, Garden Design’s site is mainly focused on content to bring in leads. The number of informational intent keywords in the Top Organic Search Terms confirms this theory.
Uncovering interesting traffic trends
Now, let’s take a look at their Channel traffic trends. Trend graphs generally help you see how the different channels influence one another. You can often find insights into the potential traffic you can achieve by strategically planning your channels.
Above, you can see the site’s organic traffic began to grow in December 2022 and peaked in May 2023. What’s interesting is that we see a similar trend with direct traffic.
Direct traffic began to grow in December 2022 and peaked in June 2023. This is a month after the organic traffic peak.
Was direct traffic influenced by organic? If so, this might indicate that by improving SEO rankings, you can also increase your direct traffic.
Ranking distribution
Another useful way to understand the latent potential of a site is to look at Ranking Distribution. This report will show you keywords that the site is already ranking for and group them by different position ranges.
You can see how many keywords could result in quick wins for your site with just a little optimization and how many existing keywords will need work before they see the light of day.
This is important to understand because improving your existing rankings is much easier than targeting new keywords.
Above, you can see that 6% of gardendesign.com’s keywords are in positions 1-3, and 11% of keywords are ranking in positions 4-10. With a little smart content marketing, perhaps those 4-10 positions could gain and become 1-3 positions.
Now that we have an understanding of the high-level traffic metrics let’s dig into the organic keywords that the site is ranking for.
To get a more granular understanding of your site’s keywords, try using the filters available in the report. For instance, to see your organic traffic potential, you can filter out branded keywords so that way you’re looking at the broader search intent within your space. What’s more, you can also filter your keywords by topic.
This will help you understand which topics the site is already ranking for and which ones could use a little attention.
All of these metrics will help you benchmark your site and will be useful when looking for untapped opportunities moving forward.
Now that you understand your traffic and rankings let’s start your audit by looking at your site-wide metrics.
2. Examine the robots.txt file and sitemaps
Robots.txt files and sitemaps can affect your entire site. Get them wrong and they can kill all of your organic traffic. This makes it important to review them and make sure they are correct and up to date.
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file is a text file meant to instruct search engine bots how to crawl and index pages. To see the file, just add /robots.txt to the root of the website.
For instance: https://www.examplesite.com/robots.txt.
Looking at the robots.txt file literally takes a few seconds and could help you find obvious mistakes that could affect how search engines crawl your entire site. And guess what, we’ve seen sites where Googlebot was not allowed to crawl. (Things like this do happen when site migrations go wrong.)
Since robots.txt files instruct how search engines crawl your site, make sure your site allows:
- Bot access to CSS and styling files
- Access to content files
It should, however, deny access to login and admin areas or any area or pages of the site that you don’t want indexed (for example, paid search landing pages.)
Above, you can see a robots.txt file that disallows bots to crawl:
- Author pages
- Login pages
- User pages
- Reset password pages
- And more
Once you’ve looked at the robots.txt file, it’s time to look at sitemaps.
Sitemaps
A sitemap is a file that lists the pages, videos, and other files on a site that you want Google to crawl and index. This is especially useful if you have poor internal linking on your site or if you have a large site and you want to tell Google how to prioritize crawling.
Ideally, your sitemap should be organized logically, and there should be a separate sitemap for each section of the site. If there are subsections and separate sitemaps, there should be a sitemap-index.xml file that includes links to the separate subsection sitemaps.
Your sitemap can be broken down by:
- Media type: content-sitemap.xml (for content), image-sitemap.xml (for images), and video-sitemap.xml (for videos)
- Subject: plants-sitemap.xml (for subject A), design-ideas-sitemap.xml (for subject B), webinars-sitemap.xml (for subject C), etc.
- Content hierarchy levels: plants-sitemap.xml (for the primary topic), flowers-sitemap.xml (for the subtopic), etc.
- Languages
Make sure there is a logical division of content and that different content types are not mixed together in the same sitemap. Also, since your sitemaps present the URLs you want indexed in search engines, make sure that only canonical URLs appear. Where video or image content is included within a URL, make sure that their URLs are included as well
3. Identify issues and opportunities using Similarweb
Similarweb’s site audit tool provides detailed technical reports that can help you optimize your website’s performance.
To get started, you need to crawl your site:
- Click “New Project”
- Enter a project name
- Initiate a crawl
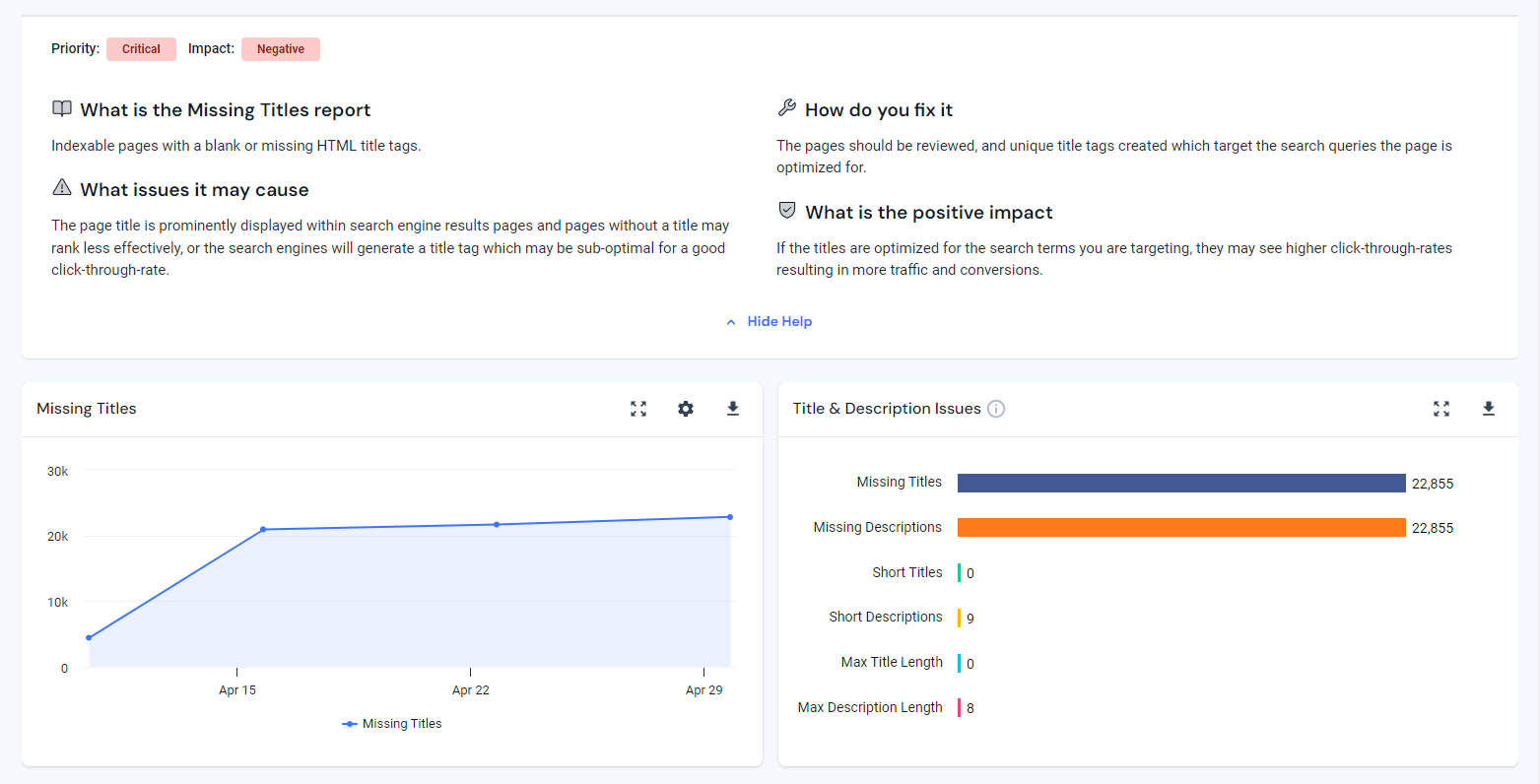
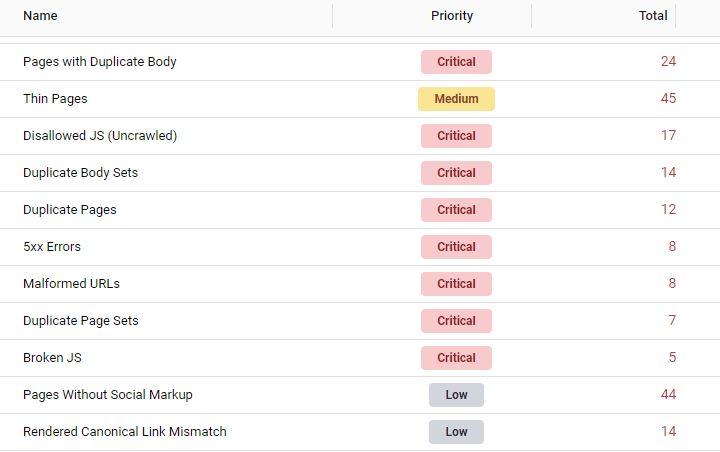
Go to the Errors report to see a detailed report of all the technical issues on your site. The report provides you with a comprehensive list of issues on your site, categorized by priority level. This enables you to address the most critical errors first and improve the overall quality and performance of your website.
If you want to understand the errors reported in the tool, click on the result, and you will be directed to a page that lists all of the URLs affected by the error. The result page also explains:
- What’s causing the issue
- What issues it may cause
- How you can fix it
4. Resolve indexing problems through Google Search Console
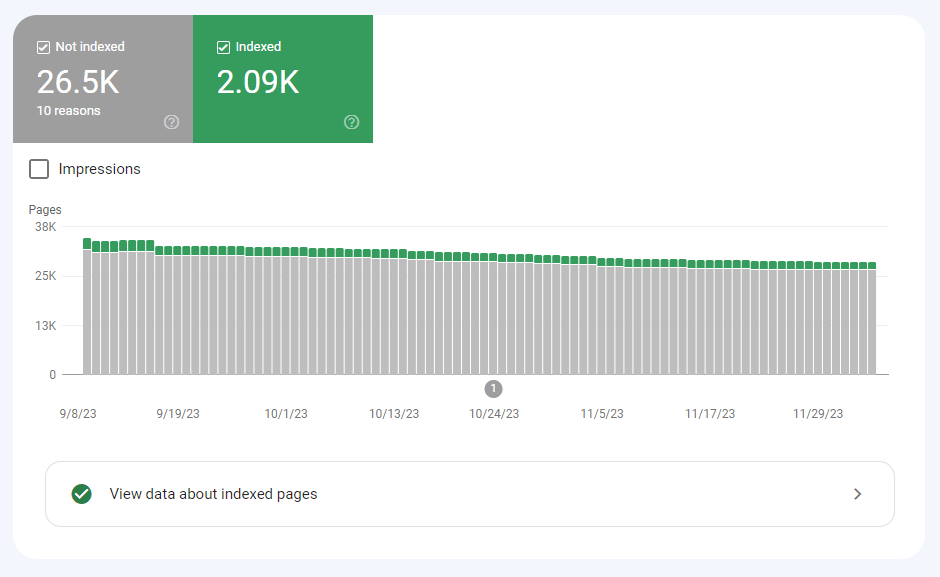
Google Search Console will tell you if any of the pages on your website are not indexed. And if your pages aren’t indexed, they simply won’t appear in search results. To find a list of these pages, look at the Pages report in the indexing tab.
In the overview, you can easily distinguish between indexed and non-indexed pages.
If any of the nonindexed pages should actually be indexed and you want to know what to do about it, scroll down to the Why pages aren’t indexed table to see a list of reasons why pages are not indexed.
You might see legitimate reasons for keeping pages out of Google’s index, including ‘Alternate page with proper canonical tag’ or ‘Page with redirect.’ Other pages might not be indexed due to an error.
For example:
- Not found (404)
- Soft 404
- Crawled – currently not indexed
Click on any of these reasons and Google will redirect you to a list of all the URLs with that issue. If you click on any of the URLs, you will be redirected to a page that gives you stats about your page.
If you want to understand how to have the page indexed, click the Learn More button at the bottom of the result.
Now, it’s time to move on to site speed.
5. Optimize your website’s speed
A good site audit tool will help you spot any site speed issues. The Similarweb Site Audit tool includes a detailed Page Speed report that will not only help you spot errors but will show you how your page speed metrics are progressing over time.
By clicking on any of the errors, you are redirected to a page that includes all the affected URLs as well as an explanation of:
- What issues the error may cause
- How to fix it
- What the positive impact might be
If you are on a tight budget, we recommend using Google’s PageSpeed Insights.
Simply drop the domain URL into the tool and hit ‘Analyze’.
Above, you can see the Core Web Vitals assessment, including metrics like:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- First Contentful Paint (FCP)
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
If you scroll down, you’ll see the report scores your site speed based on four criteria, including:
- Performance
- Accessibility
- Best practices
- SEO
This breakdown will help you decide which area to work on first.
Based on the image above, since Performance is the lowest-performing metric, we’ve scrolled down to the Performance section. As you can see below, there is an ‘Opportunities’ header and a ‘Diagnostics’ header. Under each header is a list of issues you can work on.
If you click on any of them, the tool will explain the issue and help you understand how to fix it.
6. Evaluate your site’s structure
Website structure is crucial for two reasons. Firstly, having a logical structure will help your users navigate through your site, which could directly affect their satisfaction and conversion. Secondly, a clear site architecture will help search engines find and index all of the pages on your site.
What’s more, according to Google’s John Mueller, a structured site architecture helps Google understand how things are connected and how they fit together. And the better Google understands your content, the more likely it will rank in search engines.
When auditing site structure, there are three things you are looking for:
- Content hierarchy
- URL hierarchy
- Breadcrumbs
Content hierarchy
Site content must be well organized for it to be useful to a user. Think of your website as a virtual bookshelf. If your site represents a general topic (your business), then it makes sense to categorize each bookshelf into different subtopics.
Gardendesign.com’s homepage breaks its content into subtopics, including:
- Garden ideas & inspiration
- Gardening essentials
- Plants
- Popular now
- Garden pests, plant diseases, & other problems
Clicking on ‘Garden ideas & inspiration’ takes you to a separate Garden ideas & inspiration category page that includes siloed content.
This is not only a great user experience, but by following these internal links, search engines can easily find and index all of this subtopic content. Additionally, this also helps the search engine understand how the site is segmented into topics and subtopics.
Once you have a well-structured content structure, it’s time to make sure that the content structure is built into the URL structure.
URL hierarchy
The site’s URL structure should follow the same structure that was set up by the content hierarchy. This will add an additional layer of clarity to both users and search engines. Including keywords in your URL structure will add a powerful layer of clarity. Your category pages should include generic category keywords, and every layer below that should get progressively more specific.
For instance:
https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/flowers/roses/
https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/flowers/tulips/
https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/vegetables/tomatoes/
https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/vegetables/carrots/
You’ve now baked your content hierarchy into your folder structure. There is one more layer to add.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are a great way to help your users navigate your site. They are also another way to communicate your content structure to search engines, which will improve crawling and indexing. It’s key that your breadcrumbs reflect your content hierarchy and URL structure and provide users with a way to navigate through topics and subtopics without having to use the navigation menu or the back button.
A few things to remember when creating breadcrumbs:
- Pages should not link to themselves
- Use the H1 tag as the anchor text for the target page
Here’s an example:
Target URL:
https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/vegetables/carrots/…
Suggested breadcrumbs:
Home > Plant Care > Vegetables > Carrots
- Home: https://www.gardenexample.com/
- Plant Care: https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/
- Vegetables: https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/vegetables/
- Carrots: https://www.gardenexample.com/plant-care/vegetables/carrots/ (make sure not to link to this page)
There are a few tools that will help you with this task. We recommend that you use the Similarweb Folders report to get a quick overview of your site’s folder structure.
If you need more granular information, you can download all of their URLs from the Organic Pages report.
If you find a flat architecture, you might want to plan a new site structure for your site. Just keep in mind that your crawl depth shouldn’t be too deep. In general, SEOs recommend keeping it to a maximum of three or four levels.
Now that you understand the site structure, it’s time to move on to a related topic.
7. Review internal links
Generally, we recommend reviewing internal links together with site structure. The reason is internal links are a way to influence your site structure. Internal links are one of the easiest ways to improve your rankings, and reviewing them is crucial.
There are four things you need to look at:
- Crawl depth
- Broken links
- Anchor text
- New opportunities
Crawl depth
Crawl depth refers to the number of clicks a user makes to go from your home page to a specific page on your site. Your homepage is considered the top level, and a page linked to your homepage is considered the second level.
If a user has to click too many times to find something on your site, you are likely to have a high bounce rate which might negatively impact conversions on your site. Also, the further a page is from your home page, the less important it will appear to search engines. And low importance could result in low search engine rankings.
You should solve this by working on your site structure (see above) because a well-structured site should not be deeper than three or four clicks. But, if you are not planning on making dramatic changes to your site, you can easily solve this by optimizing your internal links.
By linking from pages high up in your content hierarchy, you can bring important pages closer to your home page without dramatically changing your site structure.
How do you find pages that should move up the hierarchy? The simplest way to do that is with a site audit tool. Below, you can see the Similarweb Webcrawl Depth report showing a site that’s broken down into five levels.
Broken internal links
Broken internal links are bad for your site’s user experience. This is a high-priority error that’s easy to fix with the help of a site audit tool. To do this in Similarweb, just go to the Internal Broken Links report in the Site Audit tool.
Anchor text
Internal links help Google understand what your pages are about. One of the ways Google does this is by looking at anchor text. This means website links that point to a specific page should include the target keyword or keyword variation for that page in the anchor text.
In the Unique Internal Links view in the Links Breakdown report, you can see all of your internal links and their anchor text within Similarweb.
The Unique Internal Links report enables you to see all your internal links with their anchor texts. You can filter this list to see:
- Target URL
- Anchor text
How to find internal link opportunities
If you want to increase the amount of internal links pointing to a page you need to find where the relevant keyword is mentioned in other content on your site.
There are two ways to do this. One is free, and the other costs (a little).
If you are on a budget, you can do this using Google’s site: search operator.
Simply type site:yoursite.com + keyword
In the example below, we’ve searched site:gardendesign.com aphids, and Google displays a long list of internal pages that include the word ‘aphids.’
The problem with this method is that Google might not bring you a complete list.
If you want to be more thorough, you can make a custom extraction using the Similarweb Site Audit tool. By setting this up, the tool will crawl the site you have chosen and will look for all the instances of your anchor text. This will allow you to quickly see the pages where your chosen keyword appears.
8. Review your blog content
Since a blog has a different function to other parts of a site, you should review it separately in your audit. In this section, we’ll show you how to do a basic audit of your blog content. We will not get into a comprehensive content strategy, and that is something you should do separately.
We will, however, cover:
- Content quality
- Keyword mapping
- Search intent optimization
- Content freshness
Content quality
Google has stated many times that the goal of content is to be helpful to users. Heck, they even named one of their systems the Helpful Content Update. This means that to rank in search, all blog content must be high-quality and helpful to users.
When reviewing a blog, as a general rule, look for long-form, unique content that is detailed and thoroughly answers search intent. (This is a general rule, as there are many instances where the user intent requires a short answer. The point here is to use your common sense.)
To do that, start by comparing each blog post to the top-ranking content on Google for its target keyword. Now, it’s important to remember that word count is not a ranking factor and shouldn’t be the only thing you look at. But word count can help you see if a blog post is thin and lacking in quality information.
Once you’ve looked at the word count, have a quick look at the writing itself. Is it unnecessarily repetitive, or does the writer get to the point? In many cases, a shorter blog post with clear, actionable information is far superior to having a high word count. The key is to write for the end user.
Also, look out for unique content. If your blog post includes actionable information that your competitors’ content doesn’t, you might have a ranking advantage. Google measures content uniqueness using an information gain score. This means having more information than your competitors just might give your content a ranking edge.
Creating a competitive edge through unique content is one of the areas where Similartweb’s keyword research tools shine brightest. You can explore further details below, or jump ahead to create a free account.
Keyword mapping
Just having quality content isn’t enough to rank in search. You need to make sure that your blog content is keyword-optimized. This means each page is assigned a target keyword, and that keyword appears in the:
- Title tag
- Meta description
- H1
- First paragraph of the content
Also, add some keyword variations to the content.
But, just keyword-optimizing pages is not nearly enough to see those pages rising through the ranks. You must also make sure that those pages are accurately answering the search intent.
Search intent optimization
Search intent is defined as the primary goal or purpose behind a user’s online search. When analyzing search intent, your goal is to understand what search engines think search intent is. You can do that by Googling the target keyword for any given blog post and looking at the top results.
What results do you see?
Do you see an obvious pattern?
If you do, you’ve figured out how Google understands the users’ query intent. This means Google is likely only to rank similar content.
To analyze search intent thoroughly, look at:
- The format of the content, including list posts, complete guides, etc.
- The actual answer that the user is looking for to satisfy their query
Once you’ve analyzed your target keywords and their search intent, you might see that more than one blog post covers a similar user intent. Ideally, these posts should be merged into a single long post. If you do that, make sure to 301 redirect any content that you want removed.
Content freshness
SEO is competitive, and your organic competitors are working to outrank your content. Since content often gets outdated, you must make sure that your blog content is up to date with the most recent stats, examples, and explanations.
The best place to start is your older content. Dig up your old content and see if it could be updated or rewritten.
This could be a quick win for your site as often old content already has links pointing to it and with a little content upgrade, the blog could see quick ranking and traffic gains.
Now that you’ve optimized your blog content, it’s time to work on your backlinks.
9. Examine your site’s backlinks
By analyzing your site’s backlinks, you will be able to understand:
- Which sites link to yours
- How many unique domains link to yours
- Anchor texts
This might help you uncover backlink opportunities that are hiding in plain sight.
Sites that link to your site
The first step is to use a tool that will show you all of the external sites that link to your site. The Referring Domains in the Similarweb Backlink Analysis tool will show you the sites that link to yours as well as:
- If the links are follow or nofollow
- The amount of links pointing to your site
- The Domain Trust Score (DTS) of the links
This will help you understand which sites regularly link to your site as well as the pages most commonly linked out to.
You can use this data in two ways:
- By seeing the sites that regularly link out to yours, you can find potential link opportunities to pursue. Because sites that have linked to more than one of your assets are likely to link out again. This might result in relatively easy wins with the right amount of relationship-building
- By seeing the pages that sites regularly link out to, try to figure out what about those pages resulted in so many links. If you can figure this out, you can create more link-worthy content
10. Analyze competitors to uncover gaps in your digital strategy
As we mentioned above, SEO is highly competitive, and the site best optimized generally wins. This means the key to ranking above your competitors is to have a site that is better and more comprehensive than theirs. Analyzing your competitors will help you understand how competitive your site really is.
There are two main aspects to SEO competitor analysis when performing a site analysis:
- Keyword Gap analysis
- Backlink analysis
Both of these can be easily accomplished with Similarweb.
Keyword gap analysis
To get started, you need to first understand who your competitors really are. Because SEO competitors can be different from your direct and indirect competitors, a site that competes with yours for organic traffic might not actually compete with your products or services.
One of the easiest ways to find your SEO competitors is to use the Similarweb Organic Competitors report. The report will bring you a list of sites that rank on similar keywords to your site. Now, if you are specifically looking for direct competitors to your site, you must first set up a few filters.
Since gardendesign.com is a content publishing site in the Gardening niche, we’ve set the filters only to show content publishing sites in the Gardening niche.
Below, Similarweb is now only displaying highly relevant competitor sites.
Now that you have found your SEO direct competitors, it’s time to find keywords that your site is not yet targeting but your competitors are with the Similarweb Keyword Gap tool.
Here we are analyzing gardendesign.com and four of its closest SEO competitors:
You can see the keyword overlap between your site and your competitors. Use this report to understand the basic keywords you need to target to rank your site the highest. Then, use the report to gain ground against your closest competitors.
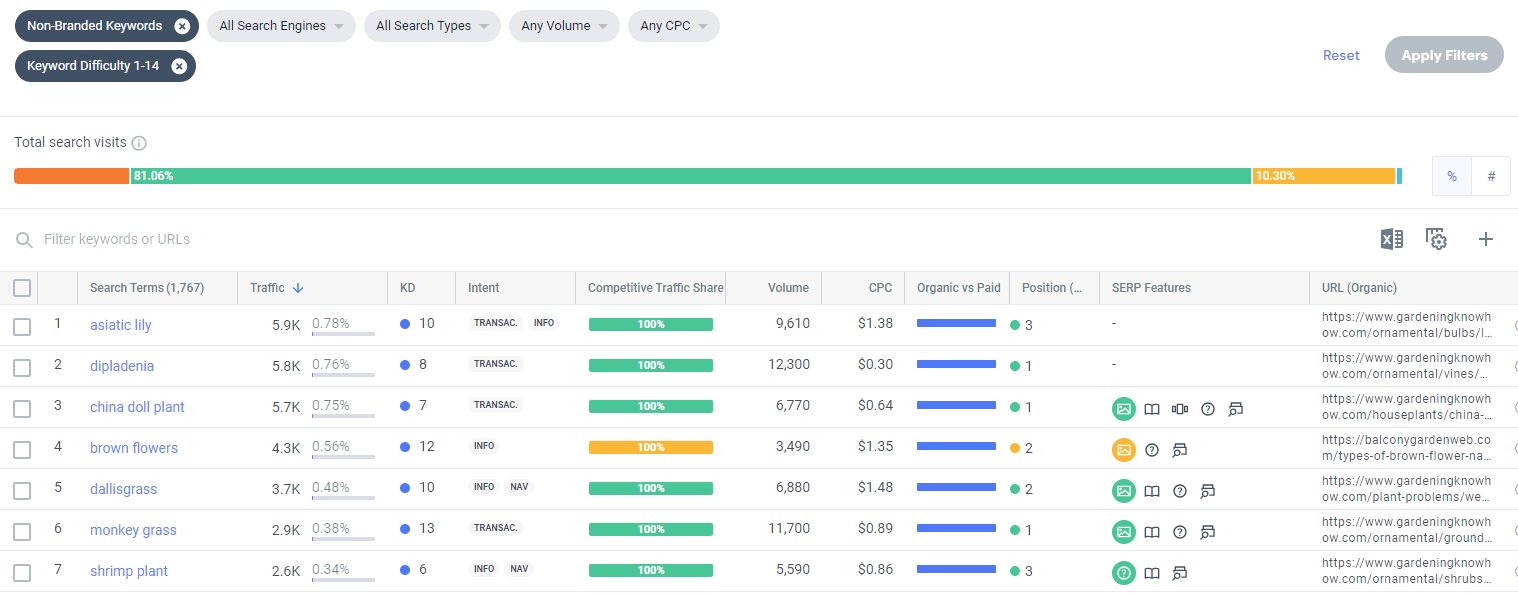
For example, if you click the Opportunities filter, you’ll see a list of keywords your competitors are ranking on that your site is not.
What’s great about this report is the ability to filter the keyword list for relevant opportunities. For example, we’ve configured the tool below to display only non-branded keywords with a low Keyword Difficulty score (KD). This approach is an effective way to gradually expand your search market share, one keyword at a time.
Now that you’ve mapped out next quarter’s content priorities, it’s time to shift your focus to your competitors’ backlinks.
Competitor backlinks analysis
Looking at your competitor’s backlinks will help you understand:
- How many links you should be aiming to build
- Which sites regularly link out to content like yours
- What are the pages that attract the most links
Competitor backlink gap analysis is similar to the backlink analysis you did on your own site, but you are analyzing your competitors’ backlinks.
You are looking to find the sites that link out to your competitors multiple times. By doing this, you might find potential partners who are dying to link to your content but are not yet aware of it.
Look for the pages that get the most links, as these tend to be the best link bait.
Now that you’ve identified all the technical issues and a few opportunities to improve your site, it’s time to devise a comprehensive plan to fix them.
Create an action plan
If you’ve completed the 10 steps above, you probably have a long list of content upgrades and technical issues to fix. While it may seem overwhelming at first, proper planning will enable you to prioritize high-impact tasks at the first stage, followed by tackling smaller changes later.
To create an action plan, start with site-wide fixes. Because these issues are likely to affect all of your content.
Sitewide issues include:
- Robots.txt files
- Sitemaps
- Navigation (main + footer)
After addressing these matters, review all of the issues you saw with your site audit tool and give top priority to the critical issues. Once you’ve resolved those, proceed to tackle the medium-priority issues.
By being systematic, you’ll be able to work through all of the issues one problem at a time. Remember, this will take time. Don’t be afraid to roll up your sleeves and get busy.
Schedule your technical and content fixes with a Gantt
When doing SEO, it’s important to work efficiently. The best way to do this is to schedule all of your work using a Gantt. A Gantt is a chart that helps you schedule all of your tasks systematically.
Create your Gantt by first listing out your key activities, such as:
- Create sitemap
- Review robots.txt and sitemaps
- Keyword mapping
List your tasks, allocate time estimates, and assign responsibilities. Ensure your tasks have milestones for progress tracking. When mapping this all out, it’s important to create a logical sequence of activities.
Creating a Gantt chart will provide a visual project timeline, aiding resource allocation and bottleneck identification. Regularly update the Gantt chart to reflect timeline and priority adjustments during the project.
Because we all understand how dynamic SEO can be.
The Similarweb Site Audit tool gives you an easy way to track all of your technical tasks.
You are almost set up. There is one more thing to do before getting started.
Track your keywords
Before you start to optimize your site, it’s crucial to track your keyword rankings. That way, you can see if your optimizations have improved your search rankings. You’ll also be able to see which pages have improved and which ones still need work.
Although it’s important to track all of your individual keywords, the Similarweb Rank Tracker also allows you to set up keyword tags. Keyword tags allow you to segment your site into different categories or topics. This way, you can improve your site one segment at a time. This works particularly well when you have a large site and you work on one segment at a time.
For instance, below, we have segmented the site into several different keyword segments.
If you plan to work on one segment at a time, you can easily set Similarweb to crawl only that area of your site.
Website audit checklist
You now have all the steps to perform a thorough website audit. If you follow all of the steps above, you’ll potentially improve every aspect of your website, including technical fixes and content improvements.
You now have the knowledge (and tools). The rest is up to you.
FAQs
What is included in an SEO site audit?
A site audit typically includes an analysis of a website’s SEO performance. This generally includes its SEO health, content quality, user experience, and technical aspects. An audit also typically covers factors like page load speed, mobile responsiveness, keyword optimization, backlinks, and overall site structure to identify areas for improvement and optimize for better performance.
How do I do a local SEO audit?
You can conduct a local SEO audit by verifying accurate business information across all of your online citations, ensuring consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) information. You must also review your Google Business Profile, obtain online reviews, and optimize website content with local keywords. Evaluate local citations and backlinks for relevance and fix any inconsistencies to enhance local search visibility.
The #1 keyword research tool
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team — don’t worry, it’s free!







































![How To Create A High Impact SEO Strategy [+Free Checklist]](https://www.similarweb.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Complete-Guide-to-Creating-a-High-Impact-SEO-Strategy-768x456.png)


